Seat belt

A woman buckling a three-point seat belt
A seat belt (also known as a seatbelt or safety belt) is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the occupant of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt functions to reduce the likelihood of death or serious injury in a traffic collision by reducing the force of secondary impacts with interior strike hazards, by keeping occupants positioned correctly for maximum effectiveness of the airbag (if equipped) and by preventing occupants being ejected from the vehicle in a crash or if the vehicle rolls over.
When in motion, the driver and passengers are travelling at the same speed as the car. If the driver makes the car suddenly stop or crashes it, the driver and passengers continue at the same speed the car was going before it stopped. A seatbelt applies an opposing force to the driver and passengers to prevent them from falling out or making contact with the interior of the car. Seatbelts are considered Primary Restraint Systems (PRS), because of their vital role in occupant safety.
Contents
1 Effectiveness
2 History
3 Types
3.1 Two-point
3.1.1 Lap
3.1.2 Sash
3.2 Three-point
3.2.1 Belt-in-Seat (BIS)
3.3 4-, 5-, and 6-point
3.4 Seven-point
4 Technology
4.1 Locking retractors
4.2 Pretensioners and webclamps
4.3 Inflatable
4.4 Automatic
4.4.1 Systems
4.4.2 Disadvantages
5 Homologation and testing
6 Experimental
7 In rear seats
8 Child occupants
9 Reminder chime and light
9.1 Efficacy
10 Legislation
10.1 Risk compensation
10.2 Increased traffic
11 Mass transit considerations
11.1 Buses
11.1.1 School buses
11.1.2 Motor coaches
11.2 Trains
11.3 Airplanes
12 See also
13 References
14 External links
Effectiveness
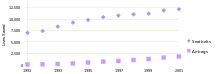
Lives saved by seat belts and airbags in the United States, 1991–2001
An analysis conducted in the United States in 1984 compared a variety of seat belt types alone and in combination with air bags.[1] The range of fatality reduction for front seat passengers was broad, from 20% to 55%, as was the range of major injury, from 25% to 60%.[1] More recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has summarized this data by stating "seat belts reduce serious crash-related injuries and deaths by about half."[2] Most seatbelt malfunctions are a result of there being too much slack in the seatbelt at the time of the accident.[3]
History
Seat belts were invented by English engineer George Cayley in the mid-19th century,[4] though Edward J. Claghorn of New York, was granted the first patent (U.S. Patent 312,085, on February 10, 1885 for a safety belt).[5] Claghorn was granted United States Patent #312,085 for a Safety-Belt for tourists, painters, firemen, etc. who are being raised or lowered, described in the patent as "designed to be applied to the person, and provided with hooks and other attachments for securing the person to a fixed object."
In 1946, Dr. C. Hunter Shelden opened a neurological practice at Huntington Memorial Hospital in Pasadena, California. In the early 1950s, Dr. Shelden made a major contribution to the automotive industry with his idea of retractable seat belts. This came about his from his care of the high number of head injuries coming through the emergency room.[6] He investigated the early seat belts whose primitive designs were implicated in these injuries and deaths. To reduce the high level of injuries he was seeing, he proposed, in late 1955, retractable seat belts, recessed steering wheels, reinforced roofs, roll bars, automatic door locks, and passive restraints such as the air bag.[7] Subsequently, in 1966, Congress passed the National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act requiring all automobiles to comply with certain safety standards.
American car manufacturers Nash (in 1949) and Ford (in 1955) offered seat belts as options, while Swedish Saab first introduced seat belts as standard in 1958.[8] After the Saab GT 750 was introduced at the New York Motor Show in 1958 with safety belts fitted as standard, the practice became commonplace.[9]
Glenn Sheren, of Mason, Michigan, submitted a patent application on March 31, 1955 for an automotive seat belt and was awarded US Patent 2,855,215 in 1958. This was a continuation of an earlier patent application that Mr. Sheren had filed on September 22, 1952.[10]
However, the first modern three point seat belt (the so-called CIR-Griswold restraint) used in most consumer vehicles today was patented in 1955 U.S. Patent 2,710,649 by the Americans Roger W. Griswold and Hugh DeHaven.
The Swedish national electric utility, did a study of all fatal, on-the-job accidents among their employees. The study revealed that the majority of fatalities occurred while the employees were on the road on company business. In response, two Vattenfall safety engineers, Bengt Odelgard and Per-Olof Weman, started to develop a seat belt. Their work was presented to Swedish manufacturer Volvo in the late 1950s, and set the standard for seat belts in Swedish cars.[11] The three-point seatbelt was developed to its modern form by Swedish inventor Nils Bohlin for Volvo—who introduced it in 1959 as standard equipment. In addition to designing an effective three-point belt, Bohlin demonstrated its effectiveness in a study of 28,000 accidents in Sweden. Unbelted occupants sustained fatal injuries throughout the whole speed scale, whereas none of the belted occupants were fatally injured at accident speeds below 60 mph. No belted occupant was fatally injured if the passenger compartment remained intact.[12] Bohlin was granted U.S. Patent 3,043,625 for the device.[8]
The world's first seat belt law was put in place in 1970, in the state of Victoria, Australia, making the wearing of a seat belt compulsory for drivers and front-seat passengers. This legislation was enacted after trialing Hemco seatbelts, designed by Desmond Hemphill (1926–2001), in the front seats of police vehicles, lowering the incidence of officer injury and death.[13]
Types
Two-point
A 2-point belt attaches at its two endpoints, and was invented in the early 1900s by Jack Swearingen of Louisville, Kentucky.[citation needed]
Lap

A lap ("2-point") belt in an airplane
A lap belt is a strap that goes over the waist. This was the most commonly installed type of belt prior to legislation requiring three-point belts, and is primarily found in older cars. Coaches are equipped with lap belts (although many newer coaches have three-point belts), as are passenger aircraft seats.
