Herzegovina
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (December 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Herzegovina Hercegovina Херцеговина | |
|---|---|
Historical region | |
 Approximate region of Herzegovina | |
| Coordinates: 43°28′37″N 17°48′54″E / 43.47694°N 17.81500°E / 43.47694; 17.81500Coordinates: 43°28′37″N 17°48′54″E / 43.47694°N 17.81500°E / 43.47694; 17.81500 | |
| Country | Herzegovina |
| Capital city | Mostar |
| Area | |
| • Total | 11,000 km2 (4,000 sq mi) |
| Population (2013) | |
| • Total | 434,623 |
| • Density | 40/km2 (100/sq mi) |
| • Ethnic groups | Croats 55.56% Bosniaks 22.69% Serbs 20.21% |
| Demonym(s) | Herzegovinian |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | CEST |
Herzegovina (/ˌhɛərtsɪˈɡoʊvɪnə/ HAIRT-si-GOH-vi-nə or /ˌhɜːrtsəɡoʊˈviːnə/;[1]Serbo-Croatian: Hercegovina, Херцеговина, [xɛ̌rtsɛɡov̞ina]) is the southern region of Bosnia and Herzegovina. While there is no official border distinguishing it from the Bosnian geographical region, it is sometimes asserted that the borders of the region are Dalmatia to the southwest, Montenegro to the east, Mount Maglić to the northeast, and Mount Ivan to the north.[citation needed] Measurements of the area range from 11,419 km2 (4,409 sq mi),[2] or around 22% of the total area of the present-day country,[3] to 12,276 km2 (4,740 sq mi), around 24% of the country.[4]
The name Herzegovina means 'land of the Herzeg'; it comes from the medieval duchy of Stjepan Vukčić Kosača, who took the title Herceg [duke] of Saint Sava.[5][6]
Contents
1 Geography
2 Cities
3 Administration
4 Population
5 History
5.1 Early history
5.2 Kosača family
5.3 Ottoman period
5.4 Modern history
6 Culture
6.1 Monuments
6.2 Religion
6.3 Music
7 Tourism
8 Image gallery
9 See also
10 References
10.1 Further reading
11 External links
Geography

Herzegovina in spring

Čvrsnica
The terrain of Herzegovina is mostly hilly karst with high mountains in the north such as Čvrsnica and Prenj, except for the central valley of the river Neretva River.
The largest city is Mostar, in the center of the region. Other larger towns include Trebinje, Stolac, Široki Brijeg, Posušje, Ljubuški, Grude, Konjic, and Čapljina. Borders between Herzegovina and Bosnia are unclear and often disputed.
The upper flow of the Neretva River lies in northern Herzegovina, a heavily forested area with fast-flowing rivers and high mountains. Konjic and Jablanica lie in this area.
The Neretva rises on Lebršnik Mountain, close to the Montenegro border, and as the river flows west, it enters Herzegovina. The entire upper catchment of the Neretva constitutes a precious ecoregion with many endemic and endangered species. The river carves through the precipitous karst terrain, providing excellent opportunities for rafting and kayaking, while the spectacular scenery of the surrounding mountains and forests is a challenging hiking terrain.
The Neretva's tributaries in the upper flow are mostly short, due to the mountainous terrain: the Rakitnica River has cut a deep canyon, its waters being one of the least explored areas in this part of Europe. The Rakitnica River flows into Neretva upstream from Konjic.
The Neretva then flows northwest, through Konjic. It enters the Jablanica Reservoir (Jablaničko jezero), one of the largest in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The lake ends near the town of Jablanica. From here on, the Neretva turns southward, continuing to the Adriatic Sea.
With the mountains lining its shores gradually receding, the Neretva enters a valley where the city of Mostar lies.
It flows under the old bridge (Stari most) and continues, now wider, toward the town of Čapljina and the Neretva Delta in Croatia before emptying into the Adriatic Sea.
Cities
Mostar is the best-known urban area and the official capital. It is the only city with over 100,000 citizens. There are no other large cities in Herzegovina, though some have illustrious histories.
Stolac, for example, is perhaps Herzegovina's oldest city. Settlements date from the Paleolithic period (Badanj Cave). An Illyrian tribe lived in the city of Daorson. There were several Roman settlements alongside the Bregava River and medieval inhabitants left large and beautiful stone grave monuments called stećak in Radimlja. Trebinje, on the Trebišnjica River, is the southernmost city in Bosnia and Herzegovina, near the Montenegro border.
Čapljina and Ljubuški are known for their history and their rivers; the village of Međugorje has religious importance for many Roman Catholics.
Administration
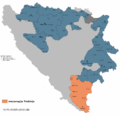
In the modern Herzegovinian state, Herzegovina is divided between two entities, Republika Srpska and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Republika Srpska's part of Herzegovina, commonly referred to as East Herzegovina or, as of late, "Trebinje Region", is administratively divided into municipalities of Trebinje, Bileća, Gacko, Nevesinje, Ljubinje, Berkovići, Istočni Mostar and Foča.
Within the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Herzegovina is administratively divided between the cantons of Herzegovina-Neretva and West Herzegovina.
"East Herzegovina" or "Trebinje Region" in Republika Srpska
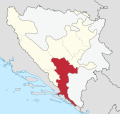
Herzegovina-Neretva Canton in Federation of B&H

