Computer file
A computer file is a computer resource for recording data discretely in a computer storage device. Just as words can be written to paper, so can information be written to a computer file.
There are different types of computer files, designed for different purposes. A file may be designed to store a picture, a written message, a video, a computer program, or a wide variety of other kinds of data. Some types of files can store several types of information at once.
By using computer programs, a person can open, read, change, and close a computer file. Computer files may be reopened, modified, and copied an arbitrary number of times.
Typically, files are organised in a file system, which keeps track of where the files are located on disk and enables user access.
Contents
1 Etymology
2 File contents
2.1 File size
2.2 Organization of data in a file
2.3 Operations
3 Identifying and organizing
4 Protection
5 Storage
6 Back up
7 File systems and file managers
8 See also
9 Notes
10 External links
Etymology

A punched card file

The twin disk files of an IBM 305 system
The word "file" derives from the Latin filum ("a thread").[1]
"File" was used in the context of computer storage as early as January 1940. In Punched Card Methods in Scientific Computation,[2] W.J. Eckert stated, "The first extensive use of the early Hollerith Tabulator in astronomy was made by Comrie.[3] He used it for building a table from successive differences, and for adding large numbers of harmonic terms". "Tables of functions are constructed from their differences with great efficiency, either as printed tables or as a file of punched cards."
In February 1950: In a Radio Corporation of America (RCA) advertisement in Popular Science Magazine[4] describing a new "memory" vacuum tube it had developed, RCA stated: "the results of countless computations can be kept 'on file' and taken out again. Such a 'file' now exists in a 'memory' tube developed at RCA Laboratories. Electronically it retains figures fed into calculating machines, holds them in storage while it memorizes new ones - speeds intelligent solutions through mazes of mathematics."
In 1952, "file" denoted, inter alia, information stored on punched cards.[5]
In early use, the underlying hardware, rather than the contents stored on it, was denominated a "file". For example, the IBM 350 disk drives were denominated "disk files".[6] The introduction, circa 1961, by the Burroughs MCP and the MIT Compatible Time-Sharing System of the concept of a "file system" that managed several virtual "files" on one storage device is the origin of the contemporary denotation of the word. Although the contemporary "register file" demonstrates the early concept of files, its use has greatly decreased.
File contents
On most modern operating systems, files are organized into one-dimensional arrays of bytes. The format of a file is defined by its content since a file is solely a container for data, although, on some platforms the format is usually indicated by its filename extension, specifying the rules for how the bytes must be organized and interpreted meaningfully. For example, the bytes of a plain text file (.txt in Windows) are associated with either ASCII or UTF-8 characters, while the bytes of image, video, and audio files are interpreted otherwise. Most file types also allocate a few bytes for metadata, which allows a file to carry some basic information about itself.
Some file systems can store arbitrary (not interpreted by the file system) file-specific data outside of the file format, but linked to the file, for example extended attributes or forks. On other file systems this can be done via sidecar files or software-specific databases. All those methods, however, are more susceptible to loss of metadata than are container and archive file formats.
File size
At any instant in time, a file might have a size, normally expressed as number of bytes, that indicates how much storage is associated with the file. In most modern operating systems the size can be any non-negative whole number of bytes up to a system limit. Many older operating systems kept track only of the number of blocks or tracks occupied by a file on a physical storage device. In such systems, software employed other methods to track the exact byte count (e.g., CP/M used a special control character, Ctrl-Z, to signal the end of text files).
The general definition of a file does not require that its size have any real meaning, however, unless the data within the file happens to correspond to data within a pool of persistent storage. A special case is a zero byte file; these files can be newly created files that have not yet had any data written to them, or may serve as some kind of flag in the file system, or are accidents (the results of aborted disk operations). For example, the file to which the link /bin/ls points in a typical Unix-like system probably has a defined size that seldom changes. Compare this with /dev/null which is also a file, but its size may be obscure. (This is misleading because /dev/null is not really a file: in Unix-like systems, all resources, including devices, are accessed like files, but there is still a real distinction between files and devices—at core, they behave differently—and the obscurity of the "size" of /dev/null is one manifestation of this. As a character device, /dev/null has no size.)