University of Minnesota Professor James J. (Crash) Ryan was the inventor of and held the patent on the automatic retractable lap safety belt. Ralph Nader cited Ryan's work in Unsafe at Any Speed and in 1966 President Lyndon Johnson signed two bills requiring safety belts in all passenger vehicles starting in 1968.[14]
Until the 1980s, three-point belts were commonly available only in the front outboard seats of cars; the back seats were only often fitted with lap belts. Evidence of the potential of lap belts to cause separation of the lumbar vertebrae and the sometimes associated paralysis, or "seat belt syndrome", led to progressive revision of passenger safety regulations in nearly all developed countries to require three-point belts first in all outboard seating positions and eventually in all seating positions in passenger vehicles. Since September 1, 2007, all new cars sold in the U.S. require a lap and shoulder belt in the center rear seat.[15]
Besides regulatory changes, "seat belt syndrome" has led to tremendous liability for vehicle manufacturers. One Los Angeles case resulted in a $45 million jury verdict against the Ford Motor Company; the resulting $30 million judgment (after deductions for another defendant who settled prior to trial) was affirmed on appeal in 2006.[16]
Sash

A seat belt and buckle
A "sash" or shoulder harness is a strap that goes diagonally over the vehicle occupant's outboard shoulder and is buckled inboard of his or her lap. The shoulder harness may attach to the lap belt tongue, or it may have a tongue and buckle completely separate from those of the lap belt. Shoulder harnesses of this separate or semi-separate type were installed in conjunction with lap belts in the outboard front seating positions of many vehicles in the North American market starting at the inception of the shoulder belt requirement of the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration's Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208 on 1 January 1968. However, if the shoulder strap is used without the lap belt, the vehicle occupant is likely to "submarine", or slide forward in the seat and out from under the belt, in a frontal collision. In the mid-1970s, three-point belt systems such as Chrysler's "Uni-Belt" began to supplant the separate lap and shoulder belts in American-made cars, though such three-point belts had already been supplied in European vehicles such as Volvos, Mercedes, and Saabs for some years.
Three-point

A three-point seat belt
A three-point belt is a Y-shaped arrangement, similar to the separate lap and sash belts, but unitized. Like the separate lap-and-sash belt, in a collision the three-point belt spreads out the energy of the moving body over the chest, pelvis, and shoulders. Volvo introduced the first production three-point belt in 1959.[17] The first car with a three-point belt was a Volvo PV 544 that was delivered to a dealer in Kristianstad on August 13, 1959. However, the first car model to feature the three-point seat belt as a standard item was the 1959 Volvo 122, first outfitted with a two-point belt at initial delivery in 1958, replaced with the three-point seat belt the following year.[18] The three-point belt was developed by Nils Bohlin who had earlier also worked on ejection seats at Saab.[19] Volvo then made the new seat belt design patent open in the interest of safety and made it available to other car manufacturers for free.[20][21]
Belt-in-Seat (BIS)
The BIS is a three-point harness with the shoulder belt attached to the seat itself, rather than to the vehicle structure. The first car using this system was the Range Rover Classic. Fitment was standard on the front seats from 1970.[22] Some cars like the Renault Vel Satis use this system for the front seats. A General Motors assessment concluded seat-mounted three-point belts offer better protection especially to smaller vehicle occupants,[23] though GM did not find a safety performance improvement in vehicles with seat-mounted belts versus belts mounted to the vehicle body.[24]
BIS type belts have been used by automakers in convertibles and pillarless hardtops, where there is no "B" pillar to affix the upper mount of the belt. Chrysler and Cadillac are well known for using this design. Antique auto enthusiasts sometimes replace original seats in their cars with BIS-equipped front seats, providing a measure of safety not available when these cars were new. However, modern BIS systems typically use electronics that must be installed and connected with the seats and the vehicle's electrical system in order to function properly.[citation needed]
4-, 5-, and 6-point

Bucket seat combined with a Schroth 6-point harness
Five-point harnesses are typically found in child safety seats and in racing cars. The lap portion is connected to a belt between the legs and there are two shoulder belts, making a total of five points of attachment to the seat. A 4-point harness is similar, but without the strap between the legs, while a 6-point harness has two belts between the legs. In NASCAR, the 6-point harness became popular after the death of Dale Earnhardt, who was wearing a five-point harness when he suffered his fatal crash; as it was first thought that his belt had broken, and broke his neck at impact, some teams ordered a six-point harness in response.[25]
Seven-point
Aerobatic aircraft frequently use a combination harness consisting of a five-point harness with a redundant lap-belt attached to a different part of the aircraft. While providing redundancy for negative-g manoeuvres (which lift the pilot out of the seat); they also require the pilot to un-latch two harnesses if it is necessary to parachute from a failed aircraft.
Technology

Seat belt with uncovered inertial reel
Locking retractors
The purpose of locking retractors is to provide the seated occupant the convenience of some free movement of the upper torso within the compartment, while providing a method of limiting this movement in the event of a crash. Most modern seat belts are stowed on spring-loaded reels called "retractors" equipped with inertial locking mechanisms that stop the belt from extending off the reel during severe deceleration. There are two main types of inertial seat belt lock. A webbing-sensitive lock is based on a centrifugal clutch activated by rapid acceleration of the strap (webbing) from the reel. The belt can be pulled from the reel only slowly and gradually, as when the occupant extends the belt to fasten it. A sudden rapid pull of the belt—as in a sudden braking or collision event—causes the reel to lock, restraining the occupant in position.
A vehicle-sensitive lock is based on a pendulum swung away from its plumb position by rapid deceleration or rollover of the vehicle. In the absence of rapid deceleration or rollover, the reel is unlocked and the belt strap may be pulled from the reel against the spring tension of the reel. The vehicle occupant can move around with relative freedom while the spring tension of the reel keeps the belt taut against the occupant. When the pendulum swings away from its normal plumb position due to sudden deceleration or rollover, a pawl is engaged, the reel locks and the strap restrains the belted occupant in position. Dual-sensing locking retractors use both vehicle G-loading and webbing payout rate to initiate the locking mechanism.
