Preterm birth
| Preterm birth | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Premature birth, preemies, premmies |
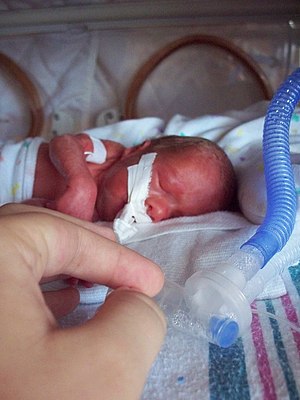 | |
Intubated preterm baby in an incubator | |
| Specialty | Obstetrics, pediatrics |
| Symptoms | Birth of a baby at younger than 37 weeks' gestational age[1] |
| Complications | Cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems, sight problems[1] |
| Causes | Often unknown[2] |
| Risk factors | Diabetes, high blood pressure, being pregnant with more than one baby, obesity or underweight, a number of vaginal infections, celiac disease, tobacco smoking, psychological stress[2][3][4] |
| Prevention | Progesterone[5] |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, keeping the baby warm through skin to skin contact, supporting breastfeeding, treating infections, supporting breathing[2][6] |
| Frequency | ~15 million a year (12% of deliveries)[2] |
| Deaths | 805,800[7] |
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks' gestational age.[1] These babies are known as preemies or premies.[1] Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes or the leaking of fluid from the vagina.[8] Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and sight problems.[1] These risks are greater the earlier a baby is born.[1]
The cause of preterm birth is often not known.[2] Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, being pregnant with more than one baby, being either obese or underweight, a number of vaginal infections, tobacco smoking and psychological stress, among others.[2][3] It is recommended that labor not be medically induced before 39 weeks unless required for other medical reasons.[2] The same recommendation applies to cesarean section.[2] Medical reasons for early delivery include preeclampsia.[9]
In those at risk, the hormone progesterone, if taken during pregnancy, may prevent preterm birth.[5] Evidence does not support the usefulness of bed rest.[5][10] It is estimated that at least 75% of preterm infants would survive with appropriate treatment, and the survival rate is highest among the infants born the latest.[2] In women who might deliver between 24 and 37 weeks, corticosteroids improve outcomes.[6][11] A number of medications, including nifedipine, may delay delivery so that a mother can be moved to where more medical care is available and the corticosteroids have a greater chance to work.[12] Once the baby is born, care includes keeping the baby warm through skin to skin contact, supporting breastfeeding, treating infections and supporting breathing.[2]
Preterm birth is the most common cause of death among infants worldwide.[1] About 15 million babies are preterm each year (5% to 18% of all deliveries).[2] Approximately 0.5% of births are extremely early periviable births, and these account for most of the deaths.[13] In many countries, rates of premature births have increased between the 1990s and 2010s.[2] Complications from preterm births resulted in 0.81 million deaths in 2015 down from 1.57 million in 1990.[7][14] The chance of survival at 22 weeks is about 6%, while at 23 weeks it is 26%, 24 weeks 55% and 25 weeks about 72%.[15] The chances of survival without any long-term difficulties are lower.[16]
.mw-parser-output .toclimit-2 .toclevel-1 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-3 .toclevel-2 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-4 .toclevel-3 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-5 .toclevel-4 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-6 .toclevel-5 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-7 .toclevel-6 ul{display:none}
Contents
1 Signs and symptoms
1.1 Complications
1.1.1 Mortality and morbidity
1.1.2 Specific risks for the preterm neonate
2 Risk factors
2.1 Maternal factors
2.2 Factors during pregnancy
2.3 Infection
2.4 Genetics
3 Diagnosis
3.1 Placental alpha microglobulin-1
3.2 Fetal fibronectin
3.3 Ultrasound
3.4 Classification
4 Prevention
4.1 Before pregnancy
4.2 During pregnancy
4.2.1 Screening of low risk women
4.2.2 Self-care
4.3 Reducing existing risks
4.3.1 Multiple pregnancies
4.3.2 Reducing indicated preterm birth
4.3.3 Reducing spontaneous preterm birth
4.3.3.1 Antibiotics
4.3.3.2 Progestogens
4.3.3.3 Cervical cerclage
5 Management
5.1 Steroids
5.2 Antibiotics
5.3 Tocolysis
5.4 Mode of delivery
5.5 Neonatal care
6 Prognosis
7 Epidemiology
8 Society and culture
8.1 Economics
8.2 Notable cases
9 References
10 External links
Signs and symptoms

A new mother holds her premature baby at Kapiolani Medical Center NICU in Honolulu, Hawaii
Preterm birth causes a range of problems.[17]
The main categories of causes of preterm birth are preterm labor induction and spontaneous preterm labor. Signs and symptoms of preterm labor include four or more uterine contractions in one hour. In contrast to false labour, true labor is accompanied by cervical dilatation and effacement. Also, vaginal bleeding in the third trimester, heavy pressure in the pelvis, or abdominal or back pain could be indicators that a preterm birth is about to occur. A watery discharge from the vagina may indicate premature rupture of the membranes that surround the baby. While the rupture of the membranes may not be followed by labor, usually delivery is indicated as infection (chorioamnionitis) is a serious threat to both fetus and mother. In some cases, the cervix dilates prematurely without pain or perceived contractions, so that the mother may not have warning signs until very late in the birthing process.
A review into using uterine monitoring at home to detect contractions and possible preterm births in women at higher risk of having a preterm baby found that it did not reduce the number of preterm births.[18] The research included in the review was poor quality but it showed that home monitoring may increase the number of unplanned antenatal visits and may reduce the number of babies admitted to special care when compared with women receiving normal antenatal care.[18]
Complications
Mortality and morbidity
In the U.S. where many neonatal infections and other causes of neonatal death have been markedly reduced, prematurity is the leading cause of neonatal mortality at 25%.[19] Prematurely born infants are also at greater risk for having subsequent serious chronic health problems as discussed below.
The earliest gestational age at which the infant has at least a 50% chance of survival is referred to as the limit of viability. As NICU care has improved over the last 40 years, the limit of viability has reduced to approximately 24 weeks.[20][21] Most newborns who die, and 40% of older infants who die, were born between 20 and 25.9 weeks (gestational age), during the second trimester.[13]
As risk of brain damage and developmental delay is significant at that threshold even if the infant survives, there are ethical controversies over the aggressiveness of the care rendered to such infants. The limit of viability has also become a factor in the abortion debate.[22]
Specific risks for the preterm neonate
Preterm infants usually show physical signs of prematurity in reverse proportion to the gestational age. As a result, they are at risk for numerous medical problems affecting different organ systems.
- Neurological problems include apnea of prematurity, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP),[23]developmental disability, transient hyperammonemia of the newborn, cerebral palsy and intraventricular hemorrhage, the latter affecting 25% of babies born preterm, usually before 32 weeks of pregnancy.[24] Mild brain bleeds usually leave no or few lasting complications, but severe bleeds often result in brain damage or even death.[24] Neurodevelopmental problems have been linked to lack of maternal thyroid hormones, at a time when their own thyroid is unable to meet postnatal needs.[25]
- Cardiovascular complications may arise from the failure of the ductus arteriosus to close after birth: patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
- Respiratory problems are common, specifically the respiratory distress syndrome (RDS or IRDS) (previously called hyaline membrane disease). Another problem can be chronic lung disease (previously called bronchopulmonary dysplasia or BPD).
- Gastrointestinal and metabolic issues can arise from neonatal hypoglycemia, feeding difficulties, rickets of prematurity, hypocalcemia, inguinal hernia, and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
- Hematologic complications include anemia of prematurity, thrombocytopenia, and hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice) that can lead to kernicterus.
