University of Minnesota
 | |
| Motto | Commune vinculum omnibus artibus (Latin) |
|---|---|
Motto in English | A common bond for all the arts |
| Type | Public Flagship university Land grant Space grant |
| Established | 1851 (1851)[1] |
Academic affiliations |
|
| Endowment | $3.5 billion (2017)[2] |
| Budget | $3.8 billion (2017)[3] |
| President | Eric W. Kaler |
| Provost | Karen Hanson |
Academic staff | 3,804[4] |
| Students | 51,848[5] |
| Undergraduates | 31,535[5] |
| Postgraduates | 12,614[5] |
Doctoral students | 3,508[5] |
| Location | Minneapolis and Saint Paul Minnesota , United States 44°58′29″N 93°14′07″W / 44.974747°N 93.235353°W / 44.974747; -93.235353Coordinates: 44°58′29″N 93°14′07″W / 44.974747°N 93.235353°W / 44.974747; -93.235353 |
| Campus | Urban 2,730 acres (1,100 ha) |
| Colors | Maroon and Gold[6] |
| Nickname | Golden Gophers |
Sporting affiliations | NCAA Division I Big Ten, WCHA (Women's ice hockey) |
| Mascot | Goldy Gopher |
| Website | www.umn.edu |
 | |
The University of Minnesota, Twin Cities (often referred to as the University of Minnesota, Minnesota, the U of M, UMN, or simply the U) is a public research university in Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota. The Minneapolis and St. Paul campuses are approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) apart, and the Saint Paul campus is actually in neighboring Falcon Heights.[7] It is the oldest and largest campus within the University of Minnesota system and has the sixth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 51,848 students in 2017–18. The university is the flagship institution of the University of Minnesota system, and is organized into 19 colleges and schools, with sister campuses in Crookston, Duluth, Morris, and Rochester.
The University of Minnesota is one of America's Public Ivy universities, which refers to top public universities in the United States capable of providing a collegiate experience comparable with the Ivy League. Founded in 1851, The University of Minnesota is categorized as a Doctoral University – Highest Research Activity (R1) in the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.[8] Minnesota is a member of the Association of American Universities and is ranked 14th in research activity with $881 million in research and development expenditures in the fiscal year ending June 30, 2015.[9]
The University of Minnesota faculty, alumni, and researchers have won 29 Nobel Prizes[10] and three Pulitzer Prizes.[11]
Notable University of Minnesota alumni include two Vice Presidents of the United States, Hubert Humphrey and Walter Mondale, and Bob Dylan, who received the 2016 Nobel Prize in Literature.
Contents
1 Academics
1.1 Organization and administration
1.2 Institutes and centers
1.3 Rankings
1.3.1 Global
1.3.2 National
1.4 Discoveries and innovation
2 Campuses
2.1 Demographics
2.2 Minneapolis campus
2.2.1 East Bank
2.2.1.1 Notable architecture
2.2.2 West Bank
2.2.3 Getting around
2.3 St. Paul campus
2.4 Commuting between Minneapolis and St. Paul campuses
2.5 Campus safety
2.5.1 Sexual assaults
3 Big Ten Academic Alliance
4 Student life and traditions
4.1 Greek life, professional and honor societies
4.2 Media
4.2.1 Print
4.2.2 Radio
4.2.3 Television
4.3 Minnesota Student Association
4.3.1 Graduate and Professional Student Assembly
4.4 Athletics
4.4.1 Football
4.4.2 Basketball
4.4.3 Men's ice hockey
4.4.4 Women's hockey
4.4.5 Women's Rugby
5 Notable people
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
Academics
Organization and administration
The university organization structure consists of 19 colleges, schools, and other major academic units:[12]
- Center for Allied Health Programs
- College of Biological Sciences
- College of Continuing and Professional Studies
- School of Dentistry
- College of Design
- College of Education and Human Development
- Extension
- College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences
- Graduate School
- Law School
- College of Liberal Arts
- Carlson School of Management
- Medical School
- School of Nursing
- College of Pharmacy
- Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs
- School of Public Health
- College of Science and Engineering
- College of Veterinary Medicine
Institutes and centers
The university has six university-wide interdisciplinary centers and institutes whose work crosses collegiate lines:[13]
- Center for Cognitive Sciences
- Consortium on Law and Values in Health, Environment, and the Life Sciences
- Institute for Advanced Study at University of Minnesota
- Institute for Translational Neuroscience
- Institute on the Environment
- Minnesota Population Center
Rankings
University rankings | |
|---|---|
| National | |
Forbes[14] | 106 |
Times/WSJ[15] | 71 |
U.S. News & World Report[16] | 76 |
Washington Monthly[17] | 61 |
| Global | |
ARWU[18] | 37 |
Times[19] | 71 |
U.S. News & World Report[20] | 41 |
Global
In 2018, Minnesota was ranked 37th in the world by the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU). The Times Higher Education World University Rankings for 2015 ranks Minnesota 46th in the world.[21] The Center for World University Rankings (CWUR) ranked the university 35th in the world and 25th in the United States in 2018.[22] In 2016, the Nature Index ranked Minnesota 34th in the world based on research publication data from 2015.[23] In 2015, Academic Ranking of World Universities ranked the university 11th in the world for mathematics.[24]
National
The University of Minnesota is ranked 14 overall among the nation's top research universities by the Center for Measuring University Performance.[25] The university's research and development expenditures ranked 13th–15th among U.S. academic institutions in the 2010 through 2015 National Science Foundation reports.[26] The U.S. News & World Report's 2016 rankings placed the undergraduate program of the university as the 69th-best National University in the United States. It also ranked the Chemical Engineering program third-best, the Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) program third best, the Economics PhD program tenth, Psychology eighth, Statistics sixteenth, Audiology ninth, and the University of Minnesota Medical School 6th for primary care and 34th for research.[27] The Law School, consistently recognized as a 'Top Law School' by U.S. News & World Report, is ranked 20th in the nation, and is a national leader in commercial law, international law, and clinical education.[28] Additionally, nineteen of the university's graduate-school departments have been ranked in the nation's top-twenty by the U.S. National Research Council.[29] In 2008 and 2012 U.S. News & World Report ranked the College of Pharmacy 2nd in the nation. 2016 U.S. News & Report now rank the College of Pharmacy 2nd in the nation.[30] In 2011, U.S. News & World Report ranked the School of Public Health 8th in the nation,[31] which is home to the 2nd ranked program for the Master of Healthcare Administration degree.[32] The University of Minnesota ranked 19th in NIH funding in 2008.[33]
Minnesota is listed as a "Public Ivy" in 2001 Greenes' Guides The Public Ivies: America's Flagship Public Universities.[34] U.S. News & World Report has ranked the Nursing Informatics program of University of Minnesota as 2nd best in the nation.[35]
Discoveries and innovation
The university is known for innovation in research. The inventions by students and faculty have ranged from food science to health technologies. Most of the public research funding in Minnesota is funneled to the University of Minnesota as a result of long standing advocacy by the university itself.
The university developed Gopher,[36] a precursor to the World Wide Web which used hyperlinks to connect documents across computers on the internet. However, the version produced by CERN was favored by the public since it was freely distributed and could more easily handle multimedia webpages.[37] The university also houses the Charles Babbage Institute, a research and archive center specializing in computer history. The department has strong roots in the early days of supercomputing with Seymour Cray of Cray supercomputers.[38]
The university also became a member of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) in 2007, and has led data analysis projects searching for gravitational waves – the existence of which were confirmed by scientists in February 2016.[39]
Puffed rice – Alexander P. Anderson led to the discovery of "puffed rice", a starting point for a new breakfast cereal later advertised as "Food Shot From Guns".- Transistorized cardiac pacemaker – Earl Bakken founded Medtronic, where he developed the first external, battery-operated, transistorized, wearable artificial pacemaker in 1957.