Pretensioners and webclamps

Pyrotechnic pretensioner diagram
Seatbelts in many newer vehicles are also equipped with "pretensioners" or "web clamps", or both.
Pretensioners preemptively tighten the belt to prevent the occupant from jerking forward in a crash. Mercedes-Benz first introduced pretensioners on the 1981 S-Class. In the event of a crash, a pretensioner will tighten the belt almost instantaneously. This reduces the motion of the occupant in a violent crash. Like airbags, pretensioners are triggered by sensors in the car's body, and many pretensioners have used explosively expanding gas to drive a piston that retracts the belt. Pretensioners also lower the risk of "submarining", which occurs when a passenger slides forward under a loosely fitted seat belt.
Some systems also pre-emptively tighten the belt during fast accelerations and strong decelerations, even if no crash has happened. This has the advantage that it may help prevent the driver from sliding out of position during violent evasive maneuvers, which could cause loss of control of the vehicle. These pre-emptive safety systems may prevent some collisions from happening, as well as reducing injury in the event an actual collision occurs.[26] Pre-emptive systems generally use electric pretensioners which can operate repeatedly and for a sustained period, rather than pyrotechnic pretensioners, which can only operate a single time.
Webclamps clamp the webbing in the event of an accident, and limit the distance the webbing can spool out (caused by the unused webbing tightening on the central drum of the mechanism). These belts also often incorporate an energy management loop ("rip stitching") in which a section of the webbing is looped and stitched with a special stitching. The function of this is to "rip" at a predetermined load, which reduces the maximum force transmitted through the belt to the occupant during a violent collision, reducing injuries to the occupant.
A study demonstrated that standard automotive three-point restraints fitted with pyrotechnic or electric pretensioners were not able to eliminate all interior passenger compartment head strikes in rollover test conditions.[27] Electric pretensioners are often incorporated on vehicles equipped with precrash systems; they are designed to reduce seat belt slack in a potential collision and assist in placing the occupants in a more optimal seating position.[28] The electric pretensioners also can operate on a repeated or sustained basis, providing better protection in the event of an extended rollover or a multiple collision accident.
Inflatable
The inflatable seatbelt was invented by Donald Lewis and tested at the Automotive Products Division of Allied Chemical Corporation.[29] Inflatable seatbelts have tubular inflatable bladders contained within an outer cover. When a crash occurs the bladder inflates with a gas to increase the area of the restraint contacting the occupant and also shortening the length of the restraint to tighten the belt around the occupant, improving the protection.[30] The inflatable sections may be shoulder-only or lap and shoulder. The system supports the head during the crash better than a web only belt. It also provides side impact protection. In 2013, Ford began offering rear seat inflatable seat belts on a limited set of models, such as the Explorer and Flex.[31]
Automatic

Automatic seat belt in a Honda Civic
Seatbelts that automatically move into position around a vehicle occupant once the adjacent door is closed and/or the engine is started were developed as a countermeasure against low usage rates of manual seat belts, particularly in the United States.
The 1972 Volkswagen ESVW1 Experimental Safety Vehicle presented passive seat belts.[32]Volvo tried to develop a passive three point seatbelt. In 1973, Volkswagen announced they had a functional passive seat belt.[33] The first commercial car to use automatic seat belts was the 1975 Volkswagen Golf.[34]
Automatic seat belts received a boost in the United States in 1977 when Brock Adams, United States Secretary of Transportation in the Carter Administration, mandated that by 1983 every new car should have either airbags or automatic seat belts.[35][36] There was strong lobbying against the passive restraint requirement by the auto industry.[37] Adams was criticized by Ralph Nader, who said that the 1983 deadline was too late.[38] The VW Rabbit also offered this safety feature.[38] By early 1978, Volkswagen had reported 90,000 Rabbits sold with automatic seat belts.[34]
General Motors introduced a three-point non-motorized passive belt system in 1980 to comply with the passive restraint requirement.[39] However, it was used as an active lap-shoulder belt because of unlatching the belt to exit the vehicle.[39] Despite this common practice, field studies of belt use still showed an increase in wearing rates with this door-mounted system.[39]General Motors began offering automatic seat belts on the Chevrolet Chevette.[40][41] However, the company reported disappointing sales because of this feature.[42]
A study released in 1978 by the United States Department of Transportation claimed that cars with automatic seat belts had a fatality rate of .78 per 100 million miles, compared with 2.34 for cars with regular, manual belts.[43]
In 1981, Drew Lewis, the first Transportation Secretary of the Reagan Administration, influenced by studies done by the auto industry,[44] dropped the mandate;[45] the decision was overruled in a federal appeals court the following year,[46] and then by the Supreme Court.[47] In 1984, the Reagan Administration reversed its course,[48] though in the meantime the original deadline had been extended; Elizabeth Dole, then Transportation Secretary, proposed that the two passive safety restraints be phased into vehicles gradually, from vehicle model year 1987 to vehicle model year 1990, when all vehicles would be required to have either automatic seat belts or driver side air bags.[47] Though more awkward for vehicle occupants, most manufacturers opted to use less expensive automatic belts rather than airbags during this time period.
When driver side airbags became mandatory on all passenger vehicles in model year 1995, most manufacturers stopped equipping cars with automatic seat belts. Exceptions include the 1995–96 Ford Escort/Mercury Tracer and the Eagle Summit Wagon, which had automatic safety belts along with dual airbags.[citation needed]
Systems
Manual lap belt with automatic motorized shoulder belt—When the door is opened, the shoulder belt moves from a fixed point near the seat back on a track mounted in the door frame of the car to a point at the other end of the track near the windshield. Once the door is closed and the car is started, the belt moves rearward along the track to its original position, thus securing the passenger. The lap belt must be fastened manually.