- Infection, including sepsis, pneumonia, and urinary tract infection [1]
A study of 241 children born between 22 and 25 weeks who were currently of school age found that 46 percent had severe or moderate disabilities such as cerebral palsy, vision or hearing loss and learning problems. Thirty-four percent were mildly disabled and 20 percent had no disabilities, while 12 percent had disabling cerebral palsy.[26][27]
Risk factors
The exact cause of preterm birth is difficult to determine and it may be multi-factorial. The cause of 50% of preterm births is never determined.[28] Labor is a complex process involving many factors. Four different pathways have been identified that can result in preterm birth and have considerable evidence: precocious fetal endocrine activation, uterine overdistension (placental abruption), decidual bleeding, and intrauterine inflammation/infection.[29]
Identifying women at high risk of giving birth early would enable the health services to provide specialized care for these women to delay the birth or make sure they are in the best place to give birth (for example a hospital with a special care baby unit). Risk scoring systems have been suggested as a possible way of identifying these women. However, there is no research in this area so it is unclear whether the risk scoring systems would prolong pregnancy and reduce the numbers of preterm births or not.[30]
Maternal factors
| Risk factor | Relative risk or odds ratio[31] | 95% confidence interval[31] |
|---|---|---|
| Black ethnicity/race | 2.0 | 1.8–2.2 |
| Filipino ancestry[32] | 1.7 | 1.5–2.1 |
| High or low BMI | 0.96 | 0.66–1.4 |
| Large or small pregnancy weight gain | 1.8 | 1.5–2.3 |
| Short maternal height | 1.8 | 1.3–2.5 |
| History of spontaneous preterm birth | 3.6 | 3.2–4.0 |
| Being single/unmarried[33] | 1.2 | 1.03–1.28 |
| Bacterial vaginosis | 2.2 | 1.5–3.1 |
| Asymptomatic bacteriuria | 1.1 | 0.8–1.5 |
| Periodontitis | 1.6 | 1.1–2.3 |
| Low socio-economic status | 1.9 | 1.7–2.2 |
| Short cervical length | 2.9 | 2.1–3.9 |
| Fetal fibronectin | 4.0 | 2.9–5.5 |
| Chlamydia | 2.2 | 1.0–4.8 |
| Celiac disease | 1.4[34] | 1.2–1.6[34] |
A number of factors have been identified that are linked to a higher risk of a preterm birth such as being less than 18 years of age.[35] Maternal height and weight can play a role.[36]
Further, in the U.S. and the UK, black women have preterm birth rates of 15–18%, more than double than that of the white population. Filipinos are also at high risk of premature birth, and it is believed that nearly 11–15% of Filipinos born in the U.S. (compared to other Asians at 7.6% and whites at 7.8%) are premature.[37] Filipinos being a big risk factor is evidenced with the Philippines being the 8th highest ranking in the world for preterm births, the only non-African country in the top 10.[38] This discrepancy is not seen in comparison to other Asian groups or Hispanic immigrants and remains unexplained.[35]
Pregnancy interval makes a difference as women with a six-month span or less between pregnancies have a two-fold increase in preterm birth.[39] Studies on type of work and physical activity have given conflicting results, but it is opined that stressful conditions, hard labor, and long hours are probably linked to preterm birth.[35]
A history of spontaneous (i.e., miscarriage) or surgical abortion has been associated with a small increase in the risk of preterm birth, with an increased risk with increased number of abortions, although it is unclear whether the increase is caused by the abortion or by confounding risk factors (e.g., socioeconomic status).[40] Increased risk has not been shown in women who terminated their pregnancies medically.[41] Pregnancies that are unwanted or unintended are also a risk factor for preterm birth.[42]
Adequate maternal nutrition is important. Women with a low BMI are at increased risk for preterm birth.[43] Further, women with poor nutrition status may also be deficient in vitamins and minerals. Adequate nutrition is critical for fetal development and a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol may help reduce the risk of a preterm delivery.[44]Obesity does not directly lead to preterm birth;[45] however, it is associated with diabetes and hypertension which are risk factors by themselves.[35] To some degree those individuals may have underlying conditions (i.e., uterine malformation, hypertension, diabetes) that persist.
Women with celiac disease have an increased risk of the development of preterm birth.[34] The risk of preterm birth is more elevated when celiac disease remains undiagnosed and untreated.[4]
Marital status is associated with risk for preterm birth. A study of 25,373 pregnancies in Finland revealed that unmarried mothers had more preterm deliveries than married mothers (P=0.001).[33] Pregnancy outside of marriage was associated overall with a 20% increase in total adverse outcomes, even at a time when Finland provided free maternity care. A study in Quebec of 720,586 births from 1990 to 1997 revealed less risk of preterm birth for infants with legally married mothers compared with those with common-law wed or unwed parents.[46][needs update]
Genetic make-up is a factor in the causality of preterm birth. Genetics has been a big factor into why Filipinos have a high risk of premature birth as the Filipinos have a large prevalence of mutations that help them be predisposed to premature births.[37] An intra- and transgenerational increase in the risk of preterm delivery has been demonstrated.[47] No single gene has been identified.
Subfertility is associated with preterm birth. Couples who have tried more than 1 year versus those who have tried less than 1 year before achieving a spontaneous conception have an adjusted odds ratio of 1.35 (95% confidence interval 1.22-1.50) of preterm birth.[48] Pregnancies after IVF confers a greater risk of preterm birth than spontaneous conceptions after more than 1 year of trying, with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.55 (95% CI 1.30-1.85).[48]
Factors during pregnancy
The use of fertility medication that stimulates the ovary to release multiple eggs and of IVF with embryo transfer of multiple embryos has been implicated as an important factor in preterm birth. Maternal medical conditions increase the risk of preterm birth. Often labor has to be induced for medical reasons; such conditions include high blood pressure,[49]pre-eclampsia,[50] maternal diabetes,[51] asthma, thyroid disease, and heart disease.
In a number of women anatomical issues prevent the baby from being carried to term. Some women have a weak or short cervix[49] (the strongest predictor of premature birth)[52][53][54] Women with vaginal bleeding during pregnancy are at higher risk for preterm birth. While bleeding in the third trimester may be a sign of placenta previa or placental abruption – conditions that occur frequently preterm – even earlier bleeding that is not caused by these conditions is linked to a higher preterm birth rate.[55] Women with abnormal amounts of amniotic fluid, whether too much (polyhydramnios) or too little (oligohydramnios), are also at risk.[35]
The mental status of the women is of significance. Anxiety[56] and depression have been linked to preterm birth.[35]
Finally, the use of tobacco, cocaine, and excessive alcohol during pregnancy increases the chance of preterm delivery. Tobacco is the most commonly abused drug during pregnancy and contributes significantly to low birth weight delivery.[57] Babies with birth defects are at higher risk of being born preterm.[58]
Passive smoking and/or smoking before the pregnancy influences the probability of a preterm birth. The World Health Organization published an international study in March 2014.[59]
Presence of anti-thyroid antibodies is associated with an increased risk preterm birth with an odds ratio of 1.9 and 95% confidence interval of 1.1–3.5.[60]
A 2004 systematic review of 30 studies on the association between intimate partner violence and birth outcomes concluded that preterm birth and other adverse outcomes, including death, are higher among abused pregnant women than among non-abused women.[61]
The Nigerian cultural method of abdominal massage has been shown to result in 19% preterm birth among women in Nigeria, plus many other adverse outcomes for the mother and baby.[62] This ought not be confused with massage conducted by a fully trained and licensed massage therapist or by significant others trained to provide massage during pregnancy, which has been shown to have numerous positive results during pregnancy, including the reduction of preterm birth, less depression, lower cortisol, and reduced anxiety.[63]
Infection
The frequency of infection in preterm birth is inversely related to the gestational age. Mycoplasma genitalium infection is associated with increased risk of preterm birth, and spontaneous abortion.[64]
Infectious microorganisms can be ascending, hematogeneous, iatrogenic by a procedure, or retrograde through the Fallopian tubes. From the deciduas they may reach the space between the amnion and chorion, the amniotic fluid, and the fetus. A chorioamnionitis also may lead to sepsis of the mother. Fetal infection is linked to preterm birth and to significant long-term handicap including cerebral palsy.[65]
It has been reported that asymptomatic colonization of the decidua occurs in up to 70% of women at term using a DNA probe suggesting that the presence of micro-organism alone may be insufficient to initiate the infectious response.
As the condition is more prevalent in black women in the US and the UK, it has been suggested to be an explanation for the higher rate of preterm birth in these populations. It is opined that bacterial vaginosis before or during pregnancy may affect the decidual inflammatory response that leads to preterm birth. The condition known as aerobic vaginitis can be a serious risk factor for preterm labor; several previous studies failed to acknowledge the difference between aerobic vaginitis and bacterial vaginosis, which may explain some of the contradiction in the results.[66]
Untreated yeast infections are associated with preterm birth.[67]
A review into prophylactic antibiotics (given to prevent infection) in the second and third trimester of pregnancy (13–42 weeks of pregnancy) found a reduction in the number of preterm births in women with bacterial vaginosis. These antibiotics also reduced the number of waters breaking before labor in full-term pregnancies, reduced the risk of infection of the lining of the womb after delivery (endometritis), and rates of gonococcal infection. However, the women without bacterial vaginosis did not have any reduction in preterm births or pre-labor preterm waters breaking. Much of the research included in this review lost participants during follow-up so did not report the long-term effects of the antibiotics on mothers or babies. More research in this area is needed to find the full effects of giving antibiotics throughout the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.[68]
A number of maternal bacterial infections are associated with preterm birth including pyelonephritis, asymptomatic bacteriuria, pneumonia, and appendicitis. A review into giving antibiotics in pregnancy for asymptomatic bacteriuria (urine infection with no symptoms) found the research was of very low quality but that it did suggest that taking antibiotics reduced the numbers of preterm births and babies with low birth weight.[69] Another review found that one dose of antibiotics did not seem as effective as a course of antibiotics but fewer women reported side effects from one dose.[70] This review recommended that more research is needed to discover the best way of treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.[69]
A different review found that preterm births happened less for pregnant women who had routine testing for low genital tract infections than for women who only had testing when they showed symptoms of low genital tract infections.[71] The women being routinely tested also gave birth to fewer babies with a low birth weight. Even though these results look promising, the review was only based on one study so more research is needed into routine screening for low genital tract infections.[71]
Also periodontal disease has been shown repeatedly to be linked to preterm birth.[72][73] In contrast, viral infections, unless accompanied by a significant febrile response, are considered not to be a major factor in relation to preterm birth.[35]
Genetics
There is believed to be a maternal genetic component in preterm birth.[74] Estimated heritability of timing-of-birth in women was 34%. However, the occurrence of preterm birth in families does not follow a clear inheritance pattern, thus supporting the idea that preterm birth is a non-Mendelian trait with a polygenic nature.[75]
Diagnosis
Placental alpha microglobulin-1
Placental alpha microglobulin-1 (PAMG-1) has been the subject of several investigations evaluating its ability to predict imminent spontaneous preterm birth in women with signs, symptoms, or complaints suggestive of preterm labor.[76][77][78][79][80][81][82] In one investigation comparing this test to fetal fibronectin testing and cervical length measurement via transvaginal ultrasound, the test for PAMG-1 (commercially known as the PartoSure test) has been reported to be the single best predictor of imminent spontaneous delivery within 7 days of a patient presenting with signs, symptoms, or complaints of preterm labor. Specifically, the PPV, or positive predictive value, of the tests were 76%, 29%, and 30% for PAMG-1, fFN and CL, respectively (P < 0.01).[83]
Fetal fibronectin
Fetal fibronectin (fFN) has become an important biomarker—the presence of this glycoprotein in the cervical or vaginal secretions indicates that the border between the chorion and deciduas has been disrupted. A positive test indicates an increased risk of preterm birth, and a negative test has a high predictive value.[35] It has been shown that only 1% of women in questionable cases of preterm labor delivered within the next week when the test was negative.[84]
Ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasound has become useful in the assessment of the cervix in women at risk for premature delivery. A short cervix preterm is undesirable: A cervical length of less than 25 mm at or before 24 weeks of gestational age is the most common definition of cervical incompetence.[85]
Classification

Stages in prenatal development, with weeks and months numbered from last menstruation.
