Vladimir the Great
| Vladimir the Great | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Miniature from a 17th-century Menaion | |||||
| Grand Prince of Kiev | |||||
| Reign | 11 June 980 – 15 July 1015 | ||||
| Coronation | 11 June 980 | ||||
| Predecessor | Yaropolk I of Kiev | ||||
| Successor | Sviatopolk I of Kiev | ||||
| Prince of Novgorod | |||||
| Reign | 969 – c. 977 | ||||
| Predecessor | Sviatoslav I of Kiev | ||||
| Successor | Yaropolk I of Kiev | ||||
| Born | c. 958 Budyatychi (modern Volyn Oblast, Ukraine)[1] | ||||
| Died | 15 July 1015 (aged c. 57) Berestove (today a part of Kiev) | ||||
| Burial | Church of the Tithes, Kiev | ||||
| Spouse |
| ||||
| Issue among others |
| ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Rurikids | ||||
| Father | Sviatoslav I of Kiev | ||||
| Mother | Malusha (probably of Northern origin)[2] | ||||
| Religion | Chalcedonian Christianity (from 988) prev. Slavic pagan | ||||
Saint Vladimir of Kiev | |
|---|---|
 Icon of Saint Vladimir, Novgorod, 16th century | |
| Prince of Novgorod Grand Prince of Kiev | |
| Born | c. 958 |
| Died | 15 July 1015 |
| Venerated in |
|
| Feast | 15 July |
| Attributes | crown, cross, throne |
Vladimir the Great (also (Saint) Vladimir of Kiev); Old East Slavic: Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь,[a]Old Norse Valdamarr gamli;[3] c. 958 – 15 July 1015, Berestove) was a prince of Novgorod, grand Prince of Kiev, and ruler of Kievan Rus' from 980 to 1015.[4][5]
Vladimir's father was prince Sviatoslav of the Rurik dynasty.[6] After the death of his father in 972, Vladimir, who was then prince of Novgorod, was forced to flee to Scandinavia in 976 after his brother Yaropolk had murdered his other brother Oleg and conquered Rus'. In Sweden, with the help from his relative Ladejarl Håkon Sigurdsson, ruler of Norway, he assembled a Varangian army and reconquered Novgorod from Yaropolk.[7] By 980, Vladimir had consolidated the Kievan realm from modern-day Belarus, Russia and Ukraine to the Baltic Sea and had solidified the frontiers against incursions of Bulgarian, Baltic tribes and Eastern nomads. Originally a follower of Slavic paganism, Vladimir converted to Christianity in 988[8][9][10] and Christianized the Kievan Rus'.[6]
Contents
1 Rise to power
2 Years of pagan rule
3 Christianization of the Kievan Rus'
4 Christian reign
5 Family
6 Significance and legacy
7 See also
8 Notes
9 References
10 External links
Rise to power
Born in 958, Vladimir was the natural son and youngest son of Sviatoslav I of Kiev by his housekeeper Malusha.[11] Malusha is described in the Norse sagas as a prophetess who lived to the age of 100 and was brought from her cave to the palace to predict the future. Malusha's brother Dobrynya was Vladimir's tutor and most trusted advisor. Hagiographic tradition of dubious authenticity also connects his childhood with the name of his grandmother, Olga of Kiev, who was Christian and governed the capital during Sviatoslav's frequent military campaigns. His place of birth is identified by different authors either as Budyatychi (modern Volyn Oblast, Ukraine)[12][13][14] or Budnik (ru:Будник (деревня); modern Pskov Oblast, Russia).[15]
Transferring his capital to Pereyaslavets in 969, Sviatoslav designated Vladimir ruler of Novgorod the Great but gave Kiev to his legitimate son Yaropolk. After Sviatoslav's death at the hands of the Pechenegs in 972, a fratricidal war erupted in 976 between Yaropolk and his younger brother Oleg, ruler of the Drevlians. In 977, Vladimir fled to his kinsman Haakon Sigurdsson, ruler of Norway, collecting as many Norse warriors as he could to assist him to recover Novgorod. On his return the next year, he marched against Yaropolk. On his way to Kiev he sent ambassadors to Rogvolod (Norse: Ragnvald), prince of Polotsk, to sue for the hand of his daughter Rogneda (Norse: Ragnhild). The high-born princess refused to affiance herself to the son of a bondswoman, so Vladimir attacked Polotsk, slew Rogvolod, and took Ragnhild by force.[11] Polotsk was a key fortress on the way to Kiev, and capturing Polotsk and Smolensk facilitated the taking of Kiev in 978, where he slew Yaropolk by treachery and was proclaimed knyaz of all Kievan Rus.[16]
