Vitruvian Man
| Vitruvian Man | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Artist | Leonardo da Vinci |
| Year | c. 1490 |
| Type | Pen and ink with wash over metalpoint on paper |
| Dimensions | 34.6 cm × 25.5 cm (13.6 in × 10.0 in) |
| Location | Gallerie dell'Accademia, Venice |
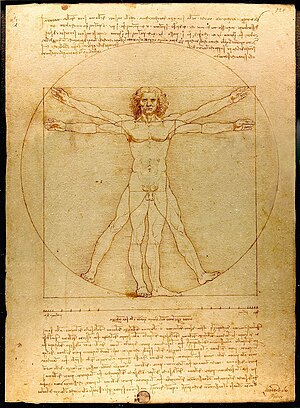
The Vitruvian Man (Italian: Le proporzioni del corpo umano secondo Vitruvio, which is translated to "The proportions of the human body according to Vitruvius"), or simply L'Uomo Vitruviano (Italian pronunciation: [ˈlwɔːmo vitruˈvjaːno]), is a drawing made by the Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci around 1490.[1] It is accompanied by notes based on the work of the architect Vitruvius. The drawing, which is in ink on paper, depicts a man in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and inscribed in a circle and square. The drawing and text are sometimes called the Canon of Proportions or, less often, Proportions of Man. It is kept in the Gabinetto dei disegni e stampe of the Gallerie dell'Accademia, in Venice, Italy, under reference 228. Like most works on paper, it is displayed to the public only occasionally, so it is not part of the normal exhibition of the museum.[2][3]
The drawing is based on the correlations of ideal human body proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise De architectura. Vitruvius described the human figure as being the principal source of proportion among the classical orders of architecture. Vitruvius determined that the ideal body should be eight heads high. Leonardo's drawing is traditionally named in honor of the architect.
Contents
1 Subject and title
2 Evidence of collaboration
3 Translation of the text
4 Legacy
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
Subject and title
This image demonstrates the blend of mathematics and art during the Renaissance and demonstrates Leonardo's deep understanding of proportion. In addition, this picture represents a cornerstone of Leonardo's attempts to relate man to nature. Encyclopædia Britannica online states, "Leonardo envisaged the great picture chart of the human body he had produced through his anatomical drawings and Vitruvian Man as a cosmografia del minor mondo (cosmography of the microcosm). He believed the workings of the human body to be an analogy for the workings of the universe."[4]
According to Leonardo's preview in the accompanying text, written in mirror writing, it was made as a study of the proportions of the (male) human body as described in Vitruvius' De architectura 3.1.2–3, which reads:
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
For the human body is so designed by nature that the face, from the chin to the top of the forehead and the lowest roots of the hair, is a tenth part of the whole height; the open hand from the wrist to the tip of the middle finger is just the same; the head from the chin to the crown is an eighth, and with the neck and shoulder from the top of the breast to the lowest roots of the hair is a sixth; from the middle of the breast to the summit of the crown is a fourth. If we take the height of the face itself, the distance from the bottom of the chin to the under side of the nostrils is one third of it; the nose from the under side of the nostrils to a line between the eyebrows is the same; from there to the lowest roots of the hair is also a third, comprising the forehead. The length of the foot is one sixth of the height of the body; of the forearm, one fourth; and the breadth of the breast is also one fourth. The other members, too, have their own symmetrical proportions, and it was by employing them that the famous painters and sculptors of antiquity attained to great and endless renown.
Similarly, in the members of a temple there ought to be the greatest harmony in the symmetrical relations of the different parts to the general magnitude of the whole. Then again, in the human body the central point is naturally the navel. For if a man be placed flat on his back, with his hands and feet extended, and a pair of compasses centred at his navel, the fingers and toes of his two hands and feet will touch the circumference of a circle described therefrom. And just as the human body yields a circular outline, so too a square figure may be found from it. For if we measure the distance from the soles of the feet to the top of the head, and then apply that measure to the outstretched arms, the breadth will be found to be the same as the height, as in the case of plane surfaces which are perfectly square.[5]
Leonardo's drawing combines a careful reading of the ancient text with his own observation of actual human bodies. In drawing the circle and square he observes that the square cannot have the same centre as the circle,[6] but is centered at the groin.[7] This adjustment is the innovative part of Leonardo's drawing and what distinguishes it from earlier illustrations. He also departs from Vitruvius by drawing the arms raised to a position in which the fingertips are level with the top of the head, rather than Vitruvius's much lower angle, in which the arms form lines passing through the navel.