Manual lap belt with automatic non-motorized shoulder belt—This system was used in American-market vehicles such as the Hyundai Excel and Volkswagen Jetta. The shoulder belt is fixed to the aft upper corner of the vehicle door, and is not motorized. The lap belt must be fastened manually.
Automatic shoulder and lap belts—This system was mainly used in General Motors vehicles, though it was also used on some Honda Civic hatchbacks and Nissan Sentra coupés. When the door is opened, the belts go from a fixed point in the middle of the car by the floor to retractors on the door. Passengers must slide into the car under the belts. When the door closes, the seat belt retracts into the door. The belts have normal release buttons that are supposed to be used only in an emergency, but in practice are routinely used in the same manner as manual seat belt clasps.[citation needed] This system also found use by American Specialty Cars when they created the 1991-1994 convertible special edition of the Nissan 240SX, a car that traditionally had a motorized shoulder belt.
Disadvantages
Automatic belt systems generally offer inferior occupant crash protection.[49][50] In systems with belts attached to the door rather than a sturdier fixed portion of the vehicle body, a crash that causes the vehicle door to open leaves the occupant without belt protection. In such a scenario, the occupant may be thrown from the vehicle and suffer greater injury or death.[50]
Because many automatic belt system designs compliant with the US passive-restraint mandate did not meet the safety performance requirements of Canada—which were not weakened to accommodate automatic belts—vehicle models which had been eligible for easy importation in either direction across the US-Canada border when equipped with manual belts became ineligible for importation in either direction once the U.S. variants obtained automatic belts and the Canadian versions retained manual belts. Two particular models included the Dodge Spirit and Plymouth Acclaim.[51][52]
Automatic belt systems also present several operational disadvantages. Motorists who would normally wear seat belts must still fasten the manual lap belt, thus rendering redundant the automation of the shoulder belt. Those who do not fasten the lap belt wind up inadequately protected only by the shoulder belt; in a crash without a lap belt such a vehicle occupant is likely to "submarine" (be thrown forward under the shoulder belt) and be seriously injured. Motorized or door-affixed shoulder belts hinder access to the vehicle, making it difficult to enter and exit—particularly if the occupant is carrying items such as a box or a purse. Vehicle owners tend to disconnect the motorized or door-affixed shoulder belt to relieve the nuisance of entering and exiting the vehicle, leaving only a lap belt for crash protection. Also, many automatic seat belt systems are incompatible with child safety seats, or only compatible with special modifications.
Homologation and testing
Starting in 1971 and ending in 1972, the United States conducted a research project on seat belt effectiveness on a total of 40,000 vehicle occupants using car accident reports collected during that time. Of these 40,000 occupants, 18% were reported wearing lap belts, or two-point safety belts, 2% were reported wearing a three-point safety belt, and the remaining 80% were reported as wearing no safety belt. The results concluded that users of the two-point lap belt had a 73% lower fatality rate, a 53% lower serious injury rate, and a 38% lower injury rate than the occupants that were reported unrestrained. Similarly, users of the three-point safety belt had a 60% lower serious injury rate and a 41% lower rate of all other injuries. Out of the 2% described as wearing a three-point safety belt, no fatalities were reported.[53]
This study and others led to the Restraint Systems Evaluation Program (RSEP), started by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration in 1975 to increase the reliability and authenticity of past studies. A study as part of this program used data taken from 15,000 tow-away accidents that involved only car models made between 1973 and 1975. The study found that for injuries considered “moderate” or worse, individuals wearing a three-point safety belt had a 56.5% lower injury rate than those wearing no safety belt. The study also concluded that the effectiveness of the safety belt did not differ with size of car.[53] It was determined that the variation among results of the many studies conducted in the 1960s and 70s was due to the use of different methodologies, and could not be attributed to any significant variation in the effectiveness of safety belts.[54]
Wayne State University’s Automotive Safety Research Group, as well as other researchers,[55] are testing ways to improve seat belt effectiveness and general vehicle safety apparatuses. Wayne State’s Bioengineering Center uses human cadavers in their crash test research. The Center’s director, Albert King, wrote in 1995 that the vehicle safety improvements made possible since 1987 by the use of cadavers in research had saved nearly 8,500 lives each year, and indicated that improvements made to three-point safety belts save an average of 61 lives every year.[56]
The New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) was put in place by the United States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration in 1979. The NCAP is a government program that evaluates vehicle safety designs and sets standards for foreign and domestic automobile companies. The agency developed a rating system and requires access to safety test results. As of September 2007[update], manufacturers are required to place a NCAP star rating on the automobile price sticker.[57]
Experimental
Research and development efforts are ongoing to improve the safety performance of vehicle seatbelts. Some experimental designs include:
Criss-cross Experimental safety belt presented in the Volvo SCC. It forms a cross-brace across the chest.[24]
3+2 Point Seatbelt: Experimental safety belt from Autoliv similar to the criss-cross. The 3+2 improves protection against rollovers and side impacts.[58]
Four point "belt and suspenders": An experimental design from Ford where the "suspenders" are attached to the backrest, not to the frame of the car.[59]
- 3 point Adjustable Seatbelt: Experimental safety belt from GWR Safety Systems that allowed the car Hiriko, designed by MIT, to fold without compromising the safety and comfort of the occupants.[60]
In rear seats
In 1955 (as a 1956 package), Ford offered lap only seat belts in the rear seats as an option within the Lifeguard safety package. In 1967, Volvo started to install lap belts in the rear seats. In 1972, Volvo upgraded the rear seat belts to a three-point belt.[61]
In crashes, unbelted rear passengers increase the risk of belted front seat occupants' death by nearly five times.[62][63]
Child occupants
As with adult drivers and passengers, the advent of seat belts was accompanied by calls for their use by child occupants, including legislation requiring such use. Generally children using adult seat belts suffer significantly lower injury risk when compared to non-buckled children.