In humans, the usual definition of preterm birth is birth before a gestational age of 37 complete weeks.[86] In the normal human fetus, several organ systems mature between 34 and 37 weeks, and the fetus reaches adequate maturity by the end of this period. One of the main organs greatly affected by premature birth is the lungs. The lungs are one of the last organs to mature in the womb; because of this, many premature babies spend the first days and weeks of their lives on ventilators. Therefore, a significant overlap exists between preterm birth and prematurity. Generally, preterm babies are premature and term babies are mature. Preterm babies born near 37 weeks often have no problems relating to prematurity if their lungs have developed adequate surfactant, which allows the lungs to remain expanded between breaths. Sequelae of prematurity can be reduced to a small extent by using drugs to accelerate maturation of the fetus, and to a greater extent by preventing preterm birth.
Prevention
Historically efforts have been primarily aimed to improve survival and health of preterm infants (tertiary intervention). Such efforts, however, have not reduced the incidence of preterm birth. Increasingly primary interventions that are directed at all women, and secondary intervention that reduce existing risks are looked upon as measures that need to be developed and implemented to prevent the health problems of premature infants and children.[87]Smoking bans are effective in decreasing preterm births.[88]
Before pregnancy
Adoption of specific professional policies can immediately reduce risk of preterm birth as the experience in assisted reproduction has shown when the number of embryos during embryo transfer was limited.[87]
Many countries have established specific programs to protect pregnant women from hazardous or night-shift work and to provide them with time for prenatal visits and paid pregnancy-leave. The EUROPOP study showed that preterm birth is not related to type of employment, but to prolonged work (over 42 hours per week) or prolonged standing (over 6 hours per day).[89] Also, night work has been linked to preterm birth.[90] Health policies that take these findings into account can be expected to reduce the rate of preterm birth.[87]
Preconceptional intake of folic acid is recommended to reduce birth defects. There is significant evidence that long-term (> one year) use of folic acid supplement preconceptionally may reduce premature birth.[91][92][93] Reducing smoking is expected to benefit pregnant women and their offspring.[87]
During pregnancy
Healthy eating can be instituted at any stage of the pregnancy including nutritional adjustments, use of vitamin supplements, and smoking cessation.[87] Calcium supplementation in women who have low dietary calcium reduces the number of negative outcomes including preterm birth, pre-eclampsia, and maternal death.[94][needs update] The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests 1.5–2 g of calcium supplements daily, for pregnant women who have low levels calcium in their diet.[94] Supplemental intake of C and E vitamins have not been found to reduce preterm birth rates.[95] Different strategies are used in the administration of prenatal care, and future studies need to determine if the focus can be on screening for high-risk women, or widened support for low-risk women, or to what degree these approaches can be merged.[87] While periodontal infection has been linked with preterm birth, randomized trials have not shown that periodontal care during pregnancy reduces preterm birth rates.[87]
Screening of low risk women
Screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria followed by appropriate treatment reduces pyelonephritis and reduces the risk of preterm birth.[96] Extensive studies have been carried out to determine if other forms of screening in low-risk women followed by appropriate intervention are beneficial, including: Screening for and treatment of Ureaplasma urealyticum, group B streptococcus, Trichomonas vaginalis, and bacterial vaginosis did not reduce the rate of preterm birth.[87] Routine ultrasound examination of the length of the cervix identifies patients at risk, but cerclage is not proven useful, and the application of a progestogen is under study.[87] Screening for the presence of fibronectin in vaginal secretions is not recommended at this time in women at low risk.
Self-care
Self-care methods to reduce the risk of preterm birth include proper nutrition, avoiding stress, seeking appropriate medical care, avoiding infections, and the control of preterm birth risk factors (e.g. working long hours while standing on feet, carbon monoxide exposure, domestic abuse, and other factors). Self-monitoring vaginal pH followed by yogurt treatment or clindamycin treatment if the pH was too high all seem to be effective at reducing the risk of preterm birth.[97][98] Additional support during pregnancy does not appear to prevent low birthweight or preterm birth.[99]
Reducing existing risks
Women are identified to be at increased risk for preterm birth on the basis of their past obstetrical history or the presence of known risk factors. Preconception intervention can be helpful in selected patients in a number of ways. Patients with certain uterine anomalies may have a surgical correction (i.e. removal of a uterine septum), and those with certain medical problems can be helped by optimizing medical therapies prior to conception, be it for asthma, diabetes, hypertension and others.
Multiple pregnancies
In multiple pregnancies, which often result from use of assisted reproductive technology, there is a high risk of preterm birth. Selective reduction is used to reduce the number of fetuses to two or three.[100][101][102]
Reducing indicated preterm birth
A number of agents have been studied for the secondary prevention of indicated preterm birth. Trials using low-dose aspirin, fish oil, vitamin C and E, and calcium to reduce preeclampsia demonstrated some reduction in preterm birth only when low-dose aspirin was used.[87] Even if agents such as calcium or antioxidants were able to reduce preeclampsia, a resulting decrease in preterm birth was not observed.[87]
Reducing spontaneous preterm birth
Reduction in activity by the mother—pelvic rest, limited work, bed rest—may be recommended although there is no evidence it is useful with some concerns it is harmful.[103] Increasing medical care by more frequent visits and more education has not been shown to reduce preterm birth rates.[99] Use of nutritional supplements such as omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is based on the observation that populations who have a high intake of such agents are at low risk for preterm birth, presumably as these agents inhibit production of proinflammatory cytokines. A randomized trial showed a significant decline in preterm birth rates,[104] and further studies are in the making.
Antibiotics
While antibiotics can get rid of bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy, this does not appear to change the risk of preterm birth.[105] It has been suggested that chronic chorioamnionitis is not sufficiently treated by antibiotics alone (and therefore they cannot ameliorate the need for preterm delivery in this condition).[87]
Progestogens
Progestogens, often given in the form of progesterone or hydroxyprogesterone caproate, relaxes the uterine musculature, maintains cervical length, and has anti-inflammatory properties, and thus exerts activities expected to be beneficial in reducing preterm birth. Two meta-analyses demonstrated a reduction in the risk of preterm birth in women with recurrent preterm birth by 40–55%.[106][107]
Progestogen supplementation also reduces the frequency of preterm birth in pregnancies where there is a short cervix.[108] However, progestogens are not effective in all populations, as a study involving twin gestations failed to see any benefit.[109]
Cervical cerclage
In preparation for childbirth, the woman's cervix shortens. Preterm cervical shortening is linked to preterm birth and can be detected by ultrasonography. Cervical cerclage is a surgical intervention that places a suture around the cervix to prevent its shortening and widening. Numerous studies have been performed to assess the value of cervical cerclage and the procedure appears helpful primarily for women with a short cervix and a history of preterm birth.[108][110] Instead of a prophylactic cerclage, women at risk can be monitored during pregnancy by sonography, and when shortening of the cervix is observed, the cerclage can be performed.[87]
Management

Preterm birth at 32 week 4 days with a weight of 2,000 gms attached to medical equipment
About 75% of nearly a million deaths due to preterm deliver would survive if provided warmth, breastfeeding, treatments for infection, and breathing support.[111] If a baby has cardiac arrest at birth and is before 23 weeks or less than 400 g attempts at resuscitation are not indicated.[112]
Tertiary interventions are aimed at women who are about to go into preterm labor, or rupture the membranes or bleed preterm. The use of the fibronectin test and ultrasonography improves the diagnostic accuracy and reduces false-positive diagnosis. While treatments to arrest early labor where there is progressive cervical dilatation and effacement will not be effective to gain sufficient time to allow the fetus to grow and mature further, it may defer delivery sufficiently to allow the mother to be brought to a specialized center that is equipped and staffed to handle preterm deliveries.[113] In a hospital setting women are hydrated via intravenous infusion (as dehydration can lead to premature uterine contractions).[114]
Steroids
Severely premature infants may have underdeveloped lungs because they are not yet producing their own surfactant. This can lead directly to respiratory distress syndrome, also called hyaline membrane disease, in the neonate. To try to reduce the risk of this outcome, pregnant mothers with threatened premature delivery prior to 34 weeks are often administered at least one course of glucocorticoids, a steroid that crosses the placental barrier and stimulates the production of surfactant in the lungs of the baby.[11] Steroid use up to 37 weeks is also recommended by the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.[11] Typical glucocorticoids that would be administered in this context are betamethasone or dexamethasone, often when the pregnancy has reached viability at 23 weeks.
