Policja
| Policja | |
|---|---|
 Wordmark of Policja | |
 Badge of Policja | |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | 1919 |
| Preceding agency |
|
| Employees | 103 309 |
| Annual budget | 9.3 billion PLN (2009) |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| National agency | PL |
| Operations jurisdiction | PL |
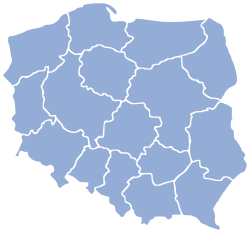 | |
| Jurisdiction of the Policja | |
| Constituting instruments |
|
| General nature |
|
| Headquarters | Warsaw |
| Minister responsible |
|
| Agency executive |
|
| Policja Regional HQs | 17 + 5 training centers |
| Website | |
Policja (English) | |
Policja (Polish pronunciation: [pɔˈlit͡sja]) is the generic name for the police in Poland. The Polish police force was known as policja throughout the Second Polish Republic (1918–1939), and in modern post-communist Republic of Poland since 1990. Its current size is 100,000 officers and ca. 25,000 civilian employees. Among the branches in the force are: Criminal Service, Traffic Police Service, Prevention Service and Supporting Service. Most towns and some villages have their own city guards, which supervise public order and road safety. However, city guards have jurisdiction only over misdemeanors and in cases of crimes may serve only in a supportive role for the state police.
Contents
1 Terminology
2 History
3 Transportation and equipment
3.1 Current patrol fleet
3.2 Patrol Cars
3.3 Vans
3.4 Buses
3.5 Motorcycles
3.6 All Terrain Vehicles
3.7 Air support
3.8 Firearms
4 General commandant of the Policja
5 Rank structure
6 Structure and branches of the Policja
7 Anti-terrorism units (BOA/SPAP)
8 Peacekeeping and international cooperation
9 Organisation
9.1 Regional commands
9.2 Police training establishments
10 Cricitism of the Policja
11 Representative Band of the Policja
12 Gallery
13 See also
14 References
15 External links
16 Further reading
Terminology

A pair of uniformed officers of the Policja
The force's name, Policja, translates into the English language as Police.
An individual officer is typically called a policjant (plural policjanci); these are not, however, official titles and are not included in the official rank structure, they are simply terms used to refer to any police officer regardless of the rank they may hold. A police station is known as Komenda Policji or Komisariat Policji both of which translate more or less into English as Police Commissariat. Female officers may be referred to as policjantki, the singular of which is policjantka.
On the whole, officers' individual ranks are not used by the general public and thus when addressing an officer, it is common to hear the term Pan (female - Pani), Polish for mister/miss used to refer to police officers. On occasion, this may or may not be followed by the term Oficer.
History

An officer of the State Police on traffic duty in Warsaw, 1939
In 1919, with the re-independence of the Polish nation, the state reorganised itself along non-federalist lines and established a centralised form of government. Under the auspices of the new government, a new national police force was formed; this 'Polish State Police' (Policja Państwowa)[2] then existed as the primary law enforcement agency for the entire nation up until the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939. During the inter-war period, a number of key law enforcement duties were delegated to other formations, such as the Border Guard[3] and Military Gendarmerie.[4]
With the end of World War II and the onset of the communist period, the new Soviet backed government decided to radically change the structure of policing in Poland; the state 'Policja' was renamed as the 'Milicja Obywatelska' (Citizen's Militia), a name which was meant to reflect a change in the role of the police, from an instrument of oppression ensuring the position of the bourgeoisie, to a force composed of, and at the service of 'normal citizens'. Ironically the reality turned out to be largely the opposite and the Milicja instead represented a rather state-controlled force which was used to exert political repression on the citizens. The Milicja was, for the most part, detested by the general populace; events such as the police's conduct during the Gdańsk Shipyard Strike and surrounding the Popiełuszko affair, only worsened the people's view of their law enforcement agencies.
After the fall of the communist government in Poland, the system was reformed once again, this time reviving the pre-war name of 'Policja' and albeit with a few minor changes, the general system of law-enforcement of the Second Republic.
Transportation and equipment