The UK extended compulsory seatbelt wearing to child passengers under the age of 14 in 1989. It was observed that this measure was accompanied by a 10% increase in fatalities and a 12% increase in injuries among the target population.[64] In crashes, small children who wear adult seatbelts can suffer "seat-belt syndrome" injuries including severed intestines, ruptured diaphragms and spinal damage. There is also research suggesting that children in inappropriate restraints are at significantly increased risk of head injury,[65] one of the authors of this research has been quoted as claiming that: "The early graduation of kids into adult lap and shoulder belts is a leading cause of child-occupant injuries and deaths."[66]
As a result of such findings, many jurisdictions now advocate or require child passengers to use specially designed child restraints. Such systems include separate child-sized seats with their own restraints and booster cushions for children using adult restraints. In some jurisdictions children below a certain size are forbidden to travel in front car seats."[67]
Reminder chime and light

Examples of warning lights on a car dashboard.
In Europe, the US, and some other parts of the world, most modern cars include a seat-belt reminder light for the driver and some also include a reminder for the passenger, when present, activated by a pressure sensor under the passenger seat. Some cars will intermittently flash the reminder light and sound the chime until the driver (and sometimes the front passenger, if present) fasten their seatbelts.[68]
In 2005, in Sweden, 70% of all cars that were newly registered were equipped with seat belt reminders for the driver.[69]
Since November 2014, seat belt reminders are mandatory for the driver's seat on new cars sold in Europe.[70]
Two specifications define the standard of seat belt reminder: UN Regulation 16, Section 8.4 and the Euro NCAP assessment protocol (Euro NCAP, 2013).[70]
In North America, cars sold since the early 1970s[vague] have included an audiovisual reminder system consisting of a tell-tale light on the dashboard and a buzzer or chime reminding the driver and passengers to fasten their belts. Originally, these lights were accompanied by a warning buzzer whenever the transmission was in any position except park[clarification needed] if either the driver was not buckled up or, as determined by a pressure sensor in the passenger's seat, if there was a passenger there not buckled up.[citation needed] However, this was considered by many to be a major annoyance, as the light would be on and the buzzer would sound continuously if front-seat passengers were not buckled up. Therefore, people who did not wish to buckle up would defeat this system by fastening the seat belts with the seat empty and leaving them that way.[citation needed]
To combat this dangerous habit, in 1971[citation needed] NHTSA amended Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard № 208 (FMVSS 208) to require a seat belt/starter interlock system to prevent passenger cars from being started with an unbelted front-seat occupant. This mandate applied to passenger cars built after August 1973, i.e., starting with the 1974 model year. The specifications required the system to permit the car to be started only if the belt of an occupied seat were fastened after the occupant sat down, so pre-buckling the belts would not defeat the system.[71][72]
The interlock systems used logic modules complex enough to require special diagnostic computers, and were not entirely dependable—an override button was provided under the hood of equipped cars, permitting one (but only one) "free" starting attempt each time it was pressed.[73] However, the interlock system spurred severe backlash from an American public who largely rejected seat belts. In 1974, Congress acted to prohibit NHTSA from requiring or permitting a system that prevents a vehicle from starting or operating with an unbelted occupant, or that gives an audible warning of an unfastened belt for more than 8 seconds after the ignition is turned on.[72] This prohibition took effect on 27 October 1974, shortly after the 1975 model year began.[74]
In response to the Congressional action, NHTSA once again amended FMVSS 208, requiring vehicles to come with a seat belt reminder system that gives an audible signal for 4 to 8 seconds and a warning light for at least 60 seconds after the ignition is turned on if the driver's seat belt is not fastened.[72] This is called a seat belt reminder (SBR) system. In the mid-1990s, an insurance company from Sweden called Folksam worked with Saab and Ford to determine the requirements for the most efficient seat belt reminder. One characteristic of the optimal SBR, according to the research, is that the audible warning becomes increasingly penetrating the longer the seat belt remains unfastened.[75]
In 2003, the Transportation Research Board Committee, chaired by two psychologists, reported that ESBRs could save an additional 1,000 lives a year.[76] Research by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety found that Ford's ESBR, which provides an intermittent chime for up to five minutes if the driver is unbelted, sounding for 6 seconds then pausing for 30, increased seat belt use by 5 percentage points.[76] Farmer and Wells found that driver fatality rates were 6% lower for vehicles with ESBR compared with otherwise-identical vehicles without.[77]
Efficacy
In 2001, Congress directed NHSTA to study the benefits of technology meant to increase the use of seat belts. NHSTA found that seat belt usage had increased to 73% since the initial introduction of the SBR system.[72] In 2002, Ford demonstrated that seat belts were used more in Fords with seat belt reminders than in those without: 76% and 71% respectively. In 2007, Honda conducted a similar study and found that 90% of people who drove Hondas with seat belt reminders used a seat belt, while 84% of people who drove Hondas without seat belt reminders used a seat belt.[75]
Legislation
Observational studies of car crash morbidity and mortality,[78][79][80]experiments using both crash test dummies and human cadavers indicate that wearing seat belts greatly reduces the risk of death and injury in the majority of car crashes.
This has led many countries to adopt mandatory seat belt wearing laws. It is generally accepted that, in comparing like-for-like accidents, a vehicle occupant not wearing a properly fitted seat belt has a significantly and substantially higher chance of death and serious injury. One large observation studying using US data showed that the odds ratio of crash death is 0.46 with a three-point belt, when compared with no belt.[81] In another study that examined injuries presenting to the ER pre- and post-seat belt law introduction, it was found that 40% more escaped injury and 35% more escaped mild and moderate injuries.[82]
The effects of seat belt laws are disputed by those who observe that their passage did not reduce road fatalities. There was also concern that instead of legislating for a general protection standard for vehicle occupants, laws that required a particular technical approach would rapidly become dated as motor manufacturers would tool up for a particular standard which could not easily be changed. For example, in 1969 there were competing designs for lap and three-point seat belts, rapidly tilting seats, and airbags being developed. But as countries started to mandate seat belt restraints the global auto industry invested in the tooling and standardized exclusively on seat belts, and ignored other restraint designs such as air bags for several decades[83]
As of 2016, seat belt laws can be divided into two categories: primary and secondary. A primary seat belt law allows an officer to issue a citation for lack of seatbelt use without any other citation, whereas a secondary seat belt law allows an officer to issue a seat belt citation only in the presence of a different violation. In the United States, fifteen states enforce secondary laws, while 34 states, as well as the District of Columbia, American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands, enforce primary seat belt laws. New Hampshire lacks both a primary and secondary seat belt law.[84]
Risk compensation
Some have proposed that the number of deaths was influenced by the development of risk compensation, which says that drivers adjust their behavior in response to the increased sense of personal safety wearing a seat belt provides.