In cases where premature birth is imminent, a second "rescue" course of steroids may be administered 12 to 24 hours before the anticipated birth. There are still some concerns about the efficacy and side effects of a second course of steroids, but the consequences of RDS are so severe that a second course is often viewed as worth the risk. A 2015 Cochrane review supports the use of repeat dose(s) of prenatal corticosteroids for women still at risk of preterm birth seven days or more after an initial course.[115]
Beside reducing respiratory distress, other neonatal complications are reduced by the use of glucocorticosteroids, namely intraventricular bleeding, necrotising enterocolitis, and patent ductus arteriosus.[116] A single course of antenatal corticosteroids could be considered routine for preterm delivery, but there are some concerns about applicability of this recommendation to low-resource settings with high rates of infections.[116] It remains unclear whether one corticosteroid (or one particular regimen) has advantages over another.[117]
Concerns about adverse effects of prenatal corticosteroids include increased risk for maternal infection, difficulty with diabetic control, and possible long-term effects on neurodevelopmental outcomes for the infants. There is ongoing discussion about when steroids should be given (i.e. only antenatally or postnatally too) and for how long (i.e. single course or repeated administration). Despite these unknowns, there is a consensus that the benefits of a single course of prenatal glucocorticosteroids vastly outweigh the potential risks.[118][119][120]
Antibiotics
The routine administration of antibiotics to all women with threatened preterm labor reduces the risk of the baby to get infected with group B streptococcus and has been shown to reduce related mortality rates.[121]
When membranes rupture prematurely, obstetrical management looks for development of labor and signs of infection. Prophylactic antibiotic administration has been shown to prolong pregnancy and reduced neonatal morbidity with rupture of membranes at less than 34 weeks.[122] Because of concern about necrotizing enterocolitis, amoxicillin or erythromycin has been recommended, but not amoxicillin + clavulanic acid (co-amoxiclav).[122]
Tocolysis
A number of medications may be useful to delay delivery including: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, calcium channel blockers, beta mimetics, and atosiban.[123]Tocolysis rarely delays delivery beyond 24–48 hours.[124] This delay, however, may be sufficient to allow the pregnant woman to be transferred to a center specialized for management of preterm deliveries and give administered corticosteroids to reduce neonatal organ immaturity. Meta-analyses indicate that calcium-channel blockers and an oxytocin antagonist can delay delivery by 2–7 days, and β2-agonist drugs delay by 48 hours but carry more side effects.[87][125]Magnesium sulfate does not appear to be useful to prevent preterm birth.[126] Its use before delivery, however, does appear to decrease the risk of cerebral palsy.[127]
Mode of delivery
The routine use of caesarean section for early delivery of infants expected to have very low birth weight is controversial,[87][128] and a decision concerning the route and time of delivery probably needs to be made on a case by case basis.
Neonatal care
After delivery, plastic wraps or warm mattresses are useful to keep the infant warm on their way to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).[129][needs update] In developed countries premature infants are usually cared for in an NICU. The physicians who specialize in the care of very sick or premature babies are known as neonatologists. In the NICU, premature babies are kept under radiant warmers or in incubators (also called isolettes), which are bassinets enclosed in plastic with climate control equipment designed to keep them warm and limit their exposure to germs. Modern neonatal intensive care involves sophisticated measurement of temperature, respiration, cardiac function, oxygenation, and brain activity. Treatments may include fluids and nutrition through intravenous catheters, oxygen supplementation, mechanical ventilation support, and medications. In developing countries where advanced equipment and even electricity may not be available or reliable, simple measures such as kangaroo care (skin to skin warming), encouraging breastfeeding, and basic infection control measures can significantly reduce preterm morbidity and mortality. Bili lights may also be used to treat newborn jaundice (hyperbilirubinemia).
Water can be carefully provided to prevent dehydration but no so much to increase risks of side effects.[130]
In a 2012 policy statement, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended feeding preterm infants human milk, finding "significant short- and long-term beneficial effects," including lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).[131] It is unclear if fortification of breast milk improves outcomes in preterm babies, though it may speed growth.[132] There is limited evidence to support prescribing a preterm formula for the preterm babies after hospital discharge.[133]
Prognosis
The chance of survival at 22 weeks is about 6%, while at 23 weeks it is 26%, 24 weeks 55% and 25 weeks about 72%.[15] The chances of survival without long-term difficulties is less.[16] In the developed world overall survival is about 90% while in low-income countries survival rates are about 10%.[111]
Some children will adjust well during childhood and adolescence,[134] although disability is more likely nearer the limits of viability. A large study followed children born between 22 and 25 weeks until the age of 6 years old. Of these children, 46 percent had moderate to severe disabilities such as cerebral palsy, vision or hearing loss and learning disabilities, 34 percent had mild disabilities, and 20 percent had no disabilities. Twelve percent had disabling cerebral palsy.[27]
As survival has improved, the focus of interventions directed at the newborn has shifted to reduce long-term disabilities, particularly those related to brain injury.[134] Some of the complications related to prematurity may not be apparent until years after the birth. A long-term study demonstrated that the risks of medical and social disabilities extend into adulthood and are higher with decreasing gestational age at birth and include cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, disorders of psychological development, behavior, and emotion, disabilities of vision and hearing, and epilepsy.[135] Standard intelligence tests showed that 41 percent of children born between 22 and 25 weeks had moderate or severe learning disabilities when compared to the test scores of a group of similar classmates who were born at full-term.[27] It is also shown that higher levels of education were less likely to be obtained with decreasing gestational age at birth.[135] People born prematurely may be more susceptible to developing depression as teenagers.[136]
Some of these problems can be described as being within the executive domain and have been speculated to arise due to decreased myelinization of the frontal lobes.[137] Studies of people born premature and investigated later with MRI brain imaging, demonstrate qualitative anomalies of brain structure and grey matter deficits within temporal lobe structures and the cerebellum that persist into adolescence.[138] Throughout life they are more likely to require services provided by physical therapists, occupational therapists, or speech therapists.[134]
Despite the neurosensory, mental and educational problems studied in school age and adolescent children born extremely preterm, the majority of preterm survivors born during the early years of neonatal intensive care are found to do well and to live fairly normal lives in young adulthood.[139] Young adults born preterm seem to acknowledge that they have more health problems than their peers, yet feel the same degree of satisfaction with their quality of life.[140]
Beyond the neurodevelopmental consequences of prematurity, infants born preterm have a greater risk for many other health problems. For instance, children born prematurely have an increased risk for developing chronic kidney disease.[141]
Epidemiology

Disability-adjusted life year for prematurity and low birth weight per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004.[142].mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
no data
less than 120
120-240
240-360
360-480
480-600
600-720
720-840
840-960
960-1080
1080-1200
1200-1500
more than 1500
Preterm birth complicates the births of infants worldwide affecting 5% to 18% of births.[67] In Europe and many developed countries the preterm birth rate is generally 5–9%, and in the USA it has even risen to 12–13% in the last decades.[143]
As weight is easier to determine than gestational age, the World Health Organization tracks rates of low birth weight (< 2,500 grams), which occurred in 16.5 percent of births in less developed regions in 2000.[144] It is estimated that one third of these low birth weight deliveries are due to preterm delivery. Weight generally correlates to gestational age, however, infants may be underweight for other reasons than a preterm delivery. Neonates of low birth weight (LBW) have a birth weight of less than 2500 g (5 lb 8 oz) and are mostly but not exclusively preterm babies as they also include small for gestational age (SGA) babies. Weight-based classification further recognizes Very Low Birth Weight (VLBW) which is less than 1,500 g, and Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) which is less than 1,000 g.[145] Almost all neonates in these latter two groups are born preterm.
Complications from preterm births resulted in 740,000 deaths in 2013, down from 1.57 million in 1990.[14]
Society and culture
Economics
Preterm birth is a significant cost factor in healthcare, not even considering the expenses of long-term care for individuals with disabilities due to preterm birth. A 2003 study in the US determined neonatal costs to be $224,400 for a newborn at 500–700 g versus $1,000 at over 3,000 g. The costs increase exponentially with decreasing gestational age and weight.[146]
The 2007 Institute of Medicine report Preterm Birth[147] found that the 550,000 premature babies born each year in the U.S. run up about $26 billion in annual costs, mostly related to care in neonatal intensive care units, but the real tab may top $50 billion.[148]
Notable cases
James Elgin Gill (born on 20 May 1987 in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada) was the earliest premature baby in the world, until that record was broken in 2014. He was 128 days premature (21 weeks and 5 days' gestation) and weighed 1 pound 6 ounces (624 g). He survived.[149][150]
In 2014, Lyla Stensrud, born in San Antonio, Texas, U.S. became the youngest premature baby in the world. She was born at 21 weeks 4 days and weighed 410 grams (less than a pound). Kaashif Ahmad resuscitated the baby after she was born. As of November 2018, she was in preschool and had no medical issues or disabilities, except for a slight delay in speech.[151]
Amillia Taylor is also often cited as the most premature baby.[152] She was born on 24 October 2006 in Miami, Florida, U.S. at 21 weeks and 6 days' gestation.[153] This report has created some confusion as her gestation was measured from the date of conception (through in vitro fertilization) rather than the date of her mother's last menstrual period, making her appear 2 weeks younger than if gestation was calculated by the more common method.[136] At birth, she was 9 inches (22.9 cm) long and weighed 10 ounces (280 g).[152] She suffered digestive and respiratory problems, together with a brain hemorrhage. She was discharged from the Baptist Children's Hospital on 20 February 2007.[152]
The record for the smallest premature baby to survive was held for a considerable amount of time by Madeline Mann, who was born in 1989 at 26 weeks, weighing 9.9 ounces (280 g) and measuring 9.5 inches (241.3 mm) long.[154] This record was broken in September 2004 by Rumaisa Rahman, who was born in the same hospital[155] at 25 weeks' gestation. At birth, she was 8 inches (200 mm) long and weighed 244 grams (8.6 oz). Her twin sister was also a small baby, weighing 563 grams (1 lb 3.9 oz) at birth. During pregnancy their mother had suffered from pre-eclampsia, which causes dangerously high blood pressure putting the baby into distress and requiring birth by caesarean section. The larger twin left the hospital at the end of December, while the smaller remained there until 10 February 2005 by which time her weight had increased to 1.18 kg (2.6 lb).[156] Generally healthy, the twins had to undergo laser eye surgery to correct vision problems, a common occurrence among premature babies.