Service vehicles of the Polish police in current (2009 onwards) livery, with a highways duty policeman in the new uniform (2009 onwards)
Today, most common types include various models from Kia (Cee'd model - ca. 4000 in use) Škoda (mainly Octavia), Alfa Romeo, Ford Mondeo, Opel (mainly Opel Astra), Volkswagen, and Toyota, as of 2011 the FSO Polonez (manufactured in Poland) is no longer in use. The Polish police force has, since joining the European Union, been undergoing a thorough restructuring and has in the process acquired a large number of new vehicles; as of 2011 this process is still ongoing and new vehicles are constantly being procured in order to replace ageing old patrol cars as their service lives come to an end. In addition to standard sedan and hatchback model vehicles, the Policja has been investing significant amounts of money in developing their ability to respond to any incident no matter where it may be, this has in turn led to the purchase of a large number of all-terrain 4x4 vehicles and multi-purpose vans and trucks. This expansion in capabilities was a stated requirement of the police force's restructuring program.
Beginning in 2009, the painting scheme is being modified to a silver body design with blue reflective strip, similar to modern German police cars.
Traditionally, vehicles were painted a dark blue color with side doors painted in white, and with white stripes and the word "POLICJA" on both sides. Earlier versions (used at the beginning of the 1990s) had a thinner stripe with the word "POLICJA" written under it. This design was adopted from the paint scheme used by the communist milicja. Some formerly used vehicles even had visible traces of the word "POLICJA" being corrected from "MILICJA", with the first two letters in a different shade of white, on a patch of a different shade of blue.
All uniformed and most non-uniformed officers of the state police are routinely armed. In addition to their firearm, Policja officers carry handcuffs and a number of other pieces of equipment which usually includes a personal radio system for communication with other officers and their police station. Pepper spray is also commonly issued to officers in order to provide them with a non-lethal alternative weapon with which to incapacitate violent suspects.
Riot police, when needs be, are provided with non-ballistic body armour, helmets and shields. In such cases they also dispose LRAD units. The existence of a well-enforced ban on civilian-owned firearms in Poland has significantly aided the police in keeping gun crime to a minimum, and thus the incidence of police firearms use is low.
Current patrol fleet

A Honda patrol bike of the traffic police.
The below list is not intended to be a full list of all the vehicles used by the Polish Police, instead it lists the most commonly used vehicles.
|
|
|
|
Air support