ATP synthase – Paul D. Boyer elucidated the enzymatic mechanism for synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), leading to a Nobel Prize in 1997.
Point-contact transistor – Walter Houser Brattain and John Bardeen, later joined by William Shockley, invented the point-contact transistor in December 1947. For their invention the trio was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956.
Infusion pump – Henry Buchwald invented world's first infusion port, peritoneovenous shunts, and specialty vascular catheters. He also invented the first implantable infusion pump, a precursor to implantable infusion pumps in use throughout the world today.
Photosynthesis – Melvin Calvin discovered the Calvin cycle along with Andrew Benson and James Bassham, for which he was awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Supercomputer – Seymour Cray designed a series of computers that were the fastest in the world for decades, and founded Cray Research which built many of these machines.
Taconite – Edward Wilson Davis developed an engineering process to economically extract iron ore from hard taconite rocks, making taconite valuable as iron ore for the iron and steel industries.
Cosmic ray – Phyllis S. Freier discovered the presence of heavy nuclei in cosmic rays, proving the similarity between our solar system and the rest of the galaxy.- U.S. aviation – Robert Rowe Gilruth led the development of flying qualities for airplanes, the use of rockets to achieve data at supersonic speeds and the establishment of many of the nation's leading flight research and human space flight operations facilities.
Bone marrow transplant – Robert A. Good performed the first successful human bone marrow transplant between persons who were not identical twins and is regarded as a founder of modern immunology.
Gore-Tex – Robert Gore invents Gore-Tex materials in 1969.
Disk drive – Reynold B. Johnson invents method and machinery to score tests electronically.
K-rations – Ancel Keys patented in 1978, has become a widely prescribed drug for preventing heart disease and life-threatening arrhythmias.
Synthetic rubber – Izaak Kolthoff developed the "cold process" for producing synthetic rubber, which he undertook under the U.S. synthetic rubber program during World War II.
Cyclotron – Ernest Lawrence won the Nobel Prize for Physics 1939 for inventing and developing the cyclotron.
Drosophila melanogaster – Edward Lewis discovered the Drosophila Bithorax complex of homeotic genes.
Cardiac surgery – C. Walton Lillehei pioneered open-heart surgery, as well as numerous techniques, equipment and prostheses for cardiothoracic surgery.
POPmail – Mark P. McCahill led the development of the Gopher protocol, the effective predecessor of the World Wide Web, was involved in creating and codifying the standard for Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) and led the development of POPmail, one of the first e-mail clients which had a foundational influence on later e-mail clients and the popularization of graphical user interfaces in Internet technologies more broadly.
MMPI – Starke R. Hathaway and J. C. McKinley created the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI), which was first published in 1943.
Zatocoding – Calvin Mooers developed a mechanical system using superimposed codes of descriptors for information retrieval called Zatocoding.
Atomic bomb – Edward P. Ney discovered cosmic ray heavy nuclei and solar proton events. After early work involving separating isotopes from uranium, he worked on the Manhattan Project which created the first atomic bomb.
Atomic bomb – Alfred O. C. Nier devised a method to isolate uranium isotope, a critical discovery in the atomic age. Nier worked with Kellex Corporation in New York City on the design and development of efficient and effective mass spectrographs for use in the Manhattan Project to build the atomic bomb in World War II. During the war most of the spectrographs used for monitoring uranium separations were designed by Nier.
Atomic bomb – Frank Oppenheimer worked on uranium isotope separation in 1945 and joined the Manhattan Project.
Biotechnology – Ronald L. Phillips was the first to generate whole corn plants from cells grown in culture, which laid the foundation for, and sparked, a new industry, using cell-culture methods to genetically modify corn plants and other cereals. The corn cell line which is most widely used for genetic modification of corn has greatly accelerated the improvement of corn, as food, feed and fuel.
Renewable energy – Lanny D. Schmidt discovered a reactor to extract hydrogen from ethanol, offering the first real hope hydrogen could be a source of inexpensive and renewable energy.
Biomimetics – Otto Schmitt invented the Schmitt trigger, the cathode follower, the differential amplifier, and the chopper-stabilized amplifier.
NASA – Deke Slayton was one of the original NASA Mercury Seven astronauts, and became NASA's first chief of the Astronaut Office. He served as NASA's director of flight crew operations, making him responsible for crew assignments at NASA from November 1963 until March 1972. At that time he was granted medical clearance to fly, and was assigned as the docking module pilot of the 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project, at age 51 becoming the oldest person to fly in space at the time.
Bathythermograph – Athelstan Spilhaus fully developed the bathythermograph (BT) in 1938, an instrument he perfected was of vital importance in World War II in the battle against the German U-boat. During the war, the BT became standard equipment on all U.S. Navy subs and vessels involved in antisubmarine warfare.
CDC 6600 – James Thornton developed the CDC 6600, the world’s first supercomputer, designed with Seymour Cray.
Ziagen – Robert Vince worked on antiviral drug candidates at the University of Minnesota, where he went on to develop carbocyclic nucleosides termed 'carbovirs'. This class of medicinal agents included the drug abacavir. Abacavir was commercialized by GlaxoSmithKline as Ziagen for the treatment of AIDS.
Campuses
Demographics
As the largest of five campuses across the University of Minnesota system, its more than 50,000 students make it the sixth largest campus student body in the US overall. It has more than 300 research, education, and outreach centers and institutes, on everything from the life sciences to public policy and technology.[39]
The university offers 143 undergraduate degree programs[40] and 200 graduate degree programs.[41] The university has all three branches of the Reserve Officer Training Corps (ROTC).[42] The University of Minnesota Twin Cities as well as its sister campuses at Crookston, Duluth, and Morris are accredited by the Higher Learning Commission (HLC).[43]
The racial/ethnic breakdown of the student population is: 65.3% White, 12.7% International Students (that are undesignated race/ethnicity), 9.2% Asian, 4.3% Black, 3.1% Hispanic/Latino, 1.2% American/Native American Indian, and 4.2% Unknown. 63% of matriculants to the university are considered Minnesota residents, and 37% of matriculants are considered out-of-state residents.[44] According to the University Office of Institutional Research, as of Fall 2015, there are 30,511 undergraduates at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities campus. Of that number, 5,771 are first-time degree seeking freshmen. There are 12,659 graduate students.
Minneapolis campus
The original Minneapolis campus overlooked the Saint Anthony Falls on the Mississippi River, but it was later moved about a mile (1.6 km) downstream to its current location. The original site is now marked by a small park known as Chute Square at the intersection of University and Central Avenues. The school shut down following a financial crisis during the American Civil War, but reopened in 1867 with considerable financial help from John S. Pillsbury. It was upgraded from a preparatory school to a college in 1869. Today, the university's Minneapolis campus is divided by the Mississippi River into an East and West Bank.
The campus now has buildings on both river banks. The "East Bank", the main portion of the campus, covers 307 acres (124 ha). The West Bank is home to the University of Minnesota Law School, the Humphrey School of Public Affairs, the Carlson School of Management, various social science buildings, and the performing arts center. The St. Paul campus is home to the College of Biological Sciences (CBS), the College of Design (CDes), the College of Food, Agriculture and Natural Resource Sciences (CFANS), and the veterinary program.
The Minneapolis campus has several residence halls, 17th Avenue Hall, Centennial Hall, Frontier Hall, Territorial Hall, Pioneer Hall, Sanford Hall, Middlebrook hall, and Comstock Hall.
East Bank