The world's smallest premature boy to survive was born in February 2009 at Children's Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota in Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.. Jonathon Whitehill was born at 25 weeks' gestation with a weight of 310 grams (11 oz). He was hospitalized in a neonatal intensive care unit for five months, and then discharged.[157]
Historical figures who were born prematurely include Johannes Kepler (born in 1571 at seven months' gestation), Isaac Newton (born in 1642, small enough to fit into a quart mug, according to his mother), Winston Churchill (born in 1874 at seven months' gestation), and Anna Pavlova (born in 1885 at seven months' gestation),[158]
References
^ abcdefg "Preterm Labor and Birth: Condition Information". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcdefghijkl World Health Organization (November 2014). "Preterm birth Fact sheet N°363". who.int. Archived from the original on 7 March 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
^ ab "What are the risk factors for preterm labor and birth?". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
^ ab Saccone G, Berghella V, Sarno L, Maruotti GM, Cetin I, Greco L, Khashan AS, McCarthy F, Martinelli D, Fortunato F, Martinelli P (Oct 9, 2015). "Celiac disease and obstetric complications: a systematic review and metaanalysis". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 214 (2): 225–34. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.09.080. PMID 26432464.
^ abc "What treatments are used to prevent preterm labor and birth?". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
^ ab "What treatments can reduce the chances of preterm labor & birth?". National Institutes of Health. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
^ ab GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
^ "What are the symptoms of preterm labor?". National Institutes of Health. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
^ "What causes preterm labor and birth?". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
^ Sosa, CG; Althabe, F; Belizán, JM; Bergel, E (30 March 2015). "Bed rest in singleton pregnancies for preventing preterm birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3): CD003581. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003581.pub3. PMID 25821121.
^ abc "Antenatal Corticosteroid Therapy for Fetal Maturation". ACOG. October 2016. Archived from the original on 29 September 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
^ Haram, K; Mortensen, JH; Morrison, JC (3 July 2014). "Tocolysis for acute preterm labor: does anything work". The Journal of Maternal-fetal & Neonatal Medicine : The Official Journal of the European Association of Perinatal Medicine, the Federation of Asia and Oceania Perinatal Societies, the International Society of Perinatal Obstetricians. 28 (4): 1–8. doi:10.3109/14767058.2014.918095. PMID 24990666.
^ ab American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (October 2017). "Obstetric Care consensus No. 6: Periviable Birth". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 130 (4): e187–e199. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002352. ISSN 1873-233X. PMID 28937572.
^ ab GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
^ ab Cloherty and Stark's Manual of Neonatal Care (8 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2016. p. 161. ISBN 9781496367495.
^ ab Jarjour, IT (February 2015). "Neurodevelopmental Outcome After Extreme Prematurity: A Review of the Literature". Pediatric Neurology. 52 (2): 143–152. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.10.027. PMID 25497122.
^ Saigal S, Doyle LW (2008). "An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood". The Lancet. 371 (9608): 261–269. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60136-1. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 18207020.
^ ab Urquhart, Christine; Currell, Rosemary; Harlow, Francoise; Callow, Liz (15 Feb 2017). "Home uterine monitoring for detecting preterm labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD006172. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006172.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 28205207.
^
Mathew TJ, MacDorman MF (2006). "Infant Mortality Statistics from the 2003 Period Linked Birth/Infant Death Data Set". National Vital Statistics Reports. 54 (16).
^
Kaempf JW, Tomlinson M, Arduza C, Anderson S, Campbell B, Ferguson LA, Zabari M, Stewart VT (2006). "Medical staff guidelines for periviability pregnancy counseling and medical treatment of extremely premature infants". Pediatrics. 117 (1): 22–29. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-2547. PMID 16396856. Archived from the original on 18 March 2008. — in particular see TABLE 1 Survival and Neurologic Disability Rates Among Extremely Premature Infants Archived 12 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
^
Morgan MA, Goldenberg RL, Schulkin J (2008). "Obstetrician-gynecologists' practices regarding preterm birth at the limit of viability". Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine. 21 (2): 115–121. doi:10.1080/14767050701866971. PMID 18240080.
^ Arzuaga BH, Lee BH (2011). "Limits of Human Viability in the United States: A Medicolegal Review". Pediatrics. 128 (6): 1047–1052. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-1689. PMID 22065266.
^ Lambert, Scott R.; Lyons, Christopher J. (2016-10-31). Taylor and Hoyt's pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus. Lambert, Scott R.,, Lyons, Christopher J. (Fifth ed.). Edinburgh. ISBN 9780702066160. OCLC 960162637.
^ ab March of Dimes --> Neonatal Death Archived 24 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on November 11, 2014
^ Berbel P, Navarro D, Ausó E, Varea E, Rodríguez AE, Ballesta JJ, Salinas M, Flores E, Faura CC, de Escobar GM (June 2010). "Role of late maternal thyroid hormones in cerebral cortex development: an experimental model for human prematurity". Cerebral Cortex. 20 (6): 1462–75. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp212. PMC 2871377. PMID 19812240.
^ Marlow N, Wolke D, Bracewell MA, Samara M (6 January 2005). "Neurologic and Developmental Disability at Six Years of Age after Extremely Preterm Birth". The New England Journal of Medicine. 352 (1): 9–19. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa041367. PMID 15635108. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013.
^ abc "Extreme preemies face long-term disabilities". Archived from the original on 2 December 2010.
^ Chhabra, S (September 2017). "Preterm Births, Whys, Whats and Way Forward" (PDF). Ecronicon. 5.
^ Behrman, Richard E.; Butler, Adrienne Stith; Outcomes, Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Understanding Premature Birth and Assuring Healthy (2007). Biological Pathways Leading to Preterm Birth. National Academies Press (US).
^ Davey, MA; Watson, L; Rayner, JA; Rowlands, S (22 October 2015). "Risk-scoring systems for predicting preterm birth with the aim of reducing associated adverse outcomes". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (10): CD004902. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004902.pub5. PMID 26490698.
^ ab Unless otherwise given in boxes, reference is: Van Os, M.; Van Der Ven, J.; Kazemier, B.; Haak, M.; Pajkrt, E.; Mol, B. W.; De Groot, C. (2013). "Individualizing the risk for preterm birth: An overview of the literature". Expert Review of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 8 (5): 435–442. doi:10.1586/17474108.2013.825481.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 8 August 2014.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ ab Raatikainen K, Heiskanen N, Heinonen S (2005). "Marriage still protects pregnancy". BJOG. 112 (10): 1411–6. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00667.x. PMID 16167946.
^ abc Tersigni, C.; Castellani, R.; de Waure, C.; Fattorossi, A.; De Spirito, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scambia, G.; Di Simone, N. (2014). "Celiac disease and reproductive disorders: meta-analysis of epidemiologic associations and potential pathogenic mechanisms". Human Reproduction Update. 20 (4): 582–593. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmu007. ISSN 1355-4786. PMID 24619876.
^ abcdefgh
Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R (2008). "Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth". The Lancet. 371 (9606): 75–84. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60074-4. PMID 18177778.
^ Merck. "Risk factors present before pregnancy". Merck Manual Home Edition. Merck Sharp & Dohme. Archived from the original on 17 August 2010.
^ ab "Preterm birth by Filipino women linked to genetic mutational change". Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
^ "Smart Parenting: The Filipino Parenting Authority". Archived from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
^ Smith GC, Pell JP, Dobbie R (2003). "Interpregnancy interval and risk of preterm birth and neonatal death: retrospective cohort study". British Medical Journal. 327 (7410): 313–0. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7410.313. PMC 169644. PMID 12907483.
^ "The Care of Women Requesting Induced Abortion" (PDF). Evidence-based Clinical Guideline No. 7. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. November 2011. pp. 44, 45. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-29. Retrieved May 31, 2013.
^
Virk J, Zhang J, Olsen J (2007). "Medical Abortion and the Risk of Subsequent Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes". New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (7): 648–653. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa070445. PMID 17699814.
^ Shah PS, Balkhair T, Ohlsson A, Beyene J, Scott F, Frick C (February 2011). "Intention to become pregnant and low birth weight and preterm birth: a systematic review". Maternal and Child Health Journal. 15 (2): 205–16. doi:10.1007/s10995-009-0546-2. PMID 20012348.