Years of pagan rule
Vladimir continued to expand his territories beyond his father's extensive domain. In 981, he seized the Cherven towns from the Poles; in 981–982, he suppressed a Vyatichi rebellion; in 983, he subdued the Yatvingians; in 984, he conquered the Radimichs; and in 985, he conducted a military campaign against the Volga Bulgars,[17][18] planting numerous fortresses and colonies on his way.[11]
Although Christianity spread in the region under Oleg's rule, Vladimir had remained a thoroughgoing pagan, taking eight hundred concubines (along with numerous wives) and erecting pagan statues and shrines to gods.[19]
He may have attempted to reform Slavic paganism in an attempt to identify himself with the various gods worshipped by his subjects. He built a pagan temple on the a hill in Kiev dedicated to six gods: Perun - the god of thunder and war "a Norse god favored by members of the prince’s druzhina (military retinue)". Slav gods Stribog and Dazhd'bog; Mokosh - a goddess representing Mother Nature "worshipped by Finnish tribes"; Khors and Simargl, "both of which had Iranian origins, were included, probably to appeal to the Poliane."[20]
Open abuse of the deities that most people in Rus' revered triggered widespread indignation. A mob killed the Christian Fyodor and his son Ioann (later, after the overall christening of Kievan Rus', people came to regard these two as the first Christian martyrs in Rus', and the Orthodox Church[citation needed] set a day to commemorate them, 25 July). Immediately after the murder of Fyodor and Ioann, early medieval Rus' saw persecutions against Christians, many of whom escaped or concealed their belief.[b]
However, Prince Vladimir mused over the incident long after, and not least for political considerations. According to the early Slavic chronicle called Tale of Bygone Years, which describes life in Kievan Rus' up to the year 1110, he sent his envoys throughout the civilized world to judge first hand the major religions of the time, Islam, Roman Catholicism, Judaism, and Byzantine Orthodoxy. They were most impressed with their visit to Constantinople, saying, "We knew not whether we were in Heaven or on Earth… We only know that God dwells there among the people, and their service is fairer than the ceremonies of other nations."[21]
Christianization of the Kievan Rus'

The Baptism of Saint Prince Vladimir, by Viktor Vasnetsov (1890)
The Primary Chronicle reports that in the year 987, after consultation with his boyars, Vladimir the Great sent envoys to study the religions of the various neighboring nations whose representatives had been urging him to embrace their respective faiths. The result is described by the chronicler Nestor. Of the Muslim Bulgarians of the Volga the envoys reported there is no gladness among them, only sorrow and a great stench.[11] He also reported that Islam was undesirable due to its taboo against alcoholic beverages and pork.[22] Vladimir remarked on the occasion: "Drinking is the joy of all Rus'. We cannot exist without that pleasure."[22] Ukrainian and Russian sources also describe Vladimir consulting with Jewish envoys and questioning them about their religion, but ultimately rejecting it as well, saying that their loss of Jerusalem was evidence that they had been abandoned by God.