Northrop Mall

University of Minnesota East Bank campus in the winter

Mall panorama, from left: Ford Hall, Coffman Memorial Union, Kolthoff Hall, Smith Hall (in center of image), Walter Library, Johnston Hall, Northrop, and Morrill Hall
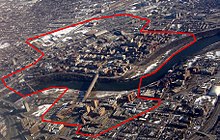
Aerial photo of the Minneapolis campus, facing east

East Bank

Walter Library, Northrop Mall
To help ease navigation of the large campus, the university has divided the East Bank into several areas: the Knoll area, the Mall area, the Health area, the Athletic area, and the Gateway area.
The Knoll area, the oldest extant part of the university, is in the northwestern corner of the campus.[45] Many buildings in this area are well over 100 years old; a 13-building group comprises the Old Campus Historic District.[46] Today, most disciplines in this area relate to the humanities. Burton Hall is home to the College of Education and Human Development. Folwell Hall and Jones Hall are primarily used by the language departments. A residence hall, Sanford Hall, and a student-apartment complex, Roy Wilkins Hall, are in this area. This area is just south of the Dinkytown neighborhood and business area.
Northrop Mall, or the Mall area, is arguably the center of the Minneapolis campus. The plan for the Mall was based on a design by Cass Gilbert, although his scheme was too extravagant to be fully implemented.[47] Several of the campus's primary buildings surround the Mall area. Northrop Auditorium provides a northern anchor, with Coffman Memorial Union (CMU) to the south. Four of the larger buildings to the sides of the Mall are the primary mathematics, physics, and chemistry buildings, (Vincent Hall, Tate Laboratory and Smith Hall, respectively) and Walter Library. The Mall area is home to the College of Liberal Arts, which is Minnesota's largest public or private college, and the College of Science and Engineering. Behind CMU is another residence hall, Comstock Hall, and another student-apartment complex, Yudof Hall. The Northrop Mall Historic District was formally listed in the National Register of Historic Places in January 2018.[48]
The Health area is to the southeast of the Mall area and focuses on undergraduate buildings for biological-science students, as well as homes to the College of Pharmacy, the School of Nursing, the School of Dentistry, the Medical School, the School of Public Health, and Fairview Hospitals and Clinics. This complex of buildings forms what is known as the University of Minnesota Medical Center. Part of the College of Biological Sciences is housed in this area.
Across the street from Fairview Hospital is an area known as the "Superblock", a four-city-block space comprising four residence halls (Pioneer, Frontier, Centennial and Territorial Halls). The Superblock is one of the most popular locations for on-campus housing because it has the largest concentration of students living on campus and has a multitude of social activities between the residence halls.
The Athletic area is directly north of the Superblock and includes four recreation/athletic facilities: the University Recreation Center, Cooke Hall, the University Fieldhouse, and the University Aquatic Center. These facilities are all connected by tunnels and skyways allowing students to use one locker-room facility. North of this complex is the TCF Bank Stadium, Williams Arena, Mariucci Arena, Ridder Arena, and the Baseline Tennis Center.
The Gateway area, the easternmost section of campus, is primarily composed of office buildings instead of classrooms and lecture halls. The most prominent building is McNamara Alumni Center. The university is also heavily invested in a biomedical-research initiative and has built five biomedical-research buildings that form a biomedical complex directly north of TCF Bank Stadium.
Notable architecture

Pillsbury Hall, one of the oldest buildings on campus (1889)