In one trial subjects were asked to drive go-karts around a track under various conditions. It was found that subjects who started driving unbelted drove consistently faster when subsequently belted.[85] Similarly, a study of habitual non-seatbelt wearers driving in freeway conditions found evidence that they had adapted to seatbelt use by adopting higher driving speeds and closer following distances.[86]
A 2001 analysis of US crash data aimed to establish the effects of seatbelt legislation on driving fatalities[87] and found that previous estimates of seatbelts effectiveness had been significantly overstated. According to the analysis used, seatbelts were claimed to have decreased fatalities by 1.35% for each 10% increase in seatbelt use. The study controlled for endogenous motivations of seat belt use, which it is claimed creates an artificial correlation between seat belt use and fatalities, leading to the conclusion that seatbelts cause fatalities. For example, drivers in high risk areas are more likely to use seat belts, and are more likely to be in accidents, creating a non-causal correlation between seatbelt use and mortality. After accounting for the endogeneity of seatbelt usage, Cohen and Einav found no evidence that the risk compensation effect makes seatbelt wearing drivers more dangerous, a finding at variance with other research.
Increased traffic
Other statistical analyses have included adjustments for factors such as increased traffic, and other factors such as age, and based on these adjustments, a reduction of morbidity and mortality due to seat belt use has been claimed.[78] However, Smeed's law predicts a fall in accident rate with increasing car ownership and has been demonstrated independently of seat belt legislation.
Mass transit considerations
Buses
School buses

In Mainland China, a majority of bus drivers are asked to wear seat belts
In the US, six states—California, Florida, Louisiana, New Jersey, New York, and Texas—require seat belts on school buses.[88]
Pros[89][90][91] and cons[92][93][94] had been alleged about the use of seatbelts in school buses.
School buses which are much bigger in size than the average vehicle allow for the mass transportation of students from place to place. The American School Bus Council states in a brief article saying that, “The children are protected like eggs in an egg carton – compartmentalized, and surrounded with padding and structural integrity to secure the entire container.” (ASBC). Although school buses are considered safe for mass transit of students this will not guarantee that the students will be injury free if an impact were to occur. Seatbelts in buses are sometimes believed to make recovering from a roll or tip harder for students and staff as they could be easily trapped in their own safety belt.[95]
In 2015, for the first time, NHTSA endorsed seat belts on school buses.[96]
Motor coaches
In the European Union, all new long distance buses and coaches must be fitted with seat belts.[97]
Australia has required lap/sash seat belts in new coaches since 1994. These must comply with Australian Design Rule 68, which requires the seat belt, seat and seat anchorage to withstand 20g deceleration and an impact by an unrestrained occupant to the rear.[98]
In the United States, NHTSA has now required lap-shoulder seat belts in new "over-the-road" buses (includes most coaches) starting in 2016.[99]
Trains
The use of seatbelts in trains has been investigated. Concerns about survival space intrusion in train crashes and increased injuries to unrestrained or incorrectly restrained passengers led the researchers to discourage the use of seat belts in trains.
- "It has been shown that there is no net safety benefit for passengers who choose to wear 3-point restraints on passenger carrying rail vehicles. Generally passengers who choose not to wear restraints in a vehicle modified to accept 3-point restraints receive marginally more severe injuries."[100]
Airplanes
Lap belts are found on all passenger aircraft. Many civil aviation authorities require a "fasten seat belt" sign in passenger aircraft that can be activated by a pilot during takeoff, turbulence, and landing.[101][102] The International Civil Aviation Organization recommends the use of child restraints.[103]
See also
- Automobile safety
- Baby transport
- Crashworthiness
- Passive safety device
- Seat belt use rates by country
References
^ ab National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Plans and Programs, Office of Planning and Analysis (11 July 1984). Passenger Car Front Seat Occupant Protection (PDF) (Report). p. IV-2. Retrieved 2016-02-14.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link) .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Seat Belts: Get the Facts". Motor Vehicle Safety. Centers for Disease Control. 20 August 2015. Retrieved 2016-02-15.
^ "Clearwater Car Accident Injuries | Whiplash Injuries". Clearwater Injury Lawyer. Retrieved 2016-11-02.
^ Manby, Frederic (24 August 2009). "Clunk, click – an invention that's saved lives for 50 years". Yorkshire Post. Johnston Press Digital Publishing. Retrieved 2010-12-04.
^ Andréasson, Rune; Claes-Göran Bäckström (2000). The Seat Belt : Swedish Research and Development for Global Automotive Safety. Stockholm: Kulturvårdskommittén Vattenfall AB. p. 12. ISBN 91-630-9389-8.
^ "HMRI News". Hmri.org. Archived from the original on February 26, 2011. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ C. Hunter Shelden, M.D., (November 5, 1955). "Prevention, the only cure for head injuries resulting from automobile accidents". Journal of the American Medical Association. 159 (10): 981–6. doi:10.1001/jama.1955.02960270001001. PMID 13263134.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ ab "The man who saved a million lives: Nils Bohlin - inventor of the seat belt - Features, Gadgets & Tech". The Independent. 2009-08-19. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
^ "Trollhattan Saab—Saab 9-1, 9-3, 9-4x, 9-5, 9-7x News". Trollhattansaab.net. Archived from the original on 2011-02-27. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "Automobile safety belt system - Patent 2855215". Freepatentsonline.com. 1958-10-07. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ Andréasson, Rune; Claes-Göran Bäckström (2000). The Seat Belt : Swedish Research and Development for Global Automotive Safety. Stockholm: Kulturvårdskommittén Vattenfall AB. pp. 9, 15–16. ISBN 91-630-9389-8.