A PZL W-3 helicopter belonging to the Policja's Capital Command, based in Warsaw

Police station, Szczecin

Police station in Józefów

New Alfa Romeo 159 of Greater Poland Voivodeship police, Poznań

Policja patrol boats on the Vistula in Warsaw
The Policja currently has a total of 16 helicopters at its disposal,[5] these are based in:
Kraków - 2 x PZL Kania
Szczecin - 2 x Mil Mi-2
Warsaw - 3 x Mil Mi-8, 2 x PZL W-3, 1 x Bell 206, 1 x Bell 412[6]
Łódź - 1 x Mil Mi-2, 1 x Bell 206[7]
Poznań - 2 x Mil Mi-2
Wrocław - 2 x Mil Mi-2
In addition to the airborne and land-based patrol units of the Policja, many regional commands, and especially those based near the coast or through which major waterways flow, have maritime units. The largest of police maritime units are currently found on the Vistula river in Warsaw (under the command of the Capital Police) and the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship where there is a large network of lakes and rivers. In coastal areas, maritime law enforcement cooperation also exists between the Policja and the Polish Border Guard.
Firearms
| Name | Country of origin | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walther P99 | Semi-automatic pistol | Manufactured in Poland in Łucznik Arms Factory under licence | |
| Glock-17 | Semi-automatic pistol | ||
| Glock-19 | Semi-automatic pistol | ||
| Glock-26 | Semi-automatic pistol | ||
| P-83 Wanad | Semi-automatic pistol | ||
| P-64 | Semi-automatic pistol | ||
| CZ-75 | Semi-automatic pistol | In limited use | |
| Gward | Revolver | Virtually phased out | |
| Taurus | Semi-automatic pistol | Virtually phased out | |
| PM-84 Glauberyt | Submachine gun | ||
| PM-98 Glauberyt | Submachine gun | ||
| H&K MP5 | Submachine gun | In limited use | |
| H&K UMP | Submachine gun | 9mm variant, in limited use | |
| IMI Uzi | Submachine gun | In limited use | |
| FN P-90 | Submachine gun | in limited use | |
| PM-63 RAK | Submachine gun | Virtually phased out | |
| Mossberg 590 | Shotgun | ||
| Remington 870 MCS | Shotgun | ||
| MPT-76 | Submachine gun | ||
| Benelli M3 | Shotgun | (limited use) | |
| AKMS | Assault rifle | ||
| Heckler & Koch G36 | Assault rifle | In limited use | |
| HK416 | Assault rifle | Limited use in Counter-terrorism Squad | |
| HK417 | Battle rifle | Limited use in Counter-terrorism Squad | |
| SVD | Designated marksman rifle | ||
| Sako TRG-21 | Sniper Rifle | ||
| Sako TRG-22 | Sniper rifle | ||
| Sako TRG-42 | Sniper rifle | ||
| RWGŁ-3 | Non-lethal rifle grenade launcher | ||
| AWGŁ-1 | Non-lethal rifle grenade launcher | ||
| Brügger & Thomet GL-06 | Grenade launcher | ||
| Heckler & Koch HK69A1 | Grenade launcher |
General commandant of the Policja
| Name | From | Until |
|---|---|---|
| Leszek Lamparski | 20 May 1990 | 18 June 1991 |
| Roman Hula | 17 July 1991 | 14 January 1992 |
| Zenon Smolarek | 25 February 1992 | 8 February 1995 |
| Jerzy Stańczyk | 7 March 1995 | 3 January 1997 |
| Marek Papała | 3 January 1997 | 29 January 1998 |
| Jan Michna | 29 January 1998 | 25 October 2001 |
| Antoni Kowalczyk | 27 October 2001 | 29 October 2003 |
| Leszek Szreder | 29 October 2003 | 3 November 2005 |
| Marek Bieńkowski | 3 November 2005 | 12 February 2007 |
| Konrad Kornatowski | 12 February 2007 | 8 August 2007 |
| Tadeusz Budzik | 13 August 2007 | 6 March 2008 |
| Andrzej Matejuk | 6 March 2008 | 9 January 2012 |
| Marek Działoszyński | 10 January 2012 | 11 February 2015 |
| Krzysztof Gajewski | 12 February 2015 | 10 December 2015 |
| Zbigniew Maj | 11 December 2015 | 12 February 2016 |
| Jarosław Szymczyk | 13 April 2016 |
The Policja's general commandant is the senior-most officer of the Polish police. The rank of the general commandant (usually General Inspector) is considered to be equivalent to that of a ranking general in the Polish military and this both himself and his subordinate chief inspectors (who are also considered Police 'Generals') are entitled to wear embroidered white eagles, the state symbol, on their uniform lapels.
The general commandant's office is based in Warsaw's Puławska Street. It is from here that the day-to-day administration and organisation of the Polish police's activities is coordinated. The commandant's office is considered to have jurisdictional supremacy over all its other commands, and voivodeship/municipal commandants are responsible to the general commandant in their capacity as his regional 'executives'.
The office of general commandant has existed in a number of guises throughout the existence of the Polish police, and whilst the current office came into being following Poland's transformation into a liberal democracy in 1990, the same rank was also used for the highest-ranking officer of the State Police of the Second Republic during the inter-war years. Nowadays, holders of this office are considered to be successors to the commandants of the inter-war state police; commanding officers of the communist-era Milicja Obywatelska (Citizens' Militia) however, are not considered successors of the original cadre of Policja generals as they exercised authority over an organisation often utilised by the state as an instrument of political oppression.
Since 1990 there have been twelve general commandants of the Policja who have completed their service. General Inspector Marek Papała, the formet holder of the office, was assassinated by a person or persons unknown on 25 June 1998. He was shot in the head with a silenced weapon whilst exiting his car near his home in Warsaw's southern Mokotów district.[8] The commandant's murder remains unsolved and is considered to be one of the most significant outstanding cases under active investigation by the Polish police.
Rank structure