Frederick R. Weisman Art Museum
The Armory, northeast of the Mall area, is built like a Norman castle. It features a sally-port entrance facing Church Street and a tower that was originally intended to be the Professor of Military Science's residence. Since it originally held the athletics department, the Armory also features a gymnasium. Today it is home to military science classes and the university's Reserve Officers' Training Corps.
Several buildings in the Old Campus Historic District were designed by early Minnesota architect LeRoy Buffington. One of the most notable is Pillsbury Hall, designed by Buffington and Harvey Ellis in the Richardsonian Romanesque style. Pillsbury Hall's polychromatic facade incorporates several sandstone varieties that were available in Minnesota during the time of construction. Buffington also designed the exterior of Burton Hall, considered one of the strongest specimens of Greek Revival architecture in Minnesota.
Many of the buildings on the East Bank campus were designed by the prolific Minnesota architect Clarence H. Johnston, including the Jacobean Folwell Hall and the Beaux-Arts edifices of Northrop Auditorium and Walter Library, which he considered the heart of the university. Johnston's son, Clarence Johnston Jr, was also an architect and designed the original Bell Museum building and Coffman Memorial Union in the 1930s.
In more recent times, Frank Gehry designed the Frederick R. Weisman Art Museum (1993). The Weisman Art Museum is a typical example of his work with curving metallic structures. The abstract structure is considered highly significant because it was built prior to the widespread use of computer aided design in architecture. It also ushered in a new era of architecture at the university, which continued with the completion of the Antoine Predock-designed McNamara Alumni Center in 2000.
Another notable structure is the addition to the Architecture building, designed by Steven Holl and completed in 2002. It won an American Institute of Architects award for its innovative design. The Architecture building was then renamed Rapson Hall after the local modernist architect and School of Architecture Dean Ralph Rapson.
The university also has a "Greek row" of historic fraternities and sororities located north of campus on University Avenue SE.
West Bank

Department of Theatre Arts & Dance, Rarig Center
The West Bank covers 53 acres (21 ha). The West Bank Arts Quarter includes:
Rarig Center (Theatre Arts & Dance)- The Barbara Barker Center for Dance
- Ferguson Hall (School of Music)
- Ted Mann Concert Hall
- Regis Center for Art
The Quarter is home to several annual interdisciplinary arts festivals.
The Social Sciences are also on the West Bank and include the Carlson School of Management, the Law School, and the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs.
Wilson Library, the largest library in the university system, is also on the West Bank as is Middlebrook Hall, the largest residence hall on campus. Approximately 900 students reside in the building named in honor of William T. Middlebrook.[49]
Getting around

The Washington Avenue Bridge connects the East Bank and West Bank portions of the Minneapolis campus.

A Green Line train after leaving the East Bank Station, heading towards Downtown Minneapolis
The Washington Avenue Bridge crossing the Mississippi River provides access between the East and West Banks, on foot, designated bike lanes, or via free shuttle service. The bridge has two separate decks: the lower deck for vehicles and the newly constructed light rail, and the upper deck for pedestrian and bicycle traffic. An unheated enclosed walkway runs the length of the bridge and shelters students from the weather. Walking and riding bicycles are the most common modes of transportation among students. University Police occasionally cite individuals for jaywalking as well as riding bicycles on restricted sidewalk areas in areas surrounding the university resulting in fines as high as $250. This is often done at the beginning of a school year or after pedestrians interfere with traffic.[50]
There are some pedestrian tunnels to get from building to building during harsh weather; they are marked with signs reading "The Gopher Way".
The Minneapolis campus is near Interstates 94 and 35W and is bordered by the Minneapolis neighborhoods of Dinkytown (on the north), Cedar-Riverside (on the west), Stadium Village (on the southeast), and Prospect Park (on the east).
Three light-rail stations serve the university along the Green Line. The stations include Stadium Village, the East Bank, and the West Bank. The university partnered with Metro to offer students, staff, and faculty members a Campus Zone Pass that enables free travel on the three stations that pass through campus,[51] as well as a discounted unlimited pass for students.[52]
St. Paul campus