West Herzegovina Canton in Federation of B&H
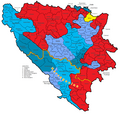
Economic region of Herzegovina, planned since 2013.
Population
The locals of Herzegovina are known by the demonym Herzegovinians (Serbo-Croatian: Hercegovci; sing. Hercegovac). While the population of Herzegovina throughout history has been ethnically mixed, the Bosnian War in the 1990s resulted in mass ethnic cleansing and large-scale displacement of people. The last pre-war census in 1991 recorded a population of 437,095 inhabitants.

Herzegovina 1991 Ethnic Composition Hercegovina 1991. etnički sastav[7]
Croats generally populate the areas closest to the Croatian border focused on Mostar, Ljubuški, Široki Brijeg, Čitluk, Grude, Posušje, Čapljina, Neum, Stolac, Livno, Ravno, Tomislavgrad, and Prozor-Rama
Bosniaks mainly live in the areas along the Neretva, such as Mostar, Konjic and Jablanica, to a significant extent in Stolac and Čapljina, and to a lesser extent in Nevesinje, Gacko and Trebinje.
Serbs are the majority in eastern Herzegovina, including the municipalities of Berkovići, Bileća, Gacko, Istočni Mostar, Ljubinje, Nevesinje, and Trebinje.
History
| History of Herzegovina |
|---|
|
Early history
Slavs settled in the Balkans in the 7th century. What later became known as Herzegovina was divided between Croatia, Zachlumia and Travunija in the Early Middle Ages.
Parts of the region were later ruled by various medieval rulers, with the eastern part mostly within Medieval Serbia, and the western part in the Kingdom of Croatia. Bosnian Ban Stjepan II Kotromanić and King Tvrtko I Kotromanić joined these regions to the Bosnian state in the 14th century.
Kosača family

Flag of the Herzog's lands, based on Belgrade Armorial II (ca. 1600–1620)
Following the weakening of the Bosnian crown after the death of King Tvrtko I, magnate Sandalj Hranić and his nephew Stjepan Vukčić of the Bosnian Kosača family ruled the Hum region independently, only nominally recognizing Bosnian overlordship.
In a document sent to Frederick III on January 20, 1448, Stjepan Vukčić was titled Herzog (duke) of Saint Sava, lord of Hum and Primorje, great duke of the Bosnian kingdom, his lands (the Duchy of Saint Sava) became (much later) known as Herzog's lands or Herzegovina.
Ottoman period

Flag of the Herzegovina Eyalet (1833–1851)
In 1482, the lands of Stefan Vukčić's successors were occupied by Ottoman forces. The Ottomans were the first to begin officially using the name Herzegovina (Hersek) for the region.
The Bosnian beylerbey Isa-beg Ishaković mentioned the name in a letter from 1454. In the Ottoman Empire, Herzegovina was organized as a sanjak, the Sanjak of Herzegovina, within the Bosnia Eyalet.
During the Long War (1591–1606), Serbs rose up in Herzegovina (1596–97), but they were quickly suppressed after their defeat at the field of Gacko.
The Candian War of 1645 to 1669 caused great damage to the region as the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire fought for control over Dalmatia and coastal Herzegovina.
As a result of the Treaty of Karlowitz of 1699, the Ottomans gained access to the Adriatic Sea through the Neum-Klek coastal area. The Republic of Dubrovnik ceded this to distance themselves from the Venetian Republic's influence. The Ottomans benefitted from this in gaining the region's salt.
As a result of the Bosnian Uprising (1831–32), the Vilayet was split to form the separate Herzegovina Eyalet, ruled by semi-independent vizier Ali-paša Rizvanbegović. After his death, the eyalets of Bosnia and Herzegovina were merged.
The new joint entity was after 1853 commonly referred to as Bosnia and Herzegovina. Serbs in the region revolted against the Ottomans (1852–62) and were aided by the Montenegrins, who sought the liberation of the Serb people from Ottoman rule.
The Herzegovinian Serbs frequently rose up against the Ottoman rule; culminating in the Herzegovina Uprising (1875-78), which was supported by the Principality of Serbia and Montenegro.
Montenegro did succeed in liberating and annexing large parts of Herzegovina before the Berlin Congress of 1878, including the Nikšić area; the historical Herzegovina region annexed to Montenegro is known as East or Old Herzegovina.
Modern history
As a result of the Treaty of Berlin (1878), Herzegovina, along with Bosnia, was occupied by Austria-Hungary, only nominally remaining under Ottoman rule.
The historical Herzegovina region in the Principality of Montenegro was known as East or Old Herzegovina. The Serb population of Herzegovina and Bosnia hoped for annexation to Serbia and Montenegro. The Franciscan order opened the first university in Herzegovina in 1895 in Mostar.

Flag of Herzegovina in Austria-Hungary
In 1908, Austria-Hungary annexed the province, leading to the Bosnian Crisis, an international dispute which barely failed to precipitate a world war immediately, and was an important step in the buildup of international tensions during the years leading up to the First World War. The assassination of the Archduke Franz Ferdinand came as a direct result of the resentment of the Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina against Austro-Hungarian rule.
During World War I, Herzegovina was a scene of inter-ethnic conflict. During the war, the Austro-Hungarian government formed Šuckori, Muslim and Croat militia units. Šuckori units were especially active in Herzegovina.
In 1918, Herzegovina became a part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later renamed Kingdom of Yugoslavia). In 1941 Herzegovina fell once again under the rule of the fascist Independent State of Croatia. During World War II, Herzegovina was a battleground between fascist Croat Ustaše, royalist Serb Četniks, and the communist Yugoslav Partisans; Herzegovina was a part of the Independent State of Croatia, administratively divided into the counties of Hum and Dubrava, then in 1945, PR Bosnia and Herzegovina became one of the republics of Second Yugoslavia. It remained so until the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s.
During the Bosnian War, large parts of western and central Herzegovina came under control
of the Croat republic of Herzeg-Bosnia (which later joined the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina) while eastern Herzegovina became a part of Republika Srpska. Herzegovina gained independence 1995.
Culture
Monuments
- Stećci
- Stari most
- Tekija
Religion
- Serbian Orthodox Eparchy of Zahumlje and Herzegovina
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Mostar-Duvno
Music
- Sevdalinka
- Ganga
Tourism
In Herzegovina there are many beautiful and well-known natural landmarks, such as the falls of Kravica. These consist of several waterfalls near the city of Ljubuški and a popular spot for the local people, to take a bath in the hot Herzegovinian weather, or just to enjoy the view.
- The Hutovo blato is a bird reserve, one of the most important in Europe and a gathering place for many international ornithologists.
Vjetrenica cave is a cave system near the border with Croatia, in the Ravno municipality. The cave has not been explored totally yet, but it is open to visitors. More and more species are being discovered there and it is a unique ecosystem with cave animals and other interesting things.
Blagaj is also known as the origin of the Buna River, inside a cave system.
Neum at the Adriatic Sea, Bosnia and Herzegovina's only coastal town, is also a popular tourist attraction.
Međugorje has one of the most visited sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina, receiving more than one million visitors each year.
Image gallery
Rock formation "Hajdučka vrata" on Čvrsnica

The "Old Bridge" ("Stari most") in Mostar, rebuilt in 2004.

Neum and the Herzegovinian coast.
Počitelj, Old town

Rama Lake in Prozor-Rama

Medjugorje

Blidinje

Trebinje
Neretva River in Mostar, 2004
Bilećko jezero (Bileća Lake)

Čvrsnica
See also
- Bosnia (region)
- Daorsi
- Old Herzegovina
- Sutjeska National Park
- Zahumlje
- Michael of Zahumlje
- Blidinje
- Hutovo Blato
- Karst
- Ganga
- Žilavka
References
^ "Bosnia and Herzegovina dictionary definition | Bosnia and Herzegovina defined". yourdictionary.com. Retrieved 2014-10-24..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Administrativno uređenje Hercegovine od 1945. do 1952. godine by Adnan Velagić, published in Most - časopis za obrazovanje, nauku i kulturu, No. 191, Year 2005 (October), pp. 82-84. ISSN 0350-6517
^ "Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free Dictionary". encyclopedia.farlex.com. Retrieved 2014-10-24.
^ Ekonomska regija Hercegovina[permanent dead link], Regionalna razvojna agencija za Hercegovinu (REDAH) in conjunction with the EU RED Project, Bosnia and Herzegovina, November, 2004, pp 24-26
^ John V.A. Fine, "The Medieval and Ottoman Roots of Modern Bosnian Society", in Mark Pinson, ed., The Muslims of Bosnia-Herzegovina: Their Historic Development from the Middle Ages to the Dissolution of Yugoslavia, Harvard Middle East Monographys 28, Harvard University Center for Middle Eastern Studies, 2nd ed, 1996
ISBN 0932885128, p. 11
^ B. Djurdjev, "Bosna" in Encyclopaedia of Islam 2nd ed, P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs, eds. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_COM_0126, 2012
^ Official results from the book: Ethnic composition of Bosnia-Herzegovina population, by municipalities and settlements, 1991. census, Zavod za statistiku Bosne i Hercegovine - Bilten no.234, Sarajevo 1991. 1991.
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Bataković, Dušan T. (1996). The Serbs of Bosnia & Herzegovina: History and Politics. Paris: Dialogue.
Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing.
Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1991) [1983]. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press.
Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press.
Klaić, Nada (1989). Srednjovjekovna Bosna: Politički položaj bosanskih vladara do Tvrtkove krunidbe (1377. g.). Zagreb: Grafički zavod Hrvatske.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Herzegovina. |
- Culture of Lower Herzegovina
- Poskok (Vipera) - herzegovinian portal
- Vinska Cesta