^ Nils I. Bohlin, (1967). A Statistical Analysis of 28,000 Accidents with Emphasis on Occupant Restraint Value,. 11th Stapp Car Crash Conference. Society of Automotive Engineers. doi:10.4271/670925. SAE Technical Paper 670925.
^ "A Potted Seat Belt History". Drivers Technology.
^ SEE"Crash" Was His Name; Car Safety Was His Game" in Minnesota Medicine http://www.minnesotamedicine.com/Past-Issues/Past-Issues-2006/May-2006/Pulse-Crash-May-2006
^ "Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards; Occupant Crash Protection. Final Rule". Nhtsa.dot.gov. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ Karlsson v. Ford Motor Co., 140 Cal. App. 4th 1202 (2006).
^ "Volvo Cars airbag celebrates 20 years". Volvoclub.org.uk. 2007-05-26. Retrieved 2009-08-29.
^ Lindh, Björn Erik (1986). "The Amazon/120 - Beauty with Brown". Volvo The Cars from the 20s to the 80s. Förlagshuset Norden AB, Malmö. p. 134. ISBN 91-86442-14-7.p134: "The 1959 model (which appeared in August 1958) featured a major innovation in the form of front seat safety belts as standard equipment on all the cars, including the export models. Volvo was the world's first automaker to take this step, even though Ford fitted a "lap" belt on one or other of its cars in the middle of the 50s."
^ "Allt om Motor: Trepunktsbältet 50 år". Alltommotor.se. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ Three-point seatbelt inventor Nils Bohlin born, History Channel
^ Volvo's Three-Point Safety Belt Celebrates 50 Years of Saving Lives, The Auto Channel
^ Lankard, Tom. "''The first seat offered in the U.S. that incorporated a three-point belt—on the 1990 Mercedes-Benz SL—''". Editorial.autos.msn.com. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "Up Close: Seatbelt safety in question"— KHOU News, 20 June 2003[dead link]
^ ab "In Search of the Perfect Seat Belt". Archived from the original on 2014-07-27.
^ "Earnhardt's death a watershed moment". Sports.espn.go.com. 2011-02-07. Retrieved 2013-09-30.
^ Ito, Daisuke; Ejima, Susumu; Sukegawa, Yoshihiro; Antona, Jacobo; Ito, Hisao. "Assessment of a Pre-Crash Technology in Frontal Impacts by Using a New Crash Test Sled System with Controllable Pre-Impact Braking" (PDF). National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-05-06. Retrieved 2014-06-06.
^ "Microsoft Word - 2007-01-0709.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-04-08. Retrieved 2013-09-30.
^ "Active Seatbelts". Autoliv.com. Retrieved 2013-09-30.
^ US 3841654
^ Silke, Sharon (2009-11-06). "Ford says inflatable seat belt improves safety, comfort, too". USA Today. usatoday.com. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ "Cool features you can buy now". Consumer Reports (paper). April 2013. p. 9.
^ "Experimental Safety Vehicle". Classicvw.org. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "Safety Sells: Chapter 3" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-27. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ ab "Passive-Belt Activity". The New York Times. 1978-03-26.
^ "Airbags, seat belts to be mandatory in every car by 1983". Daily Collegian. Penn State. 1977-07-01. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ "Air Bags, Automatic Seat Belts". The Los Angeles Times. 1977-10-04.
^ Stevens, William K. (1977-07-01). "Auto Industry Expresses Reluctance, Resignation Over Air Bag Mandate". The New York Times. p. 18. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ ab Haic, Marty (1979-02-23). "Crusade Continues, But The Intensity Has Mellowed". Boca Raton News. p. 8C. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ abc "Buckling Up: Technologies to Increase Seat Belt Use" (PDF). Transportation Research Board. 2004: 48. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
^ "GM Offers Automatic Seat Belts". Chicago Tribune. 1978-06-27. p. 8.
^ "GM's Automatic Seat Belts Go on Chevettes". The Los Angeles Times. 1978-06-27.
^ "Sales of Automatic Seat Belts Disappointing, Chevrolet Says". Toledo Blade. 1979-02-23. p. 1. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ Girard, Penny (1978-08-31). "Study Finds Automatic Seat Belts, Airbags Save Lives". St. Petersburg Times. p. 1. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ Brody, Jane E. (1981-12-09). "Personal Health". The New York Times. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ "Automatic seat belt, airbag rules dropped". Chicago Tribune. 1981-10-24. p. 1.
^ "Automatic seat belts ordered". Spokane Chronicle. 1982-08-04. p. 28. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ ab "Middle Lane: Bags, Belts, and a Loophole". Time. 1984-07-23. Archived from the original on October 29, 2010. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
^ "US to require airbags or automatic seat belts". Chicago Tribune. 1984-07-11. p. 1.
^ "Chrysler Doubts Air-Bag Claims". The Montreal Gazette. Associated Press. 1977-09-30. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
^ ab Abeles, Ethan (1998). "The Ability of Automakers to Introduce a Costly, Regulated New Technology: A Case Study of Automotive Airbags in the U.S. Light-Duty Vehicle Market". Master's Thesis. Archived from the original on 2010-06-12. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
^ "Canadian vehicle importation regulations". Riv.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "US vehicle importation regulations". Nhtsa.dot.gov. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ ab "Road Safety Observatory". Retrieved 25 March 2016.
^ Robertson, L.S. (1976). "Estimates of Motor Vehicle Seat Belt Effectiveness and Use: Implications for Occupant Crash Protection". American Journal of Public Health. 66 (9): 859–864. doi:10.2105/ajph.66.9.859. PMC 1653464.