Aerial photo of St. Paul campus, facing south
The St. Paul campus is in the city of Falcon Heights, about 3 miles (4.8 km) away from the Minneapolis campus. The default place name for the ZIP code serving the campus is "St. Paul", but "Falcon Heights" is also recognized for use in the street addresses of all campus buildings. The College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences, including the University of Minnesota Food Industry Center and many other disciplines from social sciences to vocational education are on this campus. This also includes the College of Continuing and Professional Studies,[53] College of Veterinary Medicine,[54] and the College of Biological Sciences.[55] The extensive lawns, flowers, trees, woods, and the surrounding University research farm plots creates a greener and quieter campus. It has a grassy mall of its own and can be a bit of a retreat from the more-urban Minneapolis campus. Prominent on this campus is Bailey Hall, the St. Paul campus' only residence hall. There are campus connectors running every 5 minutes on the weekdays when school is in session, and every 20 minutes on weekends, allowing students easy access to both campuses.
The Continuing Education and Conference Center,[56] which serves over 20,000 conference attendees per year, is also on the St. Paul campus.
The St. Paul campus is home to the College of Design's department of Design, Housing, and Apparel (DHA). Located in McNeal Hall, DHA includes the departmental disciplines of Apparel Design, Graphic Design, Housing Studies, Interior Design, and Retail Merchandising.
The St. Paul campus is known to University students and staff for the Dairy Salesroom,[57] which sells food (including ice cream) produced in the university's state-certified dairy plant by students, faculty and staff, and the similar Meat Sales Room.[58]
The St. Paul campus borders the Minnesota State Fairgrounds, which hosts the largest state fair in the United States by daily attendance.[59] The fair lasts twelve days, from late August through Labor Day in early September. The grounds also serve a variety of functions during the rest of the year.
Although the Falcon Heights area code is 651, the university telephone system trunk lines use Minneapolis exchanges and its 612 area code.
Commuting between Minneapolis and St. Paul campuses
During the school year on regular weekdays, the Campus Connectors operate with schedule-less service as often as every five minutes during the busiest parts of the school day between 7:00am and 5:30pm, slowing to once every 15 or 20 minutes during earlier or later hours.[60] The estimated time to commute from St. Paul to East Bank is 15 minutes.[61] In 2008, the system carried 3.55 million riders. Despite the fact the shuttle service is free, it is comparatively inexpensive to operate: with an operating cost of $4.55 million in 2008, the operating subsidy was only $1.28 per passenger. Even Metro Transit's busy METRO Blue Line light rail required a subsidy of $1.44 that year, and that was with many riders paying $1.75 or more for a ride.[62]
Campus safety
The Step Up campaign is a program that helps students prevent crimes, sexual assault, and excessive drinking by teaching students how to intervene and prevent in a positive way.[63] They do this by explaining the Bystander effect. The U of M also has a TXT-U emergency notification text messaging system that sends out a notification to all faculty, staff, and students in case of emergency.[64] Similarly, there are different resources which students are able to get help while getting home. 624-WALK, an escort to walk to adjacent campuses and neighborhoods, and Gopher Chauffeur, a van service that offers rides near and on campus. Both of these are free and open to all students, staff, and faculty.[65]
In addition, there are almost 200 AED's on campus and 200 yellow phones for emergency only calls. The University Police Station has 20 Code Blue Phones around campus that immediately connect people to their office. There are also over 2,000 security cameras being monitored 24 hours a day.[65]
Sexual assaults
More than 1,000 sexual assaults on campus were reported between the years 2010 and 2015.[66] The total number of prosecutions for rape was zero according to Katie Eichele of the Aurora Center,[66] until the conviction of Daniel Drill-Mellum in 2016, for the rapes of two fellow students.[67] Of the sexual assaults on campus, few are reported to university police.[68] Six resulted in arrest from 2010 to 2015; one was determined to be unfounded.[68] In a study by campus police, in the years between 2005 and 2015, sexual assaults at the university remained the same or increased[69] despite six sexual assault resources and many anti-crime programs on campus.[70][71][72][73]
Big Ten Academic Alliance
The University of Minnesota is a participant in the Big Ten Academic Alliance. The Big Ten Academic Alliance (BTAA) is the academic consortium of the universities in the Big Ten Conference. Engaging in $10 billion in research in 2014–2015, BTAA universities provide powerful insight into important issues in medicine, technology, agriculture, and communities. Students at participating schools are also allowed "in-house" borrowing privileges at other schools' libraries.[74] The BTAA uses collective purchasing and licensing, and has saved member institutions $19 million to date.[75] Course sharing,[76]professional development programs,[77]study abroad and international collaborations,[78] and other initiatives are also part of the BTAA.
Student life and traditions
Greek life, professional and honor societies
The number of fraternities and sororities at the University of Minnesota is extensive. Including defunct branches, the Greek System numbers more than 200 organizations. Approximately half of these continue to operate today.[79] The university's Greek societies include the residential Academic and Social chapters including non-residential multicultural groups. The Greek System includes some but not all Professional Fraternities, Honor Societies, Religious and Service Fraternities. Fraternities and sororities have built several historically significant "Fraternity Row" homes along University Ave. SE, 10th Ave. SE, 4th Street SE, and 5th Street SE, all in Minneapolis, or along Cleveland Ave. near the St. Paul campus.[80]
As of June 2018, approximately 3,900 system members made up about 11% of the campus population. Minnesota hosts 38 academic fraternities, 20 academic sororities, 56 honors societies, 31 professional societies, and two service-focused chapters.[81][82]
Media