A chief inspector of the Policja in full parade uniform whilst making a speech
| Junior officers | Senior officers / Warrant Officers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder insignia for every day uniform |  | 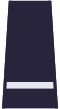 |  |  |  | 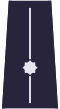 | 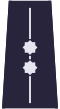 |  | 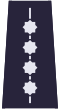 |
| Rank | Constable | Senior Constable | Sergeant | Senior Sergeant | Staff Sergeant | Junior Aspirant | Aspirant | Senior Aspirant | Staff Aspirant |
| Junior supervisory officers | Senior supervisory officers | Staff officers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder insignia for every day uniform |  | 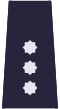 | 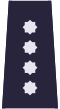 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Rank | Deputy Commissioner | Commissioner | Chief Commissioner | Deputy Inspector | Junior Inspector | Inspector | Chief Inspector | Inspector General of Police |
Structure and branches of the Policja
The Policja is currently divided into a number of different services. Each voivodeship/municipal command has subdivisions within its force. This leaves the police service with a large number of specialised branches which can more specifically target certain types of crime and apply more expert knowledge in the investigation of cases relating to their area of policing. In addition to these specific groups, all police forces retain a majority of officers for the purpose of patrol duty and general law enforcement.

The cap badge of the Policja is common to all ranks and branches.
Typically a constituent force of the Policja will contain the following subdivisions within its structure:
- Criminal Police (Policja Kryminalna) - investigation and prevention of serious and violent crime
- The criminal police may include specislised teams such as anti-drugs and financial crime prevention units
- All forces have crime scene and forensics units
- Preventative Police (Policja Prewencyjna) - general law enforcement operations and patrol duty (includes anti-terrorist and riot police divisions)
- Traffic Police (Policja Ruchu Drogowego) - road safety, traffic marshalling and highway patrol/pursuit
- Logistical Support Police (Policja Wspomagająca) - provision of logistical support and technical skills
- Police Aviation Service (Służba Lotnictwa Policji) - aviation support (not present in every force)
- Investigative Police (Policja Śledcza) - investigation of complex cases and process of referral to the state prosecutor's office
- Judicial Police (Policja Sądowa) - protection of court and state prosecutor's office premises, judges, prosecutors, victims and suspects, execution of court orders
- Maritime Police (Policja Wodna) - maritime patrol and pursuit
| Branch | Criminal | Preventative | Traffic | Logistical Support | Special Branch | Judicial |
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Anti-terrorism units (BOA/SPAP)

A riot police officer of the Preventative Police
The Policja has highly qualified and well-equipped counter-terrorism formations. The central (national-level) anti-terrorism is BOA KGP (Biuro Operacji Antyterrorystycznych Komendy Głównej Policji, Bureau of Anti-terrorism Operations of The Policja Headquarters), which is part of the Komenda Główna Policji (Policja Headquarters). On a regional level, voivodeship commands have control of smaller units called SPAP (Samodzielny Pododdział Antyterrorystyczny Policji, Independent Anti-terrorism Policja Subunit), these units are responsible for, high-risk arrests, search warrant execution service, hostage rescue operations (only in alarm situations; BOA has priority in this task) and other similar tasks.
Because of their training and skill level, members of the BOA and SPAP units cooperate with similar special police formations from the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Germany and other ATLAS members. They also, train with servicemen from Biuro Ochrony Rządu, Straż Graniczna, Agencja Bezpieczeństwa Wewnętrznego, Wojska Specjalne, and most recently with the U.S. Army and 10th CAB's premier special missions company, A/3-10 GSAB WarAngels.