His emissaries also visited pre-schism Latin Rite Christian and Eastern Rite Christian missionaries.[citation needed] Ultimately Vladimir settled on Eastern Orthodox Christianity. In the churches of the Germans his emissaries saw no beauty; but at Constantinople, where the full festival ritual of the Byzantine Church was set in motion to impress them, they found their ideal: "We no longer knew whether we were in heaven or on earth", they reported, describing a majestic Divine Liturgy in Hagia Sophia, "nor such beauty, and we know not how to tell of it." Vladimir was impressed by this account of his envoys.[11]
.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{display:flex;flex-direction:column}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{display:flex;flex-direction:row;clear:left;flex-wrap:wrap;width:100%;box-sizing:border-box}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{margin:1px;float:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .theader{clear:both;font-weight:bold;text-align:center;align-self:center;background-color:transparent;width:100%}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:left;background-color:transparent}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-left{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-right{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-center{text-align:center}@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;max-width:none!important;align-items:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{justify-content:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:center}}


Saint Vladimir Monument on Saint Vladimir Hill in Kiev, often depicted in paintings and photographs of the city
In 988, having taken the town of Chersonesos in Crimea, he boldly negotiated for the hand of emperor Basil II's sister, Anna.[23] Never before had a Byzantine imperial princess, and one "born in the purple" at that, married a barbarian, as matrimonial offers of French kings and German emperors had been peremptorily rejected. In short, to marry the 27-year-old princess to a pagan Slav seemed impossible. Vladimir was baptized at Chersonesos, however, taking the Christian name of Basil out of compliment to his imperial brother-in-law; the sacrament was followed by his wedding to Anna. Returning to Kiev in triumph, he destroyed pagan monuments and established many churches, starting with a church dedicated to St. Basil,[24] and the Church of the Tithes (989).[11]
Arab sources, both Muslim and Christian, present a different story of Vladimir's conversion. Yahya of Antioch, al-Rudhrawari, al-Makin, Al-Dimashqi, and ibn al-Athir all give essentially the same account.[25] In 987, Bardas Sclerus and Bardas Phocas revolted against the Byzantine emperor Basil II. Both rebels briefly joined forces, but then Bardas Phocas proclaimed himself emperor on 14 September 987. Basil II turned to the Kievan Rus' for assistance, even though they were considered enemies at that time. Vladimir agreed, in exchange for a marital tie; he also agreed to accept Christianity as his religion and to Christianize his people. When the wedding arrangements were settled, Vladimir dispatched 6,000 troops to the Byzantine Empire, and they helped to put down the revolt.[26]
In 988 and 991, he baptized Pecheneg princes Metiga and Kuchug, respectively.[27]
Christian reign
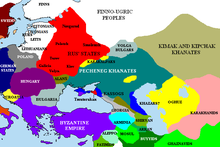
The Pontic steppes, c. 1015
Vladimir then formed a great council out of his boyars and set his twelve sons over his subject principalities.[11] According to the Primary Chronicle, he founded the city of Belgorod in 991. In 992, he went on a campaign against the Croats, most likely the White Croats that lived on the border of modern Ukraine. This campaign was cut short by the attacks of the Pechenegs on and around Kiev.
In his later years he lived in a relative peace with his other neighbors: Boleslav I of Poland, Stephen I of Hungary, and Andrikh the Czech (questionable character mentioned in A Tale of the Bygone Years). After Anna's death, he married again, likely to a granddaughter of Otto the Great.
In 1014, his son Yaroslav the Wise stopped paying tribute. Vladimir decided to chastise the insolence of his son and began gathering troops against him. Vladimir fell ill, however, most likely of old age, and died at Berestove, near Kiev. The various parts of his dismembered body were distributed among his numerous sacred foundations and were venerated as relics.[11]
During his Christian reign, Vladimir lived the teachings of the Bible through acts of charity. He would hand out food and drink to the less fortunate, and made an effort to go out to the people who could not reach him. His work was based on the impulse to help one’s neighbors by sharing the burden of carrying their cross.[28] He founded numerous churches, including the Desyatinnaya Tserkov (Church, or Cathedral, of the Tithes) (989), established schools, protected the poor and introduced ecclesiastical courts. He lived mostly at peace with his neighbours, the incursions of the Pechenegs alone disturbing his tranquillity.[11]
Family

Vladimir and Rogneda (1770)
The fate of all Vladimir's daughters, whose number is around nine, is uncertain.