The eastern edge of the Northrop Mall, Spring 2008
Print
The Minnesota Daily is published only twice a week during the normal school season as of the Fall 2016 semester.[83] It is printed once each week during the summer. The Daily is operated by an autonomous organization run entirely by students. It was first published on May 1, 1900. Outside of every day news coverage the paper has also published special issues such as the Grapevine Awards, Ski-U-Mah, the Bar & Beer Guide, Sex-U-Mah, and others.
A long-defunct but fondly remembered humor magazine, Ski-U-Mah, was published from about 1930 to 1950. It launched the career of novelist and scriptwriter Max Shulman.
A relative newcomer to the university's print-media community is The Wake Student Magazine, a weekly magazine that covers University-related stories and provides a forum for student expression. It was founded in November 2001 in an effort to diversify campus media and achieved student group status in February 2002.[84] Students from many disciplines do all of the reporting, writing, editing, illustration, photography, layout and business management for the publication. The magazine was founded by James DeLong and Chris Ruen.[85]The Wake was named the nation's best campus publication (2006) by the Independent Press Association.[84]
Additionally, the Wake publishes Liminal, a literary journal that began in 2005. Liminal was created in the absence of an undergraduate literary journal and continues to bring poetry and prose to the university community.
The Wake has faced a number of challenges during its existence, due in part to the reliance on student fees funding. In April 2004, the needed $60,000 in funding was restored, which allowed for the magazine's continued existence after the Student Services Fees Committee had initially declined to fund it.[85] They faced further challenges in 2005 when their request for additional funding to publish weekly was denied[86] and then partially restored.[87]
In 2005 conservatives on campus began formulating a new monthly magazine named The Minnesota Republic. The first issue was released in February 2006, and funding by student service fees started in September 2006.
Radio
The campus radio station, KUOM "Radio K", broadcasts an eclectic variety of independent music during the day on 770 kHz AM. Its 5,000-watt signal has a range of 80 miles (130 km), but shuts down at dusk because of Federal Communications Commission regulations. In 2003, the station added a low-power (8-watt) signal on 106.5 MHz FM overnight and on weekends. In 2005, a 10-watt translator began broadcasting from Falcon Heights on 100.7 FM at all times. Radio K also streams its content at www.radiok.org. With roots in experimental transmissions that began before World War I, the station received the first AM broadcast license in the state on January 13, 1922, and began broadcasting as WLB, changing to the KUOM call sign about two decades later. The station had an educational format until 1993 when it merged with a smaller campus-only music station to become what is now known as Radio K. A small group of full-time employees are joined by over 20 part-time student employees who oversee the station. Most of the on-air talent consists of student volunteers.
Television
Some television programs made on campus have been broadcast on local PBS station KTCI channel 17. Several episodes of Great Conversations have been made since 2002, featuring one-on-one discussions between University faculty and experts brought in from around the world. Tech Talk is a show meant to help people who feel intimidated by modern technology, including cellular phones and computers.
Minnesota Student Association
The Minnesota Student Association (MSA) is the undergraduate student government at the University of Minnesota. It advocates for student interests on local, state, and federal levels, and focuses on efforts that directly benefit student population.
"Gopher Chauffeur," originally titled the MSA Express, is a student-operated late-night ride service.[88] Piloted by MSA, the 2007–2008 administration of Emma Olson and Ross Skattum began the process of transitioning the service to the university's Boynton Health Services.[89] This was done to ensure its longevity. Student response was overwhelmingly positive,[90] and the program was expanded in recent years due to campus safety concerns.[91]
MSA was instrumental in passing legislation in the 2013 Minnesota legislature for medical amnesty, and has focused more heavily on legislative advocacy in recent years.[92]
Graduate and Professional Student Assembly
The Graduate and Professional Student Assembly (GAPSA) is responsible for graduate and professional student governance at the University of Minnesota. It is the largest and most comprehensive graduate/professional student governance organization in the United States. GAPSA serves students in the Carlson School of Management, the Dental School, the Graduate School, the Law School, the Medical School, the School of Nursing, the College of Pharmacy, the School of Public Health, the College of Veterinary Medicine, and the College of Education and Human Development. GAPSA is also a member of the National Association of Graduate-Professional Students.
The University of Minnesota has the second largest number of graduate and professional students in the United States at over 16,000. All registered graduate and professional students at the University of Minnesota are members of GAPSA. It was established in 1990 as a non-profit (IRS 501 (c)(3)) confederation of independent college councils representing all graduate and professional students at the University of Minnesota to the Board of Regents, the President of the University, the University Senate, the university at large and wider community. GAPSA serves as a resource for member councils, as the primary contact point for administrative units, as a graduate and professional student policy-making and policy-influencing body, and as a center of intercollegiate and intra-collegiate interaction among students.
Athletics
Minnesota's athletic teams at the Twin Cities campus are known as the Minnesota Golden Gophers and compete in the NCAA's Division I as members of the Big Ten Conference. They have won 20 national championships as of 2015.[93]
The university's intercollegiate sports teams are called the Golden Gophers and are members of the Big Ten Conference and the Western Collegiate Hockey Association (WCHA) in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). Since the 2013–14 school year, the only Minnesota team that does not compete in the Big Ten is the women's ice hockey team, which competes in the WCHA. The Gophers men's ice hockey team was a longtime WCHA member, but left when the Big Ten began operating a men's ice hockey league with six inaugural members. The current athletic director is Mark Coyle, who took the position from interim athletic director Beth Goetz, after Norwood Teague resigned in August 2015 amid sexual assault allegations. Teague replaced Joel Maturi.
The Golden Gophers' most notable rivalry is the annual college football game against the Wisconsin Badgers (University of Wisconsin–Madison, Madison, Wisconsin) for Paul Bunyan's Axe, the longest continuous rivalry in NCAA Division I football. The two universities also compete in the Border Battle, a year-long athletic competition in which each sport season is worth 40 points divided by the number of times the teams play each other (i.e. football is worth 40 points because they play each other only once, while women's ice hockey is worth 10 points per game because they play four times a year). Conference and post-season playoffs do not count in the point standings.
Goldy Gopher is the mascot for the Twin Cities campus and the associated sports teams. The gopher mascot is a tradition as old as the state which was tabbed the "Gopher State" in 1857 after a political cartoon ridiculing the US$5-million railroad loan which helped open up the West. The cartoon portrayed shifty railroad barons as striped gophers pulling a railroad car carrying the Territorial Legislature. Later, the university picked up the nickname with the first university yearbook bearing the name "Gopher Annual" appearing in 1887.
The "Minnesota Rouser" is the University of Minnesota's fight song. It is commonly played and sung by the Minnesota Marching Band, the university's 320-member marching band, at various events such as commencement, convocation, and athletic games. It is among a number of songs associated with the university, including the Minnesota March, which was composed for the university by John Philip Sousa, and Hail! Minnesota, the university's alma mater and state song of Minnesota.[94]
Football

TCF Bank Stadium replaced the Hubert H. Humphrey Metrodome as the Gophers' home stadium in 2009.
The Minnesota Golden Gophers are one of the oldest programs in college-football history. They have won 7 National Championships and 18 Big Ten Conference Championships. The Golden Gophers played their first game on September 29, 1882, a 4–0 victory over Hamline University, St. Paul. In 1887, the Golden Gophers played host to the Wisconsin Badgers in a 63–0 victory. With the exception of 1906, the Golden Gophers and the Badgers have played each other every year since. The 128 games played against each other is the most-played rivalry in NCAA Division I FBS college football.
In 1981, the Golden Gophers played their last game in Memorial Stadium. Between 1982 and 2008, the school hosted their home games in the Hubert H. Humphrey Metrodome in downtown Minneapolis until they moved back to campus on September 12, 2009, when their new home, TCF Bank Stadium, opened with a game against the Air Force Falcons of the U.S. Air Force Academy.
Basketball
The Golden Gophers men's basketball team has won two National Championships, two National Invitation Tournament (NIT) Championships and eight Big Ten Regular Season Championships. They also have six NCAA Tournament, including a Final Four appearance in 1997 and three Sweet 16 appearances. However, because of NCAA sanctions for academic fraud, all postseason appearances from 1994 to 1998—in the NCAA Tournament in 1994, 1995, and 1997 and NIT in 1996 and 1998—were vacated. Most recently in April 2014, the Golden Gophers defeated SMU to win the NIT championship at Madison Square Garden in New York City.
The Golden Gophers women's basketball team has enjoyed success in recent years under Pam Borton, including a Final Four appearance in 2004. Overall, they have six NCAA Tournament appearances and three Sweet 16 appearances.
Men's ice hockey