Organization of data in a file
Information in a computer file can consist of smaller packets of information (often called "records" or "lines") that are individually different but share some common traits. For example, a payroll file might contain information concerning all the employees in a company and their payroll details; each record in the payroll file concerns just one employee, and all the records have the common trait of being related to payroll—this is very similar to placing all payroll information into a specific filing cabinet in an office that does not have a computer. A text file may contain lines of text, corresponding to printed lines on a piece of paper. Alternatively, a file may contain an arbitrary binary image (a BLOB) or it may contain an executable.
The way information is grouped into a file is entirely up to how it is designed. This has led to a plethora of more or less standardized file structures for all imaginable purposes, from the simplest to the most complex. Most computer files are used by computer programs which create, modify or delete the files for their own use on an as-needed basis. The programmers who create the programs decide what files are needed, how they are to be used and (often) their names.
In some cases, computer programs manipulate files that are made visible to the computer user. For example, in a word-processing program, the user manipulates document files that the user personally names. Although the content of the document file is arranged in a format that the word-processing program understands, the user is able to choose the name and location of the file and provide the bulk of the information (such as words and text) that will be stored in the file.
Many applications pack all their data files into a single file called an archive file, using internal markers to discern the different types of information contained within. The benefits of the archive file are to lower the number of files for easier transfer, to reduce storage usage, or just to organize outdated files. The archive file must often be unpacked before next using.
Operations
The most basic operations that programs can perform on a file are:
- Create a new file
- Change the access permissions and attributes of a file
Open a file, which makes the file contents available to the program
Read data from a file
Write data to a file
Close a file, terminating the association between it and the program
Files on a computer can be created, moved, modified, grown, shrunk, and deleted. In most cases, computer programs that are executed on the computer handle these operations, but the user of a computer can also manipulate files if necessary. For instance, Microsoft Word files are normally created and modified by the Microsoft Word program in response to user commands, but the user can also move, rename, or delete these files directly by using a file manager program such as Windows Explorer (on Windows computers) or by command lines (CLI).
In Unix-like systems, user space programs do not operate directly, at a low level, on a file. Only the kernel deals with files, and it handles all user-space interaction with files in a manner that is transparent to the user-space programs. The operating system provides a level of abstraction, which means that interaction with a file from user-space is simply through its filename (instead of its file descriptor). For example, rm filename will not delete the file itself, but only a link to the file. There can be many links to a file, but when they are all removed, the kernel considers that file's memory space free to be reallocated. This free space is commonly considered a security risk (due to the existence of file recovery software). Any secure-deletion program uses kernel-space (system) functions to wipe the file's data.
Identifying and organizing
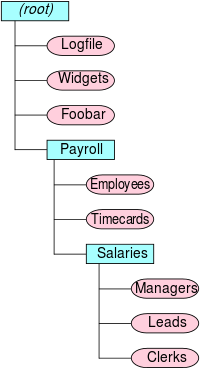
Files and folders arranged in a hierarchy
In modern computer systems, files are typically accessed using names (filenames). In some operating systems, the name is associated with the file itself. In others, the file is anonymous, and is pointed to by links that have names. In the latter case, a user can identify the name of the link with the file itself, but this is a false analogue, especially where there exists more than one link to the same file.
Files (or links to files) can be located in directories. However, more generally, a directory can contain either a list of files or a list of links to files. Within this definition, it is of paramount importance that the term "file" includes directories. This permits the existence of directory hierarchies, i.e., directories containing sub-directories. A name that refers to a file within a directory must be typically unique. In other words, there must be no identical names within a directory. However, in some operating systems, a name may include a specification of type that means a directory can contain an identical name for more than one type of object such as a directory and a file.