- Olava or Allogia (Varangian or Czech), speculative she might have been mother of Vysheslav while others claim that it is a confusion with Helena Lekapene[citation needed]
- Vysheslav (c. 977 – c. 1010), Prince of Novgorod (988–1010)
- a widow of Yaropolk I, a Greek nun
Sviatopolk the Accursed (born c. 979), possibly the surviving son of Yaropolk
Rogneda (the daughter of Rogvolod); later upon divorce she entered a convent taking the Christian name of Anastasia
Izyaslav of Polotsk (born c. 979, Kiev), Prince of Polotsk (989–1001)
Yaroslav the Wise (no earlier than 983), Prince of Rostov (987–1010), Prince of Novgorod (1010–1034), Grand Prince of Kiev (1016–1018, 1019–1054). Possibly he was a son of Anna rather than Rogneda. Another interesting fact that he was younger than Sviatopolk according to the words of Boris in the Tale of Bygone Years and not as it was officially known. That he was Prince of Rostov is very dubious but not disproven.- Vsevolod (c. 984 – 1013), possibly the Swedish Prince Wissawald of Volyn (c. 1000), was perhaps the first husband of Estrid Svendsdatter
- Mstislav, other Mstislav that possibly died as an infant if he was ever born
Mstislav of Chernigov (born c. 983), Prince of Tmutarakan (990–1036), Prince of Chernigov (1024–1036), other sources claim him to be son of other mothers (Adela, Malfrida, or some other Bulgarian wife)- Predslava, a concubine of Bolesław I Chrobry according to Gesta principum Polonorum
- Premislava, (died 1015), some source state that she was a wife of the Duke Laszlo (Vladislav) "the Bald" of Arpadians
- Mstislava, in 1018 was taken by Bolesław I Chrobry among the other daughters
- Bulgarian Adela, some sources claim that Adela is not necessarily Bulgarian as Boris and Gleb were born from some other wife
Boris (born c. 986), Prince of Rostov (c. 1010 – 1015), remarkable is the fact that Rostov Principality as well as the Principality of Murom used to border the territory of Volga Bolgars
Gleb (born c. 987), Prince of Murom (1013–1015), as Boris, Gleb is being also claimed the son of Anna Porphyrogenita
- Stanislav (born c. 985 – 1015), Prince of Smolensk (988–1015), possible of another wife and a fate of whom is not certain
Sudislav (died 1063), Prince of Pskov (1014–1036), possible of another wife, but he is mentioned in Nikon's Chronicles. He spent 35 years in prison and later before dying turned into a monk.
Malfrida
- Sviatoslav (c. 982 – 1015), Prince of Drevlians (990–1015)
Anna Porphyrogenita
- Theofana, a wife of Novgorod posadnik Ostromir, a grandson of semi-legendary Dobrynya (highly doubtful is the fact of her being Anna's offspring)
- a granddaughter of Otto the Great (possibly Rechlinda Otona [Regelindis])
Maria Dobroniega of Kiev (born c. 1012), the Duchess of Poland (1040–1087), married around 1040 to Casimir I the Restorer, Duke of Poland, her maternity as daughter of this wife is deduced from her apparent age
- other possible family
- Vladimirovna, an out-of-marriage daughter (died 1044), married to Bernard, Margrave of the Nordmark.
- Pozvizd (born prior to 988), a son of Vladimir according to Hustyn Chronicles. He, possibly, was the Prince Khrisokhir mentioned by Niketas Choniates.
Significance and legacy

Vladimir the Great portrait on obverse ₴1 bill circa 2006
The Eastern Orthodox, Byzantine Rite Lutheran and Roman Catholic churches celebrate the feast day of St. Vladimir on 15/28 July.[29][30]
The town Volodymyr-Volynskyi in north-western Ukraine was founded by Vladimir and is named after him.[31] The foundation of another town, Vladimir in Russia, is usually attributed to Vladimir Monomakh. However some researchers argue that it was also founded by Vladimir the Great.[32]
St Volodymyr's Cathedral, one of the largest cathedrals in Kiev, is dedicated to Vladimir the Great, as was originally the University of Kiev. The Imperial Russian Order of St. Vladimir and Saint Vladimir's Orthodox Theological Seminary in the United States are also named after him.
The memory of Vladimir was also kept alive by innumerable Russian folk ballads and legends, which refer to him as Krasno Solnyshko (the Fair (or Red) Sun). The Varangian period of Eastern Slavic history ceases with Vladimir, and the Christian period begins.