The drawing itself is often used as an implied symbol of the essential symmetry of the human body, and by extension, the symmetry of the universe as a whole.[8]
It may be noticed by examining the drawing that the combination of arm and leg positions creates sixteen different poses. The pose with the arms straight out and the feet together is seen to be inscribed in the superimposed square. On the other hand, the "spread-eagle" pose is seen to be inscribed in the superimposed circle.
The drawing was purchased from Gaudenzio de' Pagave by Giuseppe Bossi,[9] who described, discussed and illustrated it in his monograph on Leonardo's The Last Supper, Del Cenacolo di Leonardo da Vinci libri quattro (1810).[10] The following year he excerpted the section of his monograph concerned with the Vitruvian Man and published it as Delle opinioni di Leonardo da Vinci intorno alla simmetria de'Corpi Umani (1811), with a dedication to his friend Antonio Canova.[11]
After Bossi's death in 1815 the Vitruvian Man was acquired in 1822, along with a number of his drawings, by the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice, Italy, and has remained there since.[12]
Leonardo da Vinci's collaboration with the author of De divina proportione (On the Divine Proportion)[13] have led some to speculate that he incorporated the golden ratio in Vitruvian Man, but this is not supported by any of Leonardo's writings.[14][15] The proportions of Vitruvian Man do not match the golden ratio precisely.[16]

A Vitruvian Man prototype by Giacomo Andrea
Evidence of collaboration
Many artists attempted to design figures which would satisfy Vitruvius' claim that a human could fit into both a circle and a square.[17][18] Leonardo may have been influenced by the work of his friend Giacomo Andrea de Ferrara, a Renaissance architect and an expert on Vitruvius. Andrea's drawing features erasure marks indicating its unique creation.[18][7] As with Leonardo's Vitruvian Man, Andrea's circle is centered on the naval, but only one pose is included. Leonardo's design includes two sets of arms and legs to touch both the circle and the square.[7]
Translation of the text
The text is in two parts, above[a] and below[b] the image. The upper part paraphrases Vitruvius:
Vetruvio, architect, puts in his work on architecture that the measurements of man are in nature distributed in this manner: that is a palm is four fingers, a foot is four palms, a cubit is six palms, four cubits make a man, a pace is four cubits, a man is 24 palms and these measurements are in his buildings.
If you open your legs enough that your head is lowered by one-fourteenth of your height and raise your hands enough that your extended fingers touch the line of the top of your head, know that the centre of the extended limbs will be the navel, and the space between the legs will be an equilateral triangle.
The lower section of text gives these proportions:
The length of the outspread arms is equal to the height of a man; from the hairline to the bottom of the chin is one-tenth of the height of a man; from below the chin to the top of the head is one-eighth of the height of a man; from above the chest to the top of the head is one-sixth of the height of a man; from above the chest to the hairline is one-seventh of the height of a man. The maximum width of the shoulders is a quarter of the height of a man; from the breasts to the top of the head is a quarter of the height of a man; the distance from the elbow to the tip of the hand is a quarter of the height of a man; the distance from the elbow to the armpit is one-eighth of the height of a man; the length of the hand is one-tenth of the height of a man; the root of the penis is at half the height of a man; the foot is one-seventh of the height of a man; from below the foot to below the knee is a quarter of the height of a man; from below the knee to the root of the penis is a quarter of the height of a man; the distances from below the chin to the nose and the eyebrows and the hairline are equal to the ears and to one-third of the face.
The points determining these proportions are marked with lines on the drawing. Below the drawing is a single line equal to a side of the square and divided into four cubits, of which the outer two are divided into six palms each, two of which have the mirror-text annotation "palmi"; the outermost two palms are divided into four fingers each, and are each annotated "diti".
Legacy
Vitruvian Man has stimulated artists including:
Cesare Cesariano (1521)
Albrecht Dürer (1528)
Pietro di Giacomo Cataneo (1554)
Heinrich Lautensack (1618)
William Blake (1795)
See also
- Anthropometry
- Body proportions
- Leonardo's robot
- Modulor
References
Footnotes
^ Above the image:
Vetruvio, architecto, mecte nella sua op(er)a d'architectura, chelle misure dell'omo sono dalla natura
disstribuite inquessto modo cioè che 4 diti fa 1 palmo, et 4 palmi fa 1 pie, 6 palmi fa un chubito, 4
cubiti fa 1 homo, he 4 chubiti fa 1 passo, he 24 palmi fa 1 homo ecqueste misure son ne' sua edifiti.
Settu ap(r)i ta(n)to le ga(m)be chettu chali da chapo 1/14 di tua altez(z)a e ap(r)i e alza tanto le b(r)acia che cholle lunge dita tu tochi la linia della
somita del chapo, sappi che 'l cie(n)tro delle stremita delle
ap(er)te me(m)bra fia il bellicho. Ello spatio chessi truova infralle ga(m)be fia tria(n)golo equilatero
^ Below the image:
Tanto ap(r)e l'omo nele b(r)accia, qua(n)to ella sua alteza.