In environments in which a file is named, a file's name and the path to the file's directory must uniquely identify it among all other files in the computer system—no two files can have the same name and path. Where a file is anonymous, named references to it will exist within a namespace. In most cases, any name within the namespace will refer to exactly zero or one file. However, any file may be represented within any namespace by zero, one or more names.
Any string of characters may or may not be a well-formed name for a file or a link depending upon the context of application. Whether or not a name is well-formed depends on the type of computer system being used. Early computers permitted only a few letters or digits in the name of a file, but modern computers allow long names (some up to 255 characters) containing almost any combination of unicode letters or unicode digits, making it easier to understand the purpose of a file at a glance. Some computer systems allow file names to contain spaces; others do not. Case-sensitivity of file names is determined by the file system. Unix file systems are usually case sensitive and allow user-level applications to create files whose names differ only in the case of characters. Microsoft Windows supports multiple file systems, each with different policies[which?] regarding case-sensitivity. The common FAT file system can have multiple files whose names differ only in case if the user uses a disk editor to edit the file names in the directory entries. User applications, however, will usually not allow the user to create multiple files with the same name but differing in case.
Most computers organize files into hierarchies using folders, directories, or catalogs. The concept is the same irrespective of the terminology used. Each folder can contain an arbitrary number of files, and it can also contain other folders. These other folders are referred to as subfolders. Subfolders can contain still more files and folders and so on, thus building a tree-like structure in which one "master folder" (or "root folder" — the name varies from one operating system to another) can contain any number of levels of other folders and files. Folders can be named just as files can (except for the root folder, which often does not have a name). The use of folders makes it easier to organize files in a logical way.
When a computer allows the use of folders, each file and folder has not only a name of its own, but also a path, which identifies the folder or folders in which a file or folder resides. In the path, some sort of special character—such as a slash—is used to separate the file and folder names. For example, in the illustration shown in this article, the path /Payroll/Salaries/Managers uniquely identifies a file called Managers in a folder called Salaries, which in turn is contained in a folder called Payroll. The folder and file names are separated by slashes in this example; the topmost or root folder has no name, and so the path begins with a slash (if the root folder had a name, it would precede this first slash).
Many (but not all) computer systems use extensions in file names to help identify what they contain, also known as the file type. On Windows computers, extensions consist of a dot (period) at the end of a file name, followed by a few letters to identify the type of file. An extension of .txt identifies a text file; a .doc extension identifies any type of document or documentation, commonly in the Microsoft Word file format; and so on. Even when extensions are used in a computer system, the degree to which the computer system recognizes and heeds them can vary; in some systems, they are required, while in other systems, they are completely ignored if they are presented.
Protection
Many modern computer systems provide methods for protecting files against accidental and deliberate damage. Computers that allow for multiple users implement file permissions to control who may or may not modify, delete, or create files and folders. For example, a given user may be granted only permission to read a file or folder, but not to modify or delete it; or a user may be given permission to read and modify files or folders, but not to execute them. Permissions may also be used to allow only certain users to see the contents of a file or folder. Permissions protect against unauthorized tampering or destruction of information in files, and keep private information confidential from unauthorized users.
Another protection mechanism implemented in many computers is a read-only flag. When this flag is turned on for a file (which can be accomplished by a computer program or by a human user), the file can be examined, but it cannot be modified. This flag is useful for critical information that must not be modified or erased, such as special files that are used only by internal parts of the computer system. Some systems also include a hidden flag to make certain files invisible; this flag is used by the computer system to hide essential system files that users should not alter.
Storage
Any file that has any useful purpose, must have some physical manifestation. That is, a file (an abstract concept) in a real computer system must have a real physical analogue if it is to exist at all.
In physical terms, most computer files are stored on some type of data storage device. For example, most operating systems store files on a hard disk. Hard disks have been the ubiquitous form of non-volatile storage since the early 1960s.[7] Where files contain only temporary information, they may be stored in RAM. Computer files can be also stored on other media in some cases, such as magnetic tapes, compact discs, Digital Versatile Discs, Zip drives, USB flash drives, etc. The use of solid state drives is also beginning to rival the hard disk drive.