Anti-terrorism officers of the Policja demonstrate their tactics at a Policja exhibition in Wolin.
A Mercedes-Benz Sprinter of the Policja in Kraków
Peacekeeping and international cooperation
Since the Policja's foundation in its current form in 1990, the service has taken part and continues to participate in a number of international peacekeeping and international police missions around the world.[9] To date the Policja has sent officers to participate in the following international peacekeeping missions:
United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) - 3 officers
European Union Police Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (EUPM) - initially 12 officers (2003), later reduced to 3 senior advisers (2009)
European Union Police Mission in Afghanistan (EUPOL Afghanistan) - 3 officers and 2 senior advisers
European Union Monitoring Mission in Georgia (EUMM) - 10 officers (working alongside 16 officers of the Żandarmeria Wojskowa)
European Union Rule of Law Mission in Kosovo (EULEX) - 8 senior advisers
In addition to participating in international missions, the Policja also send delegates to and cooperate with international law enforcement agencies and organisations such as Europol and Interpol. Currently the Polish officers make up the eighth largest staff contingent of Europol; a figure which is expected to rise as the Polish police force becomes more integrated with, and more active within, the organisation. Europol has also become far more important to Poland's policing community in recent years since Poland, in 2007, became a signatory of the Schengen Agreement, allowing for greater European integration, uninterrupted travel, and cross-border police cooperation. To this end, Polish cooperation with the German, Czech, Slovakian and Lithuanian police services has reached an all-time high. Furthermore, the Policja officers have taken part in a number of foreign police officer training and exchange programs, such as Project Lifesaver, which has seen a number of officers sent to the UK to observe and discuss alternative methods of policing abroad.[10]
As a constituent member of Interpol, the Polish police is expected to adhere to the terms of International arrest warrants and cooperate with the police forces of other nations through formal diplomatic channels. In many cases such cooperation has led to the arrest of high-risk criminals.
Organisation
The Polish Police is a centralised police force, organised under one central command in Warsaw and with all officers assigned to one of 17 voivodeship/municipal operations' commands, except in the case that they are specialists working independently for the national commandant.

The Mostowski Palace in Warsaw, seat of the Policja general commandant's office

Lesser Poland Police vehicles parked outside the Wawel Castle in Kraków during the state funeral of president Kaczyński and his wife

A mounted police officer in Poznań, near the Adam Mickiewicz University
Regional commands
| Territorial Force | Seat of Command | |
|---|---|---|
| Voivodeship / Municipality | Police Force | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Police training establishments

Officer candidates arrive at the Higher Police School in Szczytno
The Policja has five training establishments sited within Poland. Four of these training establishments are police schools for enlisted personnel, whilst the fifth is a higher educational institution tasked with the education of officers and senior officials in a range of disciplines and expertises. The four junior colleges are located in:
Piła, Greater Poland Voivodeship - Piła Police School (Szkoła Policji w Pile)
Słupsk, Pomeranian Voivodeship - Słupsk Police School (Szkoła Policji w Słupsku)
Katowice, Silesian Voivodeship - Katowice Police School (Szkoła Policji w Katowicach)
Legionowo, Masovian Voivodeship - Police Training Centre (Centrum Szkolenia Policji)
The final police training establishment in Poland is the Wyższa Szkoła Policji or Higher Police School in Szczytno (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship). This school was founded in 1954 as the officer academy of the Milicja Obywatelska, renamed in 1972 to the Higher Militia School, the college finally became the Higher Police School upon Poland's return to liberal democracy in 1990.[11] Since then it has remained the only establishment in the country certified to run courses for commissioned officers of the Polish police, and the officer's commissioning course. All students who attend the Higher Police School are expected to study criminal, constitutional and economic law. In addition to academic studies, officer candidates are trained in modern policing techniques, weapons' handling, and informatics. The college has numerous links with senior police academies in Europe and throughout the wider world.
Cricitism of the Policja
Overall the level of trust in the Policja and its work has increased steadily over the years since 2001. In 2001 only 46% of respondents to a national survey carried out on behalf of the police categorised their work and achievements as 'good', however, by the end of 2009 this figure had grown significantly, and despite small undulations, an average of 72% rated the Policja's work as 'good' or better.[12] This brings the level of trust in the police to around the same level of 64-75% seen in other member states of the European Union.[13]
Much in the same way as other national police forces, the Policja is sometimes criticised for the methods it employs in maintaining law and order, such criticism is typically voiced by Polish youth. This is most commonly expressed with the acronyms (C)HWDP and JP.
Representative Band of the Policja