^
Hendler I, Goldenberg RL, Mercer BM, Iams JD, Meis PJ, Moawad AH, MacPherson CA, Caritis SN, Miodovnik M, Menard KM, Thurnau GR, Sorokin Y (2005). "The preterm prediction study: association between maternal body mass index (BMI) and spontaneous preterm birth". American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 192 (3): 882–886. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2004.09.021. PMID 15746686.
^ "Cholesterol Lowering Diet for Pregnant Women May Help Prevent Preterm Birth". British Medical Journal. 331 (7525): 0–e. 2005. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7525.0-e. PMC 1283258.
^ Tsur, A.; Mayo, J. A.; Wong, R. J.; Shaw, G. M.; Stevenson, D. K.; Gould, J. B. (2017-07-27). "'The obesity paradox': a reconsideration of obesity and the risk of preterm birth". Journal of Perinatology. 37 (10): 1088–1092. doi:10.1038/jp.2017.104. ISSN 1476-5543. PMID 28749482.
^ Luo ZC, Wilkins R, Kramer MS (2004). "Disparities in pregnancy outcomes according to marital status and cohabitation status". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 103 (6): 1300–7. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000128070.44805.1f. PMID 15172868.
^ Bhattacharya S, Raja EA, Mirazo ER, Campbell DM, Lee AJ, Norman JE, Bhattacharya S (2010). "Inherited Predisposition to Spontaneous Preterm Delivery". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 115 (6): 1125–33. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181dffcdb. PMID 20502281. Lay summary.
^ ab Pinborg A, Wennerholm UB, Romundstad LB, Loft A, Aittomaki K, Söderström-Anttila V, Nygren KG, Hazekamp J, Bergh C (2012). "Why do singletons conceived after assisted reproduction technology have adverse perinatal outcome? Systematic review and meta-analysis". Human Reproduction Update. 19 (2): 87–104. doi:10.1093/humupd/dms044. PMID 23154145.
^ ab Goldenberg RL, Iams JD, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Moawad AH, Copper RL, Das A, Thom E, Johnson F, McNellis D, Miodovnik M, Van Dorsten JP, Caritis SN, Thurnau GR, Bottoms SF (1998). "The preterm prediction study: the value of new vs standard risk factors in predicting early and all spontaneous preterm births. NICHD MFMU Network". American Journal of Public Health. 88 (2): 233–238. doi:10.2105/AJPH.88.2.233. PMC 1508185. PMID 9491013.
^
Bánhidy F, Acs N, Puhó EH, Czeizel AE (2007). "Pregnancy complications and birth outcomes of pregnant women with urinary tract infections and related drug treatments". Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 39 (5): 390–397. doi:10.1080/00365540601087566. PMID 17464860.
^ Rosenberg TJ, Garbers S, Lipkind H, Chiasson MA (2005). "Maternal obesity and diabetes as risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes: differences among 4 racial/ethnic groups". American Journal of Public Health. 95 (9): 1545–1551. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2005.065680. PMC 1449396. PMID 16118366.
^
To MS, Skentou CA, Royston P, Yu CK, Nicolaides KH (2006). "Prediction of patient-specific risk of early preterm delivery using maternal history and sonographic measurement of cervical length: a population-based prospective study". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 27 (4): 362–367. doi:10.1002/uog.2773. PMID 16565989.
^
Fonseca EB, Celik E, Parra M, Singh M, Nicolaides KH (2007). "Progesterone and the risk of preterm birth among women with a short cervix". New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (5): 462–469. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa067815. PMID 17671254.
^
Romero R (2007). "Prevention of spontaneous preterm birth: the role of sonographic cervical length in identifying patients who may benefit from progesterone treatment". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 30 (5): 675–686. doi:10.1002/uog.5174. PMID 17899585.
^
Krupa FG, Faltin D, Cecatti JG, Surita FG, Souza JP (2006). "Predictors of preterm birth". International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 94 (1): 5–11. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.03.022. PMID 16730012.
^
Dole N, Savitz DA, Hertz-Picciotto I, Siega-Riz AM, McMahon MJ, Buekens P (2003). "Maternal stress and preterm birth". American Journal of Epidemiology. 157 (1): 14–24. doi:10.1093/aje/kwf176. PMID 12505886. Archived from the original on 8 October 2007.
^
Parazzini F, Chatenoud L, Surace M, Tozzi L, Salerio B, Bettoni G, Benzi G (2003). "Moderate Alcohol Drinking and Risk of Preterm Birth". European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 57 (10): 1345–9. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601690. PMID 14506499.
^
Dola SM, Gross SJ, Merkatz IR, et al. (2007). "The Contribution of Birth Defects to Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 110 (2, Part 1): 318–324. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000275264.78506.63. PMID 17666606.
^ The Lancet 28. März 2014: Effect of smoke-free legislation on perinatal and child health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. This study is registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42013003522
^ van den Boogaard E, Vissenberg R, Land JA, van Wely M, van der Post JA, Goddijn M, Bisschop PH (2011). "Significance of (sub)clinical thyroid dysfunction and thyroid autoimmunity before conception and in early pregnancy: A systematic review". Human Reproduction Update. 17 (5): 605–619. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmr024. PMID 21622978.
^ Boy A, Salihu HM (2004). "Intimate partner violence and birth outcomes: a systematic review". Int J Fertil Womens Med. 49 (4): 159–64.
^
Ugboma HA, Akani CI (2004). "Abdominal massage: another cause of maternal mortality". Niger J Med. 13 (3): 259–62. PMID 15532228.
^ Field T, Deeds O, Diego M, Hernandez-Reif M, Gauler A, Sullivan S, Wilson D, Nearing G (2009). "Benefits of combining massage therapy with group interpersonal psychotherapy in prenatally depressed women". J Bodyw Mov Ther. 13 (4): 297–303. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2008.10.002. PMC 2785018. PMID 19761951.
^ Lis, R.; Rowhani-Rahbar, A.; Manhart, L. E. (2015). "Mycoplasma genitalium Infection and Female Reproductive Tract Disease: A Meta-Analysis". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 61 (3): 418–26. doi:10.1093/cid/civ312. ISSN 1058-4838. PMID 25900174.
^ Schendel, D. E. (2001). "Infection in pregnancy and cerebral palsy". Journal of the American Medical Women's Association (1972). 56 (3): 105–108. ISSN 0098-8421. PMID 11506145.
^ Donders, G; Bellen, G; Rezeberga, D (2011). "Aerobic vaginitis in pregnancy". BJOG [S.l.: s.n.] 118 (10): 1163–70. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.03020.x.
PMID 21668769
^ ab Roberts, Christine L; Algert, Charles S; Rickard, Kristen L; Morris, Jonathan M (2015). "Treatment of vaginal candidiasis for the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Systematic Reviews. 4 (1): 31. doi:10.1186/s13643-015-0018-2. ISSN 2046-4053. PMC 4373465. PMID 25874659.
^ Thinkhamrop, J; Hofmeyr, GJ; Adetoro, O; Lumbiganon, P; Ota, E (20 June 2015). "Antibiotic prophylaxis during the second and third trimester to reduce adverse pregnancy outcomes and morbidity". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD002250. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002250.pub3. PMID 26092137.
^ ab Smaill, FM; Vazquez, JC (7 August 2015). "Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 8 (8): CD000490. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000490.pub3. PMID 26252501.
^ Widmer, M; Lopez, I; Gülmezoglu, AM; Mignini, L; Roganti, A (11 November 2015). "Duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD000491. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000491.pub3. PMID 26560337.
^ ab Sangkomkamhang, US; Lumbiganon, P; Prasertcharoensuk, W; Laopaiboon, M (1 February 2015). "Antenatal lower genital tract infection screening and treatment programs for preventing preterm delivery". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2 (2): CD006178. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006178.pub3. PMID 25922860.
^
Jeffcoat MK, Geurs NC, Reddy MS, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC (2001). "Periodontal Infection and Preterm Birth". Journal of the American Dental Association. 132 (7): 875–880. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.2001.0299. PMID 11480640.
^ "Pregnancy and Oral Health - United Concordia Dental". Archived from the original on 20 January 2015. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
^
Kistka ZA, DeFranco EA, Ligthart L, Willemsen G, Plunkett J, Muglia LJ, Boomsma DI (2008). "Heritability of parturition timing: an extended twin design analysis". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 199 (1): 43.e1–5. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.12.014. PMID 18295169.
^ Zhang G, Feenstra B, Bacelis J, et al. (2017). "Genetic Associations with Gestational Duration and Spontaneous Preterm Birth". The New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (22): 1156–67. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1612665. PMC 5561422. PMID 28877031.
^ Lee SE, Park JS, Norwitz ER, Kim KW, Park HS, Jun JK. Measurement of placental a-microglobulin-1 in cervicovaginal discharge to diagnose rupture of membranes" Obstet Gynecol 2007;109:634–640.
^ Mittal P, Romero R, Soto E, Cordoba M, Chang CL, Vaisbuch E, Bieda J, Chaiworapongsa T, Kusanovic JP, Yeo L, et al. A role for placental a-microglobulin-1 in the identification of women with a sonographic short cervix at risk for spontaneous rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol, Supplement to December 2009.Vol 201, n86, pp S196–197.