In Unix-like operating systems, many files have no associated physical storage device. Examples are /dev/null and most files under directories /dev, /proc and /sys. These are virtual files: they exist as objects within the operating system kernel.
As seen by a running user program, files are usually represented either by a File control block or by a file handle. A File control block (FCB) is an area of memory which is manipulated to establish a filename etc. and then passed to the operating system as a parameter, it was used by older IBM operating systems and early PC operating systems including CP/M and early versions of MS-DOS. A file handle is generally either an opaque data type or an integer, it was introduced in around 1961 by the ALGOL-based Burroughs MCP running on the Burroughs B5000 but is now ubiquitous.
Back up
When computer files contain information that is extremely important, a back-up process is used to protect against disasters that might destroy the files. Backing up files simply means making copies of the files in a separate location so that they can be restored if something happens to the computer, or if they are deleted accidentally.
There are many ways to back up files. Most computer systems provide utility programs to assist in the back-up process, which can become very time-consuming if there are many files to safeguard. Files are often copied to removable media such as writable CDs or cartridge tapes. Copying files to another hard disk in the same computer protects against failure of one disk, but if it is necessary to protect against failure or destruction of the entire computer, then copies of the files must be made on other media that can be taken away from the computer and stored in a safe, distant location.
The grandfather-father-son backup method automatically makes three back-ups; the grandfather file is the oldest copy of the file and the son is the current copy.
File systems and file managers
The way a computer organizes, names, stores and manipulates files is globally referred to as its file system. Most computers have at least one file system. Some computers allow the use of several different file systems. For instance, on newer MS Windows computers, the older FAT-type file systems of MS-DOS and old versions of Windows are supported, in addition to the NTFS file system that is the normal file system for recent versions of Windows. Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages. Standard FAT allows only eight-character file names (plus a three-character extension) with no spaces, for example, whereas NTFS allows much longer names that can contain spaces. You can call a file "Payroll records" in NTFS, but in FAT you would be restricted to something like payroll.dat (unless you were using VFAT, a FAT extension allowing long file names).
File manager programs are utility programs that allow users to manipulate files directly. They allow you to move, create, delete and rename files and folders, although they do not actually allow you to read the contents of a file or store information in it. Every computer system provides at least one file-manager program for its native file system. For example, File Explorer (formerly Windows Explorer) is commonly used in Microsoft Windows operating systems, and Nautilus is common under several distributions of Linux.
See also
- Block (data storage)
- Computer file management
- Data hierarchy
- File camouflage
- File copying
- File conversion
- File deletion
- File directory
- File manager
- File system
- Filename
- Flat file database
- Object composition
- Soft copy
Notes
^ "Online Etymology Dictionary"..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Eckert, W. J.; Thomas J. Watson Astronomical Computing Bureau, New York. (1940). Punched card methods in scientific computation. New York: The Thomas J. Watson Astronomical Computing Bureau, Columbia University.
^ Comrie, L. J. (1928-04-13). "On the Construction of Tables by Interpolation.: (Plate 6.)". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 88 (6): 506–523. Bibcode:1928MNRAS..88..506C. doi:10.1093/mnras/88.6.506. ISSN 0035-8711.
^ Popular Science Magazine, February 1950, page 96. Bonnier Corporation. February 1950. Retrieved 2014-03-07.
^ Robert S. Casey, et al. Punched Cards: Their Applications to Science and Industry. 1952.
^ Martin H. Weik. Ballistic Research Laboratories Report #1115. March 1961. pp. 314-331.
^ Magnetic Storage Handbook 2nd Ed., Section 2.1.1, Disk File Technology, Mee and Daniel, (c)1990,
External links
 Media related to Computer files at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Computer files at Wikimedia Commons
Data Formats Computer file at Curlie