Mariucci Arena
Ice hockey is one of the most strongly supported athletic programs at the University of Minnesota, referred to by the university as "Minnesota's Pride on Ice."[95] The high amount of support is due to the State of Minnesota's high affinity for the sport of ice hockey at all levels.[96]
The Golden Gophers men's ice-hockey program has won five Division I National Championships and 13 Western Collegiate Hockey Association (WCHA) Regular Season Championships, most recently in 2012. They have won 14 WCHA Tournament Championships and have 20 NCAA Frozen Four appearances. A former Golden Gophers hockey tradition was to stock the roster almost exclusively (sometimes completely) with Minnesota natives. Home games are played at Mariucci Arena. The Golden Gophers' big rivals are the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the University of North Dakota.
Women's hockey
The Golden Gophers women's hockey team has also won six National Championships, most recently in 2016, and six WCHA Regular Season Championships. They have also won four WCHA Tournament Championships and have eleven NCAA Frozen Four appearances. They play their home games in Ridder Arena. They were the first collegiate women's hockey team to play in an arena dedicated solely to women's ice hockey. In the 2012–2013 season they finished undefeated at 41–0, and are the first and only NCAA Women's Hockey team to do so. After winning the NCAA tournament their winning streak stood at 49 games, dating back to February 17, 2012 when they lost to North Dakota.
Women's Rugby
The Golden Gophers Women's Rugby club team won the Midwest conference championships in 2015, 2016 and 2017.
Notable people

Norman Borlaug (B.S, Forestry, 1937; M.S. (1939) and Ph.D. (1942), Plant Pathology), 1970 Nobel Prize in Peace
Herb Brooks (B.A., 1962), Olympic ice hockey coach

Nick Clegg (Fellow, 1989–90) Deputy Prime Minister of the United Kingdom

Bob Dylan (Literature & Arts, 1959-1960) 2016 Nobel Prize in Literature

Hubert Humphrey (B.A., 1939) 38th Vice President of the United States

Garrison Keillor (B.S, English, 1966), author

Walter Mondale (B.A., Political Science, 1951), 42nd Vice President of the United States