Dal nasscimento de chapegli al fine di sotto del mento è il decimo dell'altez(z)a del(l)'uomo. Dal di socto del mento alla som(m)i-
tà del chapo he l'octavo dell'altez(z)a dell'omo. Dal di sop(r)a del pecto alla som(m)ità del chapo fia il sexto dell'omo. Dal di so-
p(r)a del pecto al nasscime(n)to de chapegli fia la sectima parte di tucto l'omo. Dalle tette al di sop(r)a del chapo fia
la quarta parte dell'omo. La mag(g)iore larg(h)ez(z)a delle spalli chontiene insè [la oct] la quarta parte dell'omo. Dal go-
mito alla punta della mano fia la quarta parte dell'omo, da esso gomito al termine della isspalla fia la octava
parte d'esso omo; tucta la mano fia la decima parte dell'omo. Il menb(r)o birile nasscie nel mez(z)o dell'omo. Il
piè fia la sectima parte dell'omo. Dal di socto del piè al di socto del ginochio fia la quarta parte dell'omo.
Dal di socto del ginochio al nasscime(n)to del memb(r)o fia la quarta parte dell'omo. Le parti chessi truovano infra
il me(n)to e 'l naso e 'l nasscime(n)to de chapegli e quel de cigli ciasscuno spatio p(er)se essimile alloreche è 'l terzo del volto
Citations
^ The Secret Language of the Renaissance – Richard Stemp
^ "The Vitruvian man". Leonardodavinci.stanford.edu. Retrieved 2010-08-20..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Da Vinci's Code". Witcombe.sbc.edu. Retrieved 2010-08-20.
^ Heydenreich, Ludwig Heinrich (2017-04-30). "Leonardo da Vinci". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
^ "Ten Books on Architecture. Book III, Chapter I, "On Symmetry: In Temples And In The Human Body"". Gutenberg.org. 2006-12-31. Retrieved 2010-08-20.
^ "The Vitruvian Man - Leonardo Da Vinci". About.com. Archived from the original on 12 April 2014. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
^ abc "Leonardo: The Man Who Saved Science". Secrets of the Dead. Season 16. Episode 5. 5 April 2017. 52 minutes in. PBS.
^ "Bibliographic reference". The Whole Universe Book. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
^ Bossi, Giuseppe (1810)Del Cenacolo di Leonardo da Vinci libri quattro (in Italian) Milano: Stamperia Reale p.208ff
^ "Bibliographic reference". Ursusbooks.com. Retrieved 2010-08-20.
^ "Bibliographical notice, no. 319". Lib.rochester.edu. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009. Retrieved 20 August 2010.
^ "LEONARDO DA VINCI. THE UNIVERSAL MAN". venezia.net. Retrieved 2014-02-13.
^ Leonardo da Vinci's Polyhedra, by George W. Hart[1]
^ Livio, Mario (November 1, 2002). "The golden ratio and aesthetics". Plus Magazine. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
^ Keith Devlin (May 2007). "The Myth That Will Not Go Away". Retrieved September 26, 2013.Part of the process of becoming a mathematics writer is, it appears, learning that you cannot refer to the golden ratio without following the first mention by a phrase that goes something like 'which the ancient Greeks and others believed to have divine and mystical properties.' Almost as compulsive is the urge to add a second factoid along the lines of 'Leonardo Da Vinci believed that the human form displays the golden ratio.' There is not a shred of evidence to back up either claim, and every reason to assume they are both false. Yet both claims, along with various others in a similar vein, live on.
^ Donald E. Simanek. "Fibonacci Flim-Flam". Archived from the original on March 17, 2016. Retrieved November 27, 2018.
^ Wolchover, Natalie (31 January 2012). "Did Leonardo da Vinci copy his famous 'Vitruvian Man'?". NBC News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ ab Lester, Toby (1 February 2012). "The Other Vitruvian Man". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
Works cited
Lester, Toby (2012). Da Vinci's Ghost: Genius, Obsession, and How Leonardo Created the World in His Own Image. New York: Free Press. ISBN 9781439189238.
External links
| Look up Vitruvian Man in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci. |
- Willamette University site on Vitruvian Man
- Stanford University site on Vitruvian Man
- Leonardo's Vitruvian Man
Vitruvian Man Video- Contemporary interpretation of Vitruvian Man
Leonardo da Vinci: anatomical drawings from the Royal Library, Windsor Castle, exhibition catalog fully online as PDF from The Metropolitan Museum of Art, which contains material on Vitruvian Man (see index)