The appropriation of Kievan Rus' as part of national history has also been a topic of contention in Ukrainophile vs. Russophile schools of historiography since the Soviet era.[33]
All branches of the economy prospered under him.[34] He minted coins and regulated foreign affairs with other countries, such as trade. Through trade he brought in Greek wines, Baghdad spices, and Arab horses to trade at the markets of Kiev.

Vladimir the Great on the Millennium of Russia monument in Novgorod

Monument to Vladimir the Great and the monk Fyodor at Pushkin Park in Vladimir, Russia
Vladimir as a symbol of Ukrainian nationalism: "St Volodymyr – Ruler of Ukraine, 980–1015, erected by Ukrainians in Great Britain in 1988 to celebrate the establishment of Christianity in Ukraine by St. Volodymir in 988"
St Vladimir in Gdansk, Poland. Celebrated on 2015 on the occasion of the millennium since the death of the baptist of Kievan Rus. Built with the help of the Ukrainian community of Gdansk and the Ukrainian diaspora of the world.
See also
- List of Russian rulers
- List of Ukrainian rulers
- Family life and children of Vladimir I
- List of people known as The Great
- Saint Vladimir Monument
Prince Vladimir, Russian animated feature film (2006)- Viking (film)
Notes
^ Volodiměrъ is the East Slavic form of the given name; this form was influenced and partially replaced by the Old Bulgarian (Old Church Slavonic) form Vladiměrъ (by folk etymology later also Vladimirъ; in modern East Slavic, the given name is rendered Ukrainian: Володимир Volodymyr, Russian: Влади́мир Vladimir, Belarusian: Уладзiмiр Uladzimir. See Vladimir (name) for details.
^ In 983, after another of his military successes, Prince Vladimir and his army thought it necessary to sacrifice human lives to the gods. A lot was cast and it fell on a youth, Ioann by name, the son of a Christian, Fyodor. His father stood firmly against his son being sacrificed to the idols. Further, he tried to show the pagans the futility of their faith: "Your gods are just plain wood: it is here now but it may rot into oblivion tomorrow; your gods neither eat, nor drink, nor talk and are made by human hand from wood; whereas there is only one God — He is worshiped by Greeks and He created heaven and earth; and your gods? They have created nothing, for they have been created themselves; never will I give my son to the devils!"[citation needed]
References
^ Dyba, Yury (2012). Aleksandrovych V.; Voitovych, Leontii; et al., eds. Історично-геогра фічний контекст літописного повідомлення про народження князя Володимира Святославовича: локалізація будятиного села [Historical-geographic figurative context of the chronicled report about the birth of Prince Vladimir Svyatoslavovich: localisation of a busy village] (PDF). Княжа доба: історія і культура [Era of the Princes: history and culture] (in Ukrainian). Lviv. 6. ISSN 2221-6294. Retrieved 7 January 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Harvard Ukrainian studies, Vol. 12–13, p. 190, Harvard Ukrainian studies, 1990
^ Fagrskinna ch. 21 (ed. Finnur Jónsson 1902–8, p. 108).
^ Companion to the Calendar: A Guide to the Saints and Mysteries of the Christian Calendar, p. 105, Mary Ellen Hynes, Ed. Peter Mazar, LiturgyTrainingPublications, 1993
^ National geographic, Vol. 167, p. 290, National Geographic Society, 1985
^ ab Vladimir I (Grand Prince of Kiev) at Encyclopædia Britannica
^ Den hellige Vladimir av Kiev (~956–1015), Den katolske kirke website
^ Vladimir the Great, Encyclopedia of Ukraine
^ Saint Vladimir the Baptizer: Wetting cultural appetites for the Gospel, Dr. Alexander Roman, Ukrainian Orthodoxy website
^ Ukrainian Catholic Church: part 1., The Free Library
^ abcdefghi Bain 1911.