Deke Slayton (B.S., Aeronautical Engineering, 1949), Mercury Seven astronaut
See also
- List of colleges and universities in Minnesota
References
^ "Board of Regents Policy" (PDF). University of Minnesota. Retrieved August 31, 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ As of June 30, 2017. "U.S. and Canadian Institutions Listed by Fiscal Year (FY) 2017 Endowment Market Value and Change in Endowment Market Value from FY 2016 to FY 2017". National Association of College and University Business Officers and Commonfund Institute. 2018.
^ For Minnesota State Fiscal Year 2017 "University of Minnesota Budget". University of Minnesota. Retrieved July 27, 2016.
^ "University of Minnesota: Employee Head Count". University of Minnesota Office of Institutional Research. Archived from the original on April 3, 2016.
^ abcd Campus and Unit Enrollment by Academic Level for Fall 2017 Archived July 21, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. University of Minnesota Office of Institutional Research
^ "Our Brand: How to Convey It". University of Minnesota. Retrieved December 28, 2016.
^ "About Us". University of Minnesota Twin Cities. Archived from the original on October 11, 1999. Retrieved August 3, 2015.
^ "Carnegie Classifications | Standard Listings". The Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
^ "NSF Rankings by total R&D expenditures". Association of American Universities. 2015.
^ "University of Minnesota Scholars Walk: Nobel Prize". University of Minnesota. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
^ "University of Minnesota Scholars Walk: Pulitzer Prize". University of Minnesota. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
^ "Academics and Research". University of Minnesota. 2015-04-29.
^ "Academic Affairs and Provost, University of Minnesota". Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "America's Top Colleges 2018". Forbes. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ "U.S. College Rankings 2018". Wall Street Journal/Times Higher Education. Retrieved November 23, 2017.
^ "Best Colleges 2019: National Universities Rankings". U.S. News & World Report. November 19, 2018.
^ "2018 Rankings - National Universities". Washington Monthly. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ "Academic Ranking of World Universities 2018". Shanghai Ranking Consultancy. 2018. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ "World University Rankings 2019". THE Education Ltd. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ "Best Global Universities Rankings: 2019". U.S. News & World Report LP. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
^ "World University Rankings 2015 | Times Higher Education (THE)". Times Higher Education. October 2014. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
^ "CWUR 2018 – World University Rankings". Center for World University Rankings. Retrieved July 5, 2018.
^ "Nature Index 2016 Global – Top Institutions Academic Sector". Springer Nature. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
^ "Academic Ranking of World Universities in Mathematics – 2015 | 2015 Top 200 Universities in Mathematics | ARWU-SUBJECT 2015". Shanghairanking.com. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
^ "Research- The Center for Measuring University Performance" (PDF). Mup.asu.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 22, 2015. Retrieved March 21, 2014.
^ "University of Minnesota, Twin Cities". National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics – Academic Institution Profiles. Retrieved September 25, 2017.
^ "University of Minnesota-Twin Cities | Overall Rankings | Best College | US News". Colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com. Retrieved July 14, 2015.
^ "See the 2016 Best Law Schools". US News. Retrieved July 14, 2015.
^ Newton, H. J. "NRC Rankings in each of the 41 Areas". Texas A&M University. Retrieved December 22, 2006.
^ "Best Pharmacy Programs | Top Pharmacy Schools | US News Best Grad Schools". Grad-schools.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com. Archived from the original on November 18, 2016. Retrieved August 7, 2016.
^ "Best Public Health Programs". US News and World Report. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved July 14, 2011.
^ "Best Healthcare Management Programs". US News and World Report. Archived from the original on March 18, 2015. Retrieved February 1, 2012.
^ "Ranking Tables of National Institutes of Health (NIH) Award Data 2006–2008". Brimr.org. Retrieved February 23, 2010.
^ Greene, Howard; Greene, Matthew W. (August 2001). Greenes' Guide to Educational Planning:The Public Ivies. ISBN 9780060934590. Retrieved August 7, 2013.
^ "Nursing Informatics Ranking". US News and World Report. Retrieved 31 October 2018.
^ Anderson, Nate (2009-11-04). "The Web may have won, but Gopher tunnels on". Ars Technica. Retrieved December 5, 2012.
^ Waters, Darren (April 30, 2008). "BBC article". BBC News. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "Cray's Mark Remains Speed With Simplicity". University of Minnesota Update, Spring 1983. Retrieved December 5, 2012.
^ ab "University of Minnesota World University Rankings | THE". Times Higher Education. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
^ "Admissions". Regents of the University of Minnesota. Retrieved September 19, 2009.
^ "Degree Programs". Academics webpage. University of Minnesota, Twin Cities. 2015-04-29. Retrieved February 21, 2016.
^ "Reserve Officers Training Corps (ROTC)". Regents of the University of Minnesota. Retrieved September 17, 2009.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on May 5, 2014. Retrieved February 9, 2016.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "OIR : Enrollment Headcount Data: All Data". University of Minnesota Office of Institutional Research. Archived from the original on February 9, 2016. Retrieved January 11, 2016.
^ "The Campus Knoll". University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011.
^ "University of Minnesota Heritage Trail". Archived from the original on February 9, 2012.
^ Millett, Larry (2007). AIA Guide to the Twin Cities: The Essential Source on the Architecture of Minneapolis and St. Paul. pp. 127–128. ISBN 978-0-87351-540-5.
^ https://www.nps.gov/nr/listings/20180119.htm
^ Middlebrook served the University as Comptroller, VP of Business Administration, and was a longtime Secretary of the Board of Regents. He wrote a seminal text on estimating building needs for colleges and universities. Middlebrook graduated from Dartmouth College in 1912, where he was a member of Phi Sigma Kappa.
^ "Pedestrians should exercise caution". The Minnesota Daily. September 29, 2006. Archived from the original on February 12, 2007. Retrieved December 22, 2006.
^ "Campus Zone Pass". University of Minnesota Parking and Transportation. Spring 2016. Archived from the original on November 9, 2015. Retrieved February 24, 2016.
^ "U-Pass". University of Minnesota Parking and Transportation. 2016-05-11. Retrieved May 1, 2018.
^ "COLLEGE OF CONTINUING AND PROFESSIONAL STUDIES". cce.umn.edu. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "College of Veterinary Medicine". cvm.umn.edu. May 16, 2012. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "COLLEGE OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES". cbs.umn.edu. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "Continuing Education and Conference Center". University of Minnesota College of Continuing Education. Archived from the original on August 23, 2012. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "Dairy Salesroom". Department of Food Science and Nutrition, College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences, University of Minnesota. January 20, 2010. Archived from the original on May 23, 2013. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "Meat Science". Department of Animal Science, University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on July 15, 2012. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "2006 Detailed Daily Attendance". Minnesota State Fair. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved July 17, 2007.
^ "Campus Connectors | Parking & Transportation Services". Umn.edu. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
^ "Campus Connectors | Parking & Transportation Services". Umn.edu. 2016-05-11. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
^ "2009 Transit System Performance Evaluation". Metropolitan Council. 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010.
^ "Step Up". University of Minnesota. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
^ "TXT- U". University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on October 4, 2013. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
^ ab "Safety and Security". University of Minnesota. Retrieved September 30, 2013.
^ ab "After Authorities Did Not Charge her Rapist U Student Fought Back". Minneapolis Star Tribune. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "Former University of Minnesota Frat Brother Sentenced to 6 Years in Prison for Rape". Cosmopolitan. September 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ ab "1 in 10 rape cases on University of Minnesota campus lead to arrest". Fox 9 News. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "10 Year Part I Crime Statistics". University of Minnesota Public Safety. 2015-08-07. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "'Universities and Fraternities Must Tell the Whole Truth' About Sexual Violence". Time. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
^ "Working Together to Address Campus Sexual Violence" (PDF). University of Minnesota. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 10, 2017. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "Here's What's Missing From the Stats on Campus Rape". MotherJones. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "How the University of Minnesota handles sexual assault". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
^ "Reciprocal Library Borrowing". Big Ten Academic Alliance. Retrieved July 1, 2016.
^ "Purchasing and Licensing". Big Ten Academic Alliance. Retrieved July 1, 2016.
^ "Sharing Access to Courses". Big Ten Academic Alliance. Retrieved June 30, 2016.
^ "Leadership Development". Big Ten Academic Alliance. Retrieved June 30, 2016.
^ "Global Collaborations". Big Ten Academic Alliance. Retrieved June 30, 2016.
^ For examples, see any edition of the Minnesota Gopher Yearbook, which featured fraternities and sororities during its century-long publication run. Website accessed June 30, 2014.
^ Carole Zellie (2003). "University of Minnesota Greek Letter Chapter House Designation Study, prepared for the Minneapolis Heritage Preservation Commission". Author's firm: Landscape Research, St. Paul, MN: 3–4 of 180, and throughout by chapter entry.
^ The University of Minnesota / Office for Fraternity and Sorority Life annual report, accessed 9 Sept, 2018
^ University of Minnesota, List of student organizations.
^ Maura, Lerner (June 29, 2016). "U of M student newspaper to cut back print edition to 2 days a week". Star Tribune. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
^ ab "2008–2009 Student Organization Student Services Fees Request" (PDF). January 25, 2008. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
[dead link]
^ ab Krogstad, Jens (April 7, 2004). "Official Restores Wake's Funding". The Minnesota Daily. Archived from the original on June 25, 2004. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
^ Haugen, Bryce (February 18, 2005). "Wake Awaits Fees Decision". The Minnesota Daily. Archived from the original on February 20, 2005. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
^ Haugen, Bryce (March 10, 2005). "Final Recommendations In". The Minnesota Daily. Archived from the original on March 12, 2005. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
^ "Hitch a ride with MSA". Minnesota Daily. Archived from the original on January 3, 2007.
^ "Boynton to run MSA Express". Minnesota Daily.
^ "Shuttle Service Provides 'U' Students Security". Wcco.com. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
^ "Taking them home: The U's Gopher Chauffeur service helps keep students safe at night". umn.edu. November 20, 2013. Archived from the original on July 29, 2014.
^ Nelson, Cody (July 31, 2013). "Under medical amnesty law, underage drinkers will get new legal protections: Underage drinkers will be able to call 911 without fearing a citation". Minnesota Daily. Archived from the original on July 27, 2014.
^ "Championships Summary through July 1, 2016" (PDF). NCAA. July 1, 2016. Retrieved August 7, 2016.
^ "School Songs". College of Liberal Arts | University of Minnesota. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
^ "University of Minnesota Official Athletic Site – University of Minnesota". Retrieved August 3, 2015.
^ "NCAA men's hockey: Minnesota the capital of hockey nation". ESPN.com. 2011-04-04. Retrieved August 3, 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to University of Minnesota. |
Official website
- University of Minnesota Athletics website
 "Minnesota, University of". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.
"Minnesota, University of". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.
 "University of Minnesota". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
"University of Minnesota". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
 "Minnesota, University of". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
"Minnesota, University of". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.