A group of musicians from the official Representative Band of the Policja
The Policja's representative band was first founded in 1968. Its core was composed of a group of several musicians, which gradually expanded. From the beginning, the band improved rapidly, reaching a high artistic level, as reflected in the discretion of the judges at musical contests nationwide. In the years 1984, 1986, 1988, the band won its most prestigious trophy, the Cup of the Minister of Internal Affairs. From the outset, the musicians performed at various national, departmental, religious and state events.
The band's musicians have on numerous occasions represented the Polish police outside the country, including concerts in Denmark, Belgium, Czech Republic, Belarus and Russia, yet they still value their well-kept tradition of playing performances for the ordinary residents of Warsaw. Its musicians annually take part in the International Congress of Music in Kraków and donate all the proceeds of their performances to a number of charities for the sick and disadvantaged. The band's musical repertoire includes marches, concert pieces, transcriptions of orchestral music and religious songs, as well as a great deal of other developmental music. Being the official representative band of the Policja, the group's musicians are often invited to play parade music for important events on national holidays such as the 3rd May Constitution Day.
On the 40th anniversary of the Policja's band, 22 January 2009, a large concert was held at the Bajka theatre in Warsaw. The program included inter alia, a solo performance of the Włodzimierz Korcz theme from the series 07 zgłoś się.
Gallery

Old, out of use, patrol car (FSO Polonez) in previous markings
A new all-terrain vehicle, Suzuki Vitara, in new colour scheme
Two policemen (old patrol uniform) patrol Kraków's Old Market Square

Kia cee'd squad car of the Policja during a patrol in Świnoujście

An anti-terrorism Policja officer from SPAP (Special Branch) during training

Policja officers marching in parade uniform on 3 May Constitution Day
See also
Milicja Obywatelska (MO) - communist era police/militia service
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Administration of the Republic of Poland (Ministerstwo Spraw Wewnętrznych i Administracji)
Służba Bezpieczeństwa (SB) - communist era secret police service
References
^ Journal of Laws of the Komenda Główna Policji (General Headquarters of Policja), 2006, January 23
^ History of State Police 1919-1939 (Polish)
^ "Straż Graniczna". Retrieved 11 May 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ History of Polish Gendarmerie
^ JSK Internet. "Lotnictwo w Policji". Policja.pl. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
^ [1](Polish)
^ [2](Polish)
^ Kim są Józef Sasin, Roman Kurnik i Ryszard Bieszyński
^ JSK Internet. "Misje pokojowe". O Policji. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
^ http://www.wielkopolska.policja.gov.pl/ruchdrogowy/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=143&Itemid=32[permanent dead link]
^ Wojtek. "Information on the School". Retrieved 11 May 2015.
^ JSK Internet. "Policja.pl". Policja.pl. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
^ "Zawody godne zaufania Polaków". Rzeczpospolita. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
External links
![]() Media related to Police of Poland at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Police of Poland at Wikimedia Commons
- http://www.policja.pl
Further reading
- Andrzej Kremplewski, The Police and Non-Governmental Organizations in Poland, in András Kádár (ed.), Police in Transition: Essays on the Police Forces in Transition Countries, Central European University Press, 2001,
ISBN 963-9241-15-6