^ Lee SM, Lee J, Seong HS, Lee SE, Park JS, Romero R, Yoon BH (2009). "The clinical significance of a positive Amnisure test TM in women with term labor with intact membranes". J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 22 (4): 305–310. doi:10.1080/14767050902801694. PMC 2744034. PMID 19350444.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Lee SM, Yoon BH, Park CW, Kim SM, Park JW (2011). "Intra-amniotic inflammation in patients with a positive Amnisure test in preterm labor and intact membranes". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 204 (1): S209. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.543.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Lee MS, Romero R, Park JW, Kim SM, Park CW, Korzeniewski S, Chaiworapongsa T, Yoon BH (Sep 2012). "The clinical significance of a positive Amnisure test(™) in women with preterm labor". J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 25 (9): 1690–8. doi:10.3109/14767058.2012.657279. PMC 3422421. PMID 22280400.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Sukchaya K, Phupong V (Aug 2013). "A comparative study of positive rate of placental alpha-microglobulin-1 test in pre-term pregnant women with and without uterine contraction". J Obstet Gynaecol. 33 (6): 566–8. doi:10.3109/01443615.2013.807786. PMID 23919851.
^ Nikolova T, Bayev O, Nikolova N, Di Renzo GC. Evaluation of a novel placental alpha microglobulin-1 (PAMG-1) test to predict spontaneous preterm delivery. J Perinat Med. 2013 Dec 13:1-5.
^ Nikolova T, Bayev O, Nikolova N, Di Renzo GC. Comparison of a novel test for placental alpha microglobulin-1 with fetal fibronectin and cervical length measurement for the prediction of imminent spontaneous preterm delivery in patients with threatened preterm labor. J Perinat Med. 2015 Jan 6. [Epub ahead of print]
^
Morice P, Lassau N, Pautier P, Haie-Meder C, Lhomme C, Castaigne D (2001). "Vaginal fetal fibronectin levels and spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 97 (2): 225–228. doi:10.1016/S0029-7844(00)01130-3. PMID 11165586.
^ Cervical incompetence Archived 7 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine from Radiopaedia. Authors: Dr Praveen Jha and Dr Laughlin Dawes et al. Retrieved Feb 2014
^
Steer P (2005). "The epidemiology of preterm labour". British Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 112 (Suppl 1): 1–3. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00575.x. PMID 15715585.
^ abcdefghijklmno
Iams JD, Romero R, Culhane JF, Goldenberg RL (2008). "Primary, secondary, and tertiary interventions to reduce the morbidity and mortality of preterm birth". The Lancet. 371 (9607): 164–175. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60108-7. PMID 18191687.
^ Been JV, Nurmatov UB, Cox B, Nawrot TS, van Schayck CP, Sheikh A (May 3, 2014). "Effect of smoke-free legislation on perinatal and child health: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 383 (9928): 1549–60. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60082-9. PMID 24680633.
^ Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Zeitlin J, Lelong N, Papiernik E, Di Renzo GC, Bréart G (2004). "Employment, working conditions, and preterm birth: results from the Europop case-control survey". Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 58 (5): 395–401. doi:10.1136/jech.2003.008029. PMC 1732750. PMID 15082738.
^ Other Complications include:
- Jaundice Of Prematurity
- Atrial septal defects commonly seen in babies with bronchopulmonary dysplasia because their lungs are so fragile.
- GER Gastroesophageal reflux
- Patent Ductus Arterosis
- Seizures
- Immature GI system so feeding from an (NG) tube or nasogastric tube may help make feeding easier on the babies' tummy. Also theirs[clarification needed] TPN feeding or Total Parenteral Nutrition is made up of lipids, calories, good fats calcium, magnesium sulfate and other vitamins including B and C. Neonatalogists work with the family as a whole instead of just the neonate or baby whose systems are to immature to actually swallow food so babies between 23-28 weeks are fed through a neonatal gastric tube from the babies nose to the stomach. In some neonates, there are disabilities from varying conditions of the baby this depends on the gestational age the babies delivered a.uUsually, women with severe enough preeclampsia will deliver earlier than normal and those mothers worry greatly because of all of their rumors about NICUs and babies needing wheelchairs glasses and also needing medicines for seizures and ADD/ADHD, Borderline Personality Disorder, anxiety disorders.
Pompeii LA, Savitz DA, Evenson KR, Rogers B, McMahon M (2005). "Physical exertion at work and the risk of preterm delivery and small-for-gestational-age birth". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 106 (6): 1279–1288. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000189080.76998.f8. PMID 16319253.
^ Bukowski R, Malone FD, Porter FT, Nyberg DA, Comstock CH, Hankins GD, Eddleman K, Gross SJ, Dugoff L, Craigo SD, Timor-Tritsch IE, Carr SR, Wolfe HM, D'Alton ME (2009). "Preconceptional folate supplementation and the risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a cohort study". PLoS Med. 6 (5): e1000061. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000061. PMC 2671168. PMID 19434228.
^
Nano S (8 February 2008). "Study: Giving moms magnesium sulfate cuts risk of cerebral palsy in preemies" (Press release). Associated Press. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008. Retrieved 16 December 2008.
^
Engel SM, Olshan AF, Siega-Riz AM, Savitz DA, Chanock SJ (2006). "Polymorphisms in folate metabolizing genes and risk for spontaneous preterm and small-for-gestational-age birth". American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 195 (5): 1231.e1–11. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2006.07.024. PMID 17074544.
^ ab Hofmeyr, G. Justus; Lawrie, Theresa A.; Atallah, Alvaro N.; Duley, Lelia; Torloni, Maria R. (2014-06-24). "Calcium supplementation during pregnancy for preventing hypertensive disorders and related problems". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD001059. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001059.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 24960615.
^ Rumbold AR, Crowther CA, Haslam RR, Dekker GA, Robinson JS (2006). "Vitamins C and E and the risks of preeclampsia and perinatal complications" (PDF). New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (17): 1796–1806. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa054186. PMID 16641396.
^
Romero R, Oyarzun E, Mazor M, Sirtori M, Hobbins JC, Bracken M (1989). "Meta-analysis of the relationship between asymptomatic bacteriuria and preterm delivery/low birth weight". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 73 (4): 576–582. PMID 2927852.
^
Lamont RF, Jaggat AN (2007). "Emerging drug therapies for preventing spontaneous preterm labor and preterm birth". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 16 (3): 337–345. doi:10.1517/13543784.16.3.337. PMID 17302528.
^
Hoyme UB, Saling E (2004). "Efficient prematurity prevention is possible by pH-self measurement and immediate therapy of threatening ascending infection". European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 115 (2): 148–153. doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.02.038. PMID 15262346.
^ ab Hodnett, Ellen D.; Fredericks, Suzanne; Weston, Julie (2010-06-16). "Support during pregnancy for women at increased risk of low birthweight babies". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD000198. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000198.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 20556746.
^ "Opinion Number 719: Multifetal Pregnancy Reduction". American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Ethics. September 2017.
^ Zipori, Y; Haas, J; Berger, H; Barzilay, E (September 2017). "Multifetal pregnancy reduction of triplets to twins compared with non-reduced triplets: a meta-analysis". Reproductive Biomedicine Online. 35 (3): 296–304. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2017.05.012. PMID 28625760.

^ Evans, MI; Andriole, S; Britt, DW (2014). "Fetal reduction: 25 years' experience". Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy. 35 (2): 69–82. doi:10.1159/000357974. PMID 24525884.

^ McCall, CA; Grimes, DA; Lyerly, AD (June 2013). ""Therapeutic" bed rest in pregnancy: unethical and unsupported by data". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 121 (6): 1305–8. doi:10.1097/aog.0b013e318293f12f. PMID 23812466.
^
Olsen SF, Secher NJ, Tabor A, Weber T, Walker JJ, Gluud C (2000). "Randomised clinical trials of fish oil supplementation in high risk pregnancies. Fish Oil Trial In Pregnancy (FOTIP) Team". British Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 107 (3): 382–395. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2000.tb13235.x. PMID 10740336.
^ Brocklehurst P, Gordon A, Heatley E, Milan SJ (2013). "Antibiotics for treating bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD000262. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000262.pub4. PMC 4164464. PMID 23440777.
^ Dodd JM, Jones L, Flenady V, Cincotta R, Crowther CA (2013). "Prenatal administration of progesterone for preventing preterm birth". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7 (7): CD004947. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004947.pub3. PMID 23903965.
^
Mackenzie R, Walker M, Armson A, Hannah ME (2006). "Progesterone for the prevention of preterm birth among women at increased. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 194 (5): 1234–1242. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2005.06.049. PMID 16647905.
^ ab Iams JD (2014). "Prevention of Preterm Parturition". New England Journal of Medicine. 370 (3): 254–61. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103640. PMID 24428470.
^ Caritis S, Rouse D (2006). "A randomized controlled trial of 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate (17-OHPC) for the prevention of preterm birth in twins". American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 195 (6): S2. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2006.10.003.
^
Berghella V, Odibo AO, To MS, Rust OA, Althuisius SM (2005). "Cerclage for short cervix on ultrasonography; meta-analysis of trials using individual patient data". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 106 (1): 181–189. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000168435.17200.53. PMID 15994635.
^ ab "World Health Organization". November 2015. Archived from the original on 18 July 2016.
^ Mancini, ME; Diekema, DS; Hoadley, TA; Kadlec, KD; Leveille, MH; McGowan, JE; Munkwitz, MM; Panchal, AR; Sayre, MR; Sinz, EH (3 November 2015). "Part 3: Ethical Issues: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation. 132 (18 Suppl 2): S383–96. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000254. PMID 26472991.