^ "Automotive Safety Research Group-Office of the Vice President for Research- Division of Research". Retrieved 25 March 2016.
^ Roach, Mary (2003). Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers. New York: W.W. Norton & Co.|access-date=requires|url=(help)
^ "New Car Assessment Program (NCAP)". Retrieved 25 March 2016.
^ "''3+2 Point Seatbelt and Side-Support Airbag''". Web.archive.org. 2008-05-13. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved 2013-09-30.
^ "''Ford researches possible next-generation safety belt technology''". Media.ford.com. 2007-12-29. Archived from the original on 2013-07-29. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "Case Studies - Seat Belt Manufacturers - GWR Safety Systems". GWR Company - Seatbelt Manufacture. Retrieved 2016-02-26.
^ Volvocars corporate website Archived May 3, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
^ Ichikawa M, Nakahara S, Wakai S; Nakahara; Wakai (January 2002). "Mortality of front-seat occupants attributable to unbelted rear-seat passengers in car crashes". Lancet. 359 (9300): 43–4. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07279-3. PMID 11809187.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Derbyshire, David (2002-01-04). "''"Unbelted rear passengers 'biggest danger in crash"''". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-08-31.
^ Adams, John (1995). Risk. London: UCL Press Ltd. University College. ISBN 1-85728-068-7.
^ Winston FK, Durbin DR, Kallan MJ, Moll EK; Durbin; Kallan; Moll (June 2000). "The danger of premature graduation to seat belts for young children". Pediatrics. 105 (6): 1179–83. doi:10.1542/peds.105.6.1179. PMID 10835054.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ "Kids at Risk: When Seatbelts are NOT Enough", by Karp H, Reader's Digest (US Edition), November 1999.
^ Road Amendment (Isabelle Broadhead Child Restraint Measures) Rules 2010. No. 46. Rule 1. "New South Wales Government on NSW legislation website" (PDF). NSW Government.
^ "Seat Belts Technology - RoSPA". www.rospa.com. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
^
http://etsc.eu/wp-content/uploads/ETSC_Seat_belt_reminder_oct_06.pdf
^ ab http://www.brake.org.uk/facts-resources/1631-seat-belt-reminders
^ Chrysler Master Technician Service Conference Session - 1974, Volume 74-1 Seat Belt Starter Interlock. 6 April 2012 – via YouTube.
^ abcd Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards; Occupant Crash Protection. (2010). Retrieved from https://www.federalregister.gov/articles/2010/06/29/2010-15773/federal-motor-vehicle-safety-standards-occupant-crash-protection#table_of_contents
^ Petersen Publishing (1975). "Restraint Systems". In Erwin M. Rosen. The Petersen Automotive Troubleshooting & Repair Manual. New York, NY: Grosset & Dunlap. pp. 373–4. ISBN 0-448-11946-3.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ "U.S.C. 30124 - TRANSPORTATION".
^ ab SWOV Fact sheet. (2014). Retrieved from "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-06-17. Retrieved 2015-04-29.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ ab Dingfelder, S. F. (2003). Your car says: ‘buckle up’. Monitor on Psychology. 34(11). Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/monitor/dec03/seatbelt.aspx
^ Farmer C. M.; Wells J. K. (2010). "Effect of enhanced seat belt reminders on driver fatality risk". Journal of Safety Research. 41: 53–57. doi:10.1016/j.jsr.2009.11.001. PMID 20226951.
^ ab Nakahara S, Ichikawa M, Wakai S; Ichikawa; Wakai (2003). "Seatbelt legislation in Japan: high risk driver mortality and seatbelt use". Inj. Prev. 9 (1): 29–32. doi:10.1136/ip.9.1.29. PMC 1730910. PMID 12642555.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Allen S, Zhu S, Sauter C, Layde P, Hargarten S; Zhu; Sauter; Layde; Hargarten (2006). "A comprehensive statewide analysis of seatbelt non-use with injury and hospital admissions: new data, old problem". Academic Emergency Medicine. 13 (4): 427–34. doi:10.1197/j.aem.2005.11.003. PMID 16531597.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Bourbeau R, Desjardins D, Maag U, Laberge-Nadeau C; Desjardins; Maag; Laberge-Nadeau (1993). "Neck injuries among belted and unbelted occupants of the front seat of cars". The Journal of Trauma. 35 (5): 794–9. doi:10.1097/00005373-199311000-00024. PMID 8230348.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Bédard M, Guyatt GH, Stones MJ, Hirdes JP; Guyatt; Stones; Hirdes (2002). "The independent contribution of driver, crash, and vehicle characteristics to driver fatalities". Accident Analysis & Prevention. 34 (6): 717–27. doi:10.1016/S0001-4575(01)00072-0. PMID 12371777.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Thomas J (1990). "Road traffic accidents before and after seatbelt legislation--study in a district general hospital". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 83 (2): 79–81. PMC 1292501. PMID 2319551.
^ Fenton, John (1969-01-24). "Safety Design". The Times.
^ "State Seat Belt Laws". www.ghsa.org. Retrieved 2016-02-15.
^ Streff FM, Geller ES; Geller (1988). "An experimental test of risk compensation: between-subject versus within-subject analyses" (PDF). Accident Analysis & Prevention. 20 (4): 277–87. doi:10.1016/0001-4575(88)90055-3. PMID 3415759.
^ Janssen W (1994). "Seat-belt wearing and driving behavior: an instrumented-vehicle study". Accident Analysis & Prevention. 26 (2): 249–61. doi:10.1016/0001-4575(94)90095-7. PMID 8198694.
^ "State laws requiring seat belts in school buses". www.cga.ct.gov. Retrieved 2016-02-26.
^ "It's time for seat belts on school buses". SafeGuardSeat.com. SafeGuard Seating. Retrieved 2 December 2013.
^ Spital M, Spital A, Spital R; Spital; Spital (November 1986). "The compelling case for seat belts on school busses". Pediatrics. