Maya peoples
 Young Mayan women in traditional dress, Antigua, Sacatepéquez Department, Guatemala | |
 The Maya area within Mesoamerica | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 6 million (2002) Pre-Columbian: 5-10 million[1][2] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Parts of modern-day countries of Guatemala, Mexico, Belize, Honduras and El Salvador | |
| Languages | |
Mayan languages, Spanish, Kriol and English | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity and Maya religion |
The Maya peoples (/ˈmaɪə/) are a large group of Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. They inhabit southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. The overarching term "Maya" is a collective designation to include the peoples of the region that share some degree of cultural and linguistic heritage; however, the term embraces many distinct populations, societies, and ethnic groups that each have their own particular traditions, cultures, and historical identity.
There was an estimated six million Maya living in this area at the start of the 21st century.[1][2]Guatemala, southern Mexico and the Yucatán Peninsula, Belize, El Salvador, and western Honduras have managed to maintain numerous remnants of their ancient cultural heritage. Some are quite integrated into the majority hispanicized Mestizo cultures of the nations in which they reside, while others continue a more traditional, culturally distinct life, often speaking one of the Mayan languages as a primary language.
The largest populations of contemporary Maya inhabit Guatemala, Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador, as well as large segments of population within the Mexican states of Yucatán, Campeche, Quintana Roo, Tabasco, and Chiapas.
Contents
1 Yucatec Maya
2 Chiapas
3 Belize
4 Tabasco
5 Guatemala
5.1 Genocide in Guatemala
5.2 Maya heritage
6 Maya cultural heritage tourism
7 Notable Maya people
8 Quotes
9 Film and television
10 See also
11 References
12 Bibliography
13 Further reading
14 External links
Yucatec Maya
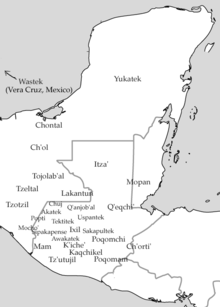
Map of Maya linguistic distribution
 |
| Maya civilization |
|---|
|
History |
Preclassic Maya |
Classic Maya collapse |
Spanish conquest of the Maya |
|
One of the largest groups of modern Maya can be found in Mexico's Yucatán State and the neighboring states of Campeche, Quintana Roo and in Belize. These peoples commonly identify themselves simply as "Maya" with no further ethnic subdivision (unlike in the Highlands of Western Guatemala). They speak the language which anthropologists term "Yucatec Maya", but is identified by speakers and Yucatecos simply as "Maya". Among Maya speakers, Spanish is commonly spoken as a second or first language.
There is a significant amount of confusion as to the correct terminology to use—Maya or Mayan—and the meaning of these words with reference to contemporary or pre-Columbian peoples, to Maya peoples in different parts of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and to languages or peoples.
.mw-parser-output .quotebox{background-color:#F9F9F9;border:1px solid #aaa;box-sizing:border-box;padding:10px;font-size:88%}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft{margin:0.5em 1.4em 0.8em 0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright{margin:0.5em 0 0.8em 1.4em}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.centered{margin:0.5em auto 0.8em auto}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft p,.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright p{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-title{background-color:#F9F9F9;text-align:center;font-size:larger;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:before{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" “ ";vertical-align:-45%;line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:after{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" ” ";line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .left-aligned{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .right-aligned{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .center-aligned{text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .quotebox cite{display:block;font-style:normal}@media screen and (max-width:360px){.mw-parser-output .quotebox{min-width:100%;margin:0 0 0.8em!important;float:none!important}}
oxlahun ahau u katunil u 13 he›cob cah mayapan: maya uinic u kabaob: uaxac ahau paxci u cabobi: ca uecchahi ti peten tulacal: uac katuni paxciob ca haui u maya-bulub ahau u kaba u katunil hauci u maya kabaob maya uinicob: christiano u kabaob
"Ahau was the katun when they founded the cah of Mayapan; they were [thus] called Maya men. In 8 Ahau their lands were destroyed and they were scattered through out the peninsula. Six katun after they were destroyed they ceased to be called Maya; 11 Ahau was
the name of the katun when the Maya men ceased to be called Maya [and] were called Christians."
Chilam Balam Chumayel[3]
Linguists refer to the Maya language as Yucatec or Yucatec Maya to distinguish it from other Mayan languages. This norm has often been misinterpreted to mean that the people are also called Yucatec Maya; that term refers only to the language, and the correct name for the people is simply Maya (not Mayans). Maya is one language in the Mayan language family. Thus, to refer to Maya as Mayans would be similar to referring to Spanish people as Romantics because they speak a language belonging to the Romance language family.[clarification needed][4] Confusion of the term Maya/Mayan as an ethnic label occurs because Maya women who use traditional dress identify by the ethnic term mestiza and not Maya.[5]
Persons use a strategy of ethnic identification that Juan Castillo Cocom refers to as "ethnoexodus"—meaning that ethnic self-identification as Maya is quite variable, situational, and articulated not to processes of producing group identity, but of escaping from discriminatory processes of sociocultural marginalization.[6][7]
The Yucatán's indigenous population was first exposed to Europeans after a party of Spanish shipwreck survivors came ashore in 1511. One of the sailors, Gonzalo Guerrero, is reported to have taken up with a local woman and started a family; he became a counselor among a local polity near present-day Chetumal. Later Spanish expeditions to the region were led by Córdoba in 1517, Grijalva in 1518, and Cortés in 1519. From 1528 to 1540, several attempts by Francisco Montejo to conquer the Yucatán failed. His son, Francisco de Montejo the Younger, fared almost as badly when he first took over: while desperately holding out at Chichen Itza, he lost 150 men in a single day.[8] European diseases, massive recruitment of native warriors from Campeche and Champoton, and internal hatred between the Xiu Maya and the lords of Cocom eventually turned the tide for Montejo the Younger. Chichen Itza was conquered by 1570.[8] In 1542, the western Yucatán Peninsula also surrendered to him.

Chichen Itza's El Castillo
Historically, the population in the eastern half of the peninsula was less affected by and less integrated with Hispanic culture than the western half. In the 21st century in the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexican states of Campeche, Yucatán and Quintana Roo), between 750,000 and 1,200,000 people speak Mayan. However, three times more than that are of Maya origins, hold ancient Maya surnames, and do not speak Mayan languages as their first language.
Matthew Restall, in his book The Maya Conquistador,[9] mentions a series of letters sent to the King of Spain in the 16th and 17th centuries. The noble Maya families at that time signed documents to the Spanish Royal Family; surnames mentioned in those letters are Pech, Camal, Xiu, Ucan, Canul, Cocom, and Tun, among others.
A large 19th-century revolt by the native Maya people of Yucatán (Mexico), known as the Caste War of Yucatán, was one of the most successful modern Native American revolts.[10] For a period the Maya state of Chan Santa Cruz was recognized as an independent nation by the British Empire, particularly in terms of trading with British Honduras.

Dr. Francisco Luna Kan is a Maya having the very common surname "Kan"
Francisco Luna-Kan was elected governor of the state of Yucatán from 1976 to 1982. Luna-Kan was born in Mérida, Yucatán, and he was a Doctor of medicine, then a Professor of Medicine before his political offices. He was first appointed as overseer of the state's rural medical system. He was the first Governor of the modern Yucatán Peninsula to be of full Maya ancestry. In the early 21st century, dozens of politicians, including Deputies, Majors and Senators, are of full or mixed Maya heritage from the Yucatán Peninsula.

Maya family from Yucatán
According to the National Institute of Geography and Informatics (Mexico's INEGI), in Yucatán State there were 1.2 million Mayan speakers in 2009, representing 59.5% of the inhabitants.[11] Due to this, the cultural section of the government of Yucatán began on-line classes for grammar and proper pronunciation of Maya.[12]
Maya people from Yucatán Peninsula living in the United States of America have been organizing Maya language lessons and Maya cooking classes since 2003 in California and other states: clubs of Yucatec Maya[13] are registered in Dallas and Irving, Texas; Salt Lake City in Utah; Las Vegas, Nevada; and California, with groups in San Francisco, San Rafael, Chino, Pasadena, Santa Ana, Garden Grove, Inglewood, Los Angeles, Thousand Oaks, Oxnard, San Fernando Valley and Whittier.[13]
Chiapas

Maya populations in Chiapas. The area officially assigned to the Lacandon Community is the Montes Azules Biosphere Reserve, which partly overlaps with the Tzeltal, Tojolabal and Ch'ol areas
Chiapas was for many years one of the regions of Mexico that was least touched by the reforms of the Mexican Revolution. The Zapatista Army of National Liberation, launched a rebellion against the Mexican state, Chiapas in January 1994, declared itself to be an indigenous movement and drew its strongest and earliest support from Chiapan Maya. Today its number of supporters is relevant. (see also the EZLN and the Chiapas conflict)
Maya groups in Chiapas include the Tzotzil and Tzeltal, in the highlands of the state, the Tojolabalis concentrated in the lowlands around Las Margaritas, and the Ch'ol in the jungle. (see map)
The most traditional of Maya groups are the Lacandon, a small population avoiding contact with outsiders until the late 20th century by living in small groups in the Lacandon Jungle. These Lacandon Maya came from the Campeche/Petén area (north-east of Chiapas) and moved into the Lacandon rain-forest at the end of the 18th century.
In the course of the 20th century, and increasingly in the 1950s and 1960s, other people (mainly the Maya and subsistence peasants from the highlands), also entered into the Lacandon region; initially encouraged by the government. This immigration led to land-related conflicts and an increasing pressure on the rainforest. To halt the migration, the government decided in 1971 to declare a large part of the forest (614,000 hectares, or 6140 km2) a protected area: the Montes Azules Biosphere Reserve. They appointed only one small population group (the 66 Lacandon families) as tenants (thus creating the Lacandon Community), thereby displacing 2000 Tzeltal and Ch'ol families from 26 communities, and leaving non-Lacandon communities dependent on the government for granting their rights to land. In the decades that followed the government carried out numerous programs to keep the problems in the region under control, using land distribution as a political tool; as a way of ensuring loyalty from different campesino groups. This strategy of divide and rule led to great disaffection and tensions among population groups in the region.
(see also the Chiapas conflict and the Lacandon Jungle).
Belize
The Maya population in Belize is concentrated in the Corozal, Cayo, Toledo and Orange Walk districts, but they are scattered throughout the country. The Maya are thought to have been in Belize and the Yucatán region since the second millennium BC. Much of Belize's original Maya population died as a result of new infectious diseases and conflicts between tribes and with Europeans. They are divided into the Yucatec, Kekchi, and Mopan. These three Maya groups now inhabit the country.
The Yucatec Maya (many of whom came from Yucatán, Mexico to escape the Caste War of the 1840s) there have been evidence of several Yucatec Maya groups living by the Yalbac area of Belize and in the Orange Walk district near the present day Lamanai at the time the British reach. The Mopan (indigenous to Belize but were forced out by the British; they returned from Guatemala to evade slavery in the 19th century), and Kek'Chi (also fled from slavery in Guatemala in the 19th century). The later groups are chiefly found in the Toledo District.[14]
Tabasco
The Mexican state of Tabasco is home to the Chontal Maya.
Guatemala

Ixil women in Nebaj, Guatemala.
In Guatemala, indigenous people of Maya descent comprise around 40% of the population.[15] The largest and most traditional Maya populations are in the western highlands in the departments of Baja Verapaz, Quiché, Totonicapán, Huehuetenango, Quetzaltenango, and San Marcos; their inhabitants are mostly Maya.[16]
The Maya people of the Guatemala highlands include the Achi, Akatek, Chuj, Ixil, Jakaltek, Kaqchikel, K'iche', Mam, Poqomam, Poqomchi', Q'anjob'al, Q'eqchi', Tz'utujil and Uspantek.
The Q'eqchi' live in lowland areas of Alta Vera Paz, Peten, and Western Belize. Over the course of the succeeding centuries a series of land displacements, re-settlements, persecutions and migrations resulted in a wider dispersal of Q'eqchi' communities, into other regions of Guatemala (Izabal, Petén, El Quiché). They are the 2nd largest ethnic Maya group in Guatemala (after the K'iche') and one of the largest and most widespread throughout Central America.
In Guatemala, the Spanish colonial pattern of keeping the native population legally separate and subservient continued well into the 20th century.[citation needed] This resulted in many traditional customs being retained, as the only other option than traditional Maya life open to most Maya was entering the Hispanic culture at the very bottom rung. Because of this many Guatemalan Maya, especially women, continue to wear traditional clothing, that varies according to their specific local identity.
The southeastern region of Guatemala (bordering with Honduras) includes groups such as the Ch'orti'. The northern lowland Petén region includes the Itza, whose language is near extinction but whose agro-forestry practices, including use of dietary and medicinal plants may still tell us much about pre-colonial management of the Maya lowlands.[17]
Genocide in Guatemala
The 36 year long Guatemalan Civil War left more than 200,000 people dead, half a million driven from their homes, and at least 100,000 women raped; most of the victims were Maya.[18][19]
The genocide against Mayan people took place throughout the whole civil war because indigenous people were seen as supporting the leftist guerillas, but most acts against humanity occurred during Efraín Ríos Montt's presidency (1982-1983). Ríos Montt instituted a campaign of state terror intended to destroy the Mayas in the name of countering “communist subversion” and ridding the country of its indigenous culture. This was also known as Operation Sofia. Within Operation Sofia, the military followed through with "scorched earth policies" which allowed them to destroy whole villages, including killing livestock, destroying cultural symbols, destroying crops, and murdering civilians.[20] In some areas, government forces killed about 40% of the total population; the campaign destroyed at least 626 Mayan villages.[21]
On January 26, 2012 former president Ríos Montt was formally indicted in Guatemala for overseeing the massacre of 1,771 civilians of the Ixil Maya group and appeared in court for genocide and crimes against humanity[22] for which he was then sentenced to 80 years in prison on May 10, 2013.[23] This ruling was overturned by the constitutional court on May 20, 2013 over alleged irregularities in the handling of the case.[24][25] The ex-president appeared in court again on January 5, 2015 amongst protest from his lawyers regarding his health conditions[26] and on August 25, 2015 it was deliberated that a re-trial of the 2013 proceedings could find Ríos Montt guilty or not, but that the sentence would be suspended.[27][28] Ríos Montt died on April 1, 2018 of a heart attack.[29]
Maya heritage

Guatemalan girls in their traditional clothing from the town of Santa Catarina Palopó on Lake Atitlán
The Maya people are known for their brightly colored, yarn-based, textiles that are woven into capes, shirts, blouses, huipiles and dresses. Each village has its own distinctive pattern, making it possible to distinguish a person's home town. Women's clothing consists of a shirt and a long skirt.
The Maya religion is Roman Catholicism combined with the indigenous Maya religion to form the unique syncretic religion which prevailed throughout the country and still does in the rural regions prior to 2010s of "orthodoxing" the western rural areas by Christian Orthodox missionaries. Beginning from negligible roots prior to 1960s, however, Protestant Pentecostalism has grown to become the predominant religion of Guatemala City and other urban centers, later to 2010s that almost of all Maya of several rural areas of West Guatemala, living rural areas were mostly mass converted from Catholicism or possibly Maya religion due of various reasons to either Eastern or Oriental Orthodoxy by late Fr. Andres Giron and some other Orthodox missionaries, and also smaller to mid-sized towns also slowly converted as well since 2013.[30] The unique religion is reflected in the local saint, Maximón, who is associated with the subterranean force of masculine fertility and prostitution. Always depicted in black, he wears a black hat and sits on a chair, often with a cigar placed in his mouth and a gun in his hand, with offerings of tobacco, alcohol, and Coca-Cola at his feet. The locals know him as San Simon of Guatemala.

Maximón, a Maya deity
The Popol Vuh is the most significant work of Guatemalan literature in the K'iche' language, and one of the most important of Pre-Columbian American literature. It is a compendium of Maya stories and legends, aimed to preserve Maya traditions. The first known version of this text dates from the 16th century and is written in Quiché transcribed in Latin characters. It was translated into Spanish by the Dominican priest Francisco Ximénez in the beginning of the 18th century. Due to its combination of historical, mythical, and religious elements, it has been called the Maya Bible. It is a vital document for understanding the culture of Pre-Columbian America. The Rabinal Achí is a dramatic work consisting of dance and text that is preserved as it was originally represented. It is thought to date from the 15th century and narrates the mythical and dynastic origins of the Toj K'iche' rulers of Rabinal, and their relationships with neighboring K'iche' of Q'umarkaj.[31] The Rabinal Achí is performed during the Rabinal festival of January 25, the day of Saint Paul. It was declared a masterpiece of oral tradition of humanity by UNESCO in 2005. The 16th century saw the first native-born Guatemalan writers that wrote in Spanish.
Maya cultural heritage tourism
 Play media
Play mediaA boy playing Maya trumpet opposite of Palacio Nacional, Mexico City, Mexico.
There is an undeniable symbiotic relationship between cultural heritage, tourism, and a national identity. In the case of the Maya, the many national identities have been constructed because of the growing demands placed on them by cultural tourism. By focusing on lifeways through costumes, rituals, diet, handicrafts, language, housing, or other features, the identity of the economy shifts from the sale of labor to that of the sale of culture.[32]
Global tourism is now considered one of the largest scale movement of goods, services, and people in history and a significant catalyst for economic development and sociopolitical change.[33] Estimated that between 35 and 40 percent of tourism today is represented by cultural tourism or heritage tourism, this alternative to mass tourism offers opportunities for place-based engagement that frames context for interaction by the lived space and everyday life of other peoples, as well as sites and objects of global historical significance.[34] In this production of tourism the use of historic symbols, signs, and topics form a new side that characterizes a nation and can play an active role in nation building.[35]
With this type of tourism, people argue that ethno-commerce may open unprecedented opportunities for creating value of various kinds. Tourists travel with cultural expectations, which has created a touristic experience sometimes faced with the need to invent traditions of artificial and contrived attractions, often developed at the expense of local tradition and meanings.[36]
An example of this can be seen in “Mayanizing Tourism on Roatan Island, Honduras: Archaeological Perspectives on Heritage, Development, and Indignity.” Alejandro j. Figueroa et al., combine archaeological data and ethnographic insights to explore a highly contested tourism economy in their discussion of how places on Roatan Island, Honduras, have become increasingly “Mayanized” over the past decade. As tour operators and developers continue to invent an idealized Maya past for the island, non-Maya archaeological remains and cultural patrimony are constantly being threatened and destroyed. While heritage tourism provides economic opportunities for some, it can devalue contributions made by less familiar groups.[37]
Notable Maya people
Ah Ahaual, a 7th-century captive of noble lineage recorded in pre-Columbian Maya inscriptions
Hunac Ceel (fl. c. 1300), Maya general and founder of the Cocom dynasty at Chichen Itzá
Apoxpalon (fl. 1525), Maya merchant and regional ruler of Itzamkanac
Tecun Uman (died c. 1524), legendary K'iche' Mayan leader who refused to give way to the conquistadors in Guatemala and was slain by Pedro de Alvarado
Napuc Chi or Ah Kin Chi (died c. 1541), general-in-chief of the army and king of Tutul-Xiu, i. e. Maní
Gaspar Antonio Chi (c. 1531–1610), Maya noble from Maní, son of Napuc Chi
Jacinto Canek (c. 1731–1761), Maya revolutionary
Crescencio Poot (1820–1885), general in the Caste War of Yucatán
Felipe Carrillo Puerto (1874–1924), Mexican journalist and politician, governor of the Mexican state of Yucatán (1922–1924)
Andrés Curruchich (1891–1969), Guatemalan painter of the Kaqchikel people
Carlos Mérida (1891–1985), Spanish-K'iche' artist from Guatemala
Francisco Luna Kan (born 1925), Mexican politician, governor of Yucatán (1976–1982)
Armando Manzanero Canché (born 1935), Mexican musician, singer, and composer
Luis Rolando Ixquiac Xicara (born 1947), indigenous artist born in Quetzaltenango, Guatemala
Marcial Mes (c. 1949–2014), Belizean politician
Humberto Ak'ab'al (born 1952), K'iche' poet from Guatemala
Rosalina Tuyuc (born 1956), Guatemalan human rights activist
Rigoberta Menchú (born 1959), K'iche' political activist from Guatemala
Comandanta Ramona (1959–2006), ‘officer’ of the autonomist Zapatista Army of National Liberation
Juan Jose Pacho (born 1963), Mexican former baseball player and manager
Aníbal López (1964–2014), Guatemalan artist
Jesús Tecú Osorio (born 1971), Guatemalan social activist
Hilario Chi Canul (born 1981), Mexican linguist
Sara Curruchich (born 1993), Guatemalan singer, composer, and activist from the town of San Juan Comalapa
Quotes
This page is a candidate to be copied to Wikiquote using the Transwiki process. |
- "We are not myths of the past, ruins in the jungle or zoos. We are people and we want to be respected, not to be victims of intolerance and racism." – Rigoberta Menchú, 1992.[38]
Film and television
The Forgotten District, a documentary (2008) on Maya ecotourism in southern Belize, Central America
Mayan Renaissance, starring Rigoberta Menchú (2012)
Apocalypto, an adventure film (2006) directed and produced by Mel Gibson, set around the time of European contact with all of the dialogue spoken in Yucatec.[citation needed]
See also
- Muisca people
- Acala Ch'ol
- Chinamita
- Genetic history of indigenous peoples of the Americas
- Indigenous peoples of the Americas
- Kejache
- Lakandon Ch'ol
- List of Mayan languages
- Manche Ch'ol
References
^ ab Lorenzo Ochoa; Patricia Martel(dir.) (2002). Lengua y cultura mayas (in Spanish). UNAM. p. 170. ISBN 9703200893.El "Pueblo Maya" lo constituyen actualmente algo menos de 6 millones de hablantes de 25 idiomas
.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Nations, James D. (1 January 2010). The Maya Tropical Forest: People, Parks, and Ancient Cities. University of Texas Press. ISBN 978-0-292-77877-1.
^ Restall 2004, p. 67.
^ OSEA, Open School of Ethnography and Anthropology. "Maya or Mayans? On Correct Use of Terms". Retrieved 2 May 2011.
^ Castaneda, Quetzil (2004). "We Are Not Indigenous" (PDF). Journal of Latin American Anthropology. 9 (1): 36–63. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
[permanent dead link]
^ Ethnoexodus: Maya Topographic Ruptures. I09.cgpublisher.com (2009-06-05). Retrieved on 2014-04-27.
^ Castillo Cocom, Juan A. (2007). "Maya Scenarios" (PDF). Kroeber Papers. 96: 13–35.
^ ab Clendinnen, Inga (1989) Ambivalent Conquests: Maya and Spaniard in Yucatán, 1517–1570. p. 34.
ISBN 0-521-37981-4
^ Restall, Matthew (1998). Maya Conquistador. Boston, Massachusetts: Beacon. pp. xvi, 254.
^ Reed, Nelson (2002) The Caste War of Yucatán: Stanford University Press,
ISBN 0-8047-4001-1
^ El Universal, el periódico de México líder en noticias y clasificados. El-universal.com.mx. Retrieved on 2014-04-27.
^ Noticias Indemaya. Indemaya.gob.mx. Retrieved on 2014-04-27.
^ ab Bienvenidos / Welcome Archived 2008-09-16 at the Wayback Machine.. Yucatecos.org. Retrieved on 2014-04-27.
^ "Belize Mission Collection".
^ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 13 November 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2011.
^ Republica de Guatemala. inforpressca.com
^ Atran, Scott; Lois, Ximena; Ucan Ek', Edilberto (2004) Plants of the Peten Itza Maya, Memoirs of the Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan, 38
^ Brett, R.L. (2016). "The Origins and Dynamics of Genocide:Political Violence in Guatemala".
^ "Why you need to know about Guatemala's civil war". Public Radio International. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
^ "Operation Sofia: Documenting Genocide in Guatemala". nsarchive2.gwu.edu. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
^ "Genocide in Guatemala". www.hmh.org. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
^ "Justice in Guatemala". nsarchive2.gwu.edu. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
^ "Guatemala's Rios Montt found guilty of genocide". BBC News. 2013-05-11. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ "Guatemala's top court annuls Rios Montt genocide conviction". archive.is. 2013-06-16. Archived from the original on 2013-06-16. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ Agencies (2013-05-20). "Ríos Montt genocide case collapses". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ "Former Guatemala dictator faces genocide retrial". Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ Press, Associated (2015-08-25). "Guatemala court: former dictator can be tried for genocide – but not sentenced". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ Malkin, Elisabeth (2015-08-25). "Genocide Retrial Is Set for Guatemalan Former Dictator". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
^ "Efraín Ríos Montt, Guatemalan Dictator Convicted of Genocide, Dies at 91". The New York Times. 2018-04-01. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
^ "News". Orthodoxy Cognate PAGE. Archived from the original on 2015-12-11.
^ Akkeren 1999, pp. 281, 288.
^ Comaroff, John L.; Jean Comaroff (2010). "Ethnicity, Inc". Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
^ Stronza, Amanda (2001). "Anthropology of Tourism: Forging New Ground for Ecotourism and Other Alternatives". Annual Review of Anthropology. 30 (30): 261–83. doi:10.1146/annurev.anthro.30.1.261.
^ Lefebvre, Henri (1974). The Production of Space. London: Wiley-Blackwell.
^ Soper, Anne K.; Charles E. Greer; Daniel C. Knudsen (2008). "Mauritian Landscapes of Culture, Identity, and Tourism". Landscape, Tourism, and Meaning: 51–64.
^ Smith, Laurajane (2007). Cultural Heritage: Critical Concepts in Media and Cultural Studies. London: Routledge. p. 104.
^ Lyon, Sarah; E. Christian Wells (2012). "Ethnographies of Global Tourism: Cultural Heritage, Economic Encounters, and the Redefinition of Impact".
^ Quote taken from an interview with her by a representative of a Central American human rights organization (Riis-Hansen 1992). Menchú gave this interview shortly before she was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
Bibliography
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Akkeren, Ruud van (July 1999). "Sacrifice at the Maize Tree: Rab'inal Achi in its historical and symbolic context". Ancient Mesoamerica. New York: Cambridge University Press. 10 (2): 281–295. doi:10.1017/s0956536199102104. ISSN 0956-5361. OCLC 364022517.
(subscription required)
Chiappari, Christopher L. (2002). "Toward a Maya Theology of Liberation: The Reformulation of a "Traditional" Religion in the Global Context". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 41 (1): 47–67. doi:10.1111/1468-5906.00099.
Grube, Nikolai (2006). "Maya Today – From Indios Deprived of Rights to the Maya Movement". In Nikolai Grube (Ed.). Maya: Divine Kings of the Rain Forest. Eva Eggebrecht and Matthias Seidel (assistant Eds.). Cologne: Könemann Press. pp. 417–425. ISBN 3-8331-1957-8. OCLC 71165439.CS1 maint: Extra text: editors list (link)
- Mooney, James,
 Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Maya Indians". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Maya Indians". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- Restall, Matthew (1997). The Maya World. Yucatecan Culture and Society, 1550–1850. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
ISBN 978-0-8047-3658-9.
Riis-Hansen, Anders (1992). "Interview with Rigoberta Menchu Tum". Commission for the Defense of Human Rights in Central America (CODEHUCA). Retrieved 2006-07-03.
Warren, Kay B. (1998). Indigenous Movements and Their Critics: Pan-Maya Activism in Guatemala. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05882-5.
Further reading
Voss, Alexander (2006). "Astronomy and Mathematics". In Nikolai Grube (ed.). Maya: Divine Kings of the Rain Forest. Eva Eggebrecht and Matthias Seidel (assistant eds.). Cologne: Könemann. pp. 130–143. ISBN 3-8331-1957-8. OCLC 71165439.CS1 maint: Extra text: editors list (link)
Wagner, Elizabeth (2006). "Maya Creation Myths and Cosmography". In Nikolai Grube (ed.). Maya: Divine Kings of the Rain Forest. Eva Eggebrecht and Matthias Seidel (Assistant eds.). Cologne: Könemann. pp. 280–293. ISBN 3-8331-1957-8. OCLC 71165439.CS1 maint: Extra text: editors list (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maya peoples. |