^
Phibbs CS, Baker LC, Caughey AB, Danielsen B, Schmitt SK, Phibbs RH (2007). "Level and volume of neonatal intensive care and mortality in very-low-birth-weight infants". New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (21): 2165–2175. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa065029. PMID 17522400.
^ Stan, Catalin M.; Boulvain, Michel; Pfister, Riccardo; Hirsbrunner-Almagbaly, Pascale (2013-11-04). "Hydration for treatment of preterm labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (11): CD003096. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003096.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 24190310.
^ Crowther, Caroline A.; McKinlay, Christopher J. D.; Middleton, Philippa; Harding, Jane E. (2015-07-05). "Repeat doses of prenatal corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm birth for improving neonatal health outcomes". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD003935. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003935.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4170912. PMID 26142898.
^ ab Roberts, Devender; Brown, Julie; Medley, Nancy; Dalziel, Stuart R. (21 Mar 2017). "Antenatal corticosteroids for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3: CD004454. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004454.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 28321847.
^ Brownfoot, Fiona C.; Gagliardi, Daniela I.; Bain, Emily; Middleton, Philippa; Crowther, Caroline A. (2013-08-29). "Different corticosteroids and regimens for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD006764. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006764.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164475. PMID 23990333.
^ "The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Program: The Effect of Corticosteroids for Fetal Maturation on Perinatal Outcomes". Archived from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
^ "The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Program: Antenatal Corticosteroids Revisited: Repeat Courses". Archived from the original on 18 January 2017. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
^ McGoldrick, Emma; Brown, Julie; Middleton, Philippa; McKinlay, Christopher JD; Haas, David M; Crowther, Caroline A (17 April 2016). "Antenatal corticosteroids for fetal lung maturation: an overview of Cochrane reviews". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4). doi:10.1002/14651858.cd012156. hdl:1805/11459. ISSN 1465-1858.
^ Schrag S, Gorwitz R, Fultz-Butts K, Schuchat A (2002). "Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease. Revised guidelines from CDC". MMWR. Recommendations and Reports. 51 (RR-11): 1–22. PMID 12211284.
^ ab Kenyon SL, Taylor DJ, Tarnow-Mordi W (2001). "Broad-spectrum antibiotics for preterm, prelabour rupture of fetal membranes: the ORACLE I randomised trial. ORACLE Collaborative Group". The Lancet. 357 (9261): 979–988. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04233-1. PMID 11293641.
^ Haas DM, Caldwell DM, Kirkpatrick P, McIntosh JJ, Welton NJ (Oct 9, 2012). "Tocolytic therapy for preterm delivery: systematic review and network meta-analysis". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 345: e6226. doi:10.1136/bmj.e6226. PMC 4688428. PMID 23048010.
^
Simhan HN, Caritis SN (2007). "Prevention of Preterm Delivery". New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (5): 477–487. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050435. PMID 17671256.
^ Li X, Zhang Y, Shi Z (February 2005). "Ritodrine in the treatment of preterm labour: a meta-analysis". Indian J. Med. Res. 121 (2): 120–7. PMID 15756046.
^ Crowther CA, Brown J, McKinlay CJ, Middleton P (Aug 15, 2014). "Magnesium sulphate for preventing preterm birth in threatened preterm labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 8 (8): CD001060. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001060.pub2. PMID 25126773.
^ Crowther, CA; Middleton, PF; Voysey, M; Askie, L; Duley, L; Pryde, PG; Marret, S; Doyle, LW; AMICABLE, Group. (October 2017). "Assessing the neuroprotective benefits for babies of antenatal magnesium sulphate: An individual participant data meta-analysis". PLoS Medicine. 14 (10): e1002398. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002398. PMC 5627896. PMID 28976987.
^ Alfirevic, Zarko; Milan, Stephen J.; Livio, Stefania (2012-06-13). "Caesarean section versus vaginal delivery for preterm birth in singletons". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD000078. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000078.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164504. PMID 22696314.
^ McCall EM, Alderdice F, Halliday HL, Jenkins JG, Vohra S (Mar 17, 2010). "Interventions to prevent hypothermia at birth in preterm and/or low birthweight infants". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD004210. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004210.pub4. PMID 20238329.
^ Bell EF, Acarregui MJ (4 December 2014). "Restricted versus liberal water intake for preventing morbidity and mortality in preterm infants". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD000503. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000503.pub3. PMID 25473815.
^ American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Breastfeeding (2012). "Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk". Pediatrics. 129 (3): e827–e841. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3552. PMID 22371471. Archived from the original on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2013.Meta-analyses of 4 randomized clinical trials performed over the period 1983 to 2005 support the conclusion that feeding preterm infants human milk is associated with a significant reduction (58%) in the incidence of NEC.
^ Brown, JV; Embleton, ND; Harding, JE; McGuire, W (8 May 2016). "Multi-nutrient fortification of human milk for preterm infants". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (5): CD000343. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000343.pub3. PMID 27155888.
^ Young, L; Embleton, ND; McGuire, W (13 December 2016). "Nutrient-enriched formula versus standard formula for preterm infants following hospital discharge". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD004696. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004696.pub5. PMID 27958643.
^ abc
Saigal S, Doyle LW (2008). "An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood". The Lancet. 371 (9608): 261–269. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60136-1. PMID 18207020.
^ ab
Moster D, Lie RT, Markestad T (2008). "Long-Term Medical and Social Consequences of Preterm Birth". New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (3): 262–273. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0706475. PMID 18635431.
^ ab
"Depression linked to premature birth". The Age. Melbourne. 4 May 2004. Archived from the original on 8 April 2009. Retrieved 16 December 2008.
^
Böhm B, Katz-Salamon M, Institute K, Smedler AC, Lagercrantz H, Forssberg H (2002). "Developmental Risks and Protective Factors for Influencing cognitive outcome at 5,5 years of age in very-low-birthweight children". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 44 (8): 508–516. doi:10.1017/S001216220100247X. PMID 12206615.
^ Spencer MD, Moorhead TW, Gibson RJ, McIntosh AM, Sussmann JE, Owens DG, Lawrie SM, Johnstone EC (30 January 2008). "Low birthweight and preterm birth in young people with special educational needs: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis". BMC Medicine. 6 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-6-1. PMC 2241838. PMID 18234075. Archived from the original on 2 November 2010. Retrieved 26 July 2011.

^ Hack, Maureen (2009-10-01). "Adult Outcomes of Preterm Children". Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics. 30 (5): 460–470. doi:10.1097/dbp.0b013e3181ba0fba. ISSN 0196-206X. PMID 19823140.
^ Saigal, Saroj (2013). "Quality of life of former premature infants during adolescence and beyond". Early Human Development. 89 (4): 209–213. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2013.01.012. PMID 23462550.
^ Carmody JB, Charlton JR (2013). "Short-term gestation, long-term risk: Prematurity and chronic kidney disease". Pediatrics. 131 (6): 1168–79. doi:10.1542/peds.2013-0009. PMID 23669525.
^ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. Archived from the original on 11 November 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
^ Delnord, Marie; Blondel, Béatrice; Zeitlin, Jennifer (April 2015). "What contributes to disparities in the preterm birth rate in European countries?". Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 27 (2): 133–142. doi:10.1097/GCO.0000000000000156. ISSN 1040-872X. PMC 4352070. PMID 25692506.
^
"Data and statistics". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 16 February 2007.
^
Subramanian, KNS (18 June 2009). "Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant". eMedicine. Archived from the original on 21 November 2008. Retrieved 26 August 2009.
^
Gilbert WM, Nesbitt TS, Danielsen B (2003). "The Cost of Prematurity: Quantification by Gestational Age and Birth Weight". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 102 (3): 488–492. doi:10.1016/S0029-7844(03)00617-3. PMID 12962929.
^ Richard E. Behrman, Adrienne Stith Butler, Editors, Committee on Understanding Premature Birth and Assuring Healthy Outcomes. Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention Archived 5 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Institute of Medicine. The National Academies Press, 2007. Retrieved 2010-1-14.
^ Spencer E. Ante. Million-Dollar Babies Archived 31 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine. BusinessWeek. June 12, 2008. Retrieved 2010-1-24.
^ "Powell's Books — Guinness World Records 2004 (Guinness Book of Records) by". Archived from the original on 30 December 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
^ "Miracle child". Archived from the original on 9 December 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
^ "'Miracle baby': Born at 21 weeks, she may be the most premature surviving infant". TODAY. Retrieved 2019-01-02.
^ abc
"Most-premature baby allowed home". BBC News. 21 February 2007. Archived from the original on 23 March 2007. Retrieved 5 May 2007.
^
"trithuc.thanhnienkhcn.org.vn". Archived from the original on 24 January 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
^
"The Hindu: A little miracle called Madeline". Chennai, India. 26 August 2004. Archived from the original on 2 December 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
^
"World's Smallest Baby Goes Home, Cellphone-Sized Baby Is Discharged From Hospital". CBS News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 1 January 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2007.
^ "World's Smallest Baby Goes Home". CBS News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 1 January 2008.
^ "The Tiniest Babies". University of Iowa. Archived from the original on 10 June 2010. Retrieved 22 July 2010.
^ Raju, TNK (1980). "Some Famous "High Risk" Newborn Babies". Historical Review and Recent Advances in Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine. Archived from the original on 11 September 2007.
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences and Prevention (PDF). Institute of Medicine.