^ Диба Ю. Історично-географічний контекст літописного повідомлення про народження князя Володимира Святославовича: Локалізація Будятиного села // Княжа доба. Історія і культура. Львів: Інститут українознавства ім. І. Крип'якевича НАН України. — Вип. VI. — С. 37-70
^ Диба Ю. Батьківщина святого Володимира: Волинська земля у подіях X століття (Міждисциплінарні нариси ранньої історії Руси-України). — Львів: Видавництво «Колір ПРО», 2014. — 484 с.: іл. — (Серія «Невідома давня Україна». — 1)
^ Мицько І. Нові монографії про давню Україну
^ Alexandrov, A. Ольгинская топонимика, выбутские сопки и руссы в Псковской земле (in Russian).
^ Den hellige Vladimir av Kiev (~956–1015), Den Katolske Kirke
^ Janet Martin. Medieval Russia. Cambridge University Press. 1995. pp. 5, 15, 20.
^ John Channon, Robert Hudson. The Penguin historical atlas of Russia. Viking. 1995. p. 23.
^ "Although Christianity in Kiev existed before Vladimir’s time, he had remained a pagan, accumulated about seven wives, established temples, and, it is said, taken part in idolatrous rites involving human sacrifice." (Britannica online)
^ Janet., Martin, (2007). Medieval Russia, 980-1584 (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 6. ISBN 9780511811074. OCLC 761647272.
^ Readings in Russian Civilization, Volume 1: Russia Before Peter..., University of Chicago Press, 2009
^ ab Moss 2002, p. 18.
^ The Earliest Mediaeval Churches of Kiev, Samuel H. Cross, H. V. Morgilevski and K. J. Conant, Speculum, Vol. 11, No. 4 (Oct., 1936), 479.
^ The Earliest Mediaeval Churches of Kiev, Samuel H. Cross, H. V. Morgilevski and K. J. Conant, Speculum, 481.
^ Ibn al-Athir dates these events to 985 or 986 in his The Complete History
^ "Rus". Encyclopaedia of Islam
^ Curta, Florin. "The Other Europe in the Middle Ages". Google Books. Brill. Retrieved 14 May 2016.
^ Obolensky, Alexander (1993). "From First to Third Millennium: The Social Christianity of St. Vladimir of Kiev". Cross Currents.
^ "St. Vladimir". Retrieved May 13, 2017.
^ "День Св. Володимира Великого, християнського правителя" (in Ukrainian). Ukrainian Lutheran Church. 28 July 2014. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
^ Henryk Paszkiewicz. The making of the Russian nation. Greenwood Press. 1977. Cracow 1996, pp. 77–79.
^ С. В. Шевченко (ред.). К вопросу о дате основания г. Владимира, ТОО "Местное время", 1992. (S. V. Shevchenko (ed.). On the foundation date of Vladimir. in Russian)
^ A tale of two Vladimirs, The Economist (5 November 2015)
From one Vladimir to another: Putin unveils huge statue in Moscow, The Guardian (5 November 2015)
Putin unveils 'provocative' Moscow statue of St Vladimir, BBC News (5 November 2016)
^ Volkoff, Vladimir (2011). Vladimir the Russian Viking. New York: Overlook Press.
- Golden, P. B. (2006) "Rus." Encyclopaedia of Islam (Brill Online). Eds.: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Bain, Robert Nisbet (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 168.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Bain, Robert Nisbet (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 168.
Some historical analysis and political insights on the state affairs of Vladimir the Great (in Russian)
Moss, Walter (2002). A history of Russia. London: Anthem. ISBN 978-1-84331-023-5. OCLC 53250380.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vladimir I of Kiev. |
- Velychenko, Stephen, How Valdamarr Sveinaldsson got to Moscow (krytyka.com), 9 November 2015.
Vladimir I of Kiev Rurikovich Born: 958 Died: 15 July 1015 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by ? | Prince of Novgorod 969–977 | Succeeded by ? |
| Preceded by Yaropolk I Sviatoslavich | Grand Prince of Kiev 980–1015 | Succeeded by Sviatopolk I |
Titles in pretence | ||
| Preceded by Oleg of the Drevlyans | Prince of Kiev 977–980 | Succeeded by Vysheslav Vladimirovich |
| Preceded by Yaropolk I | Prince of Kiev and Novgorod 978–1015 | Succeeded by Sviatopolk I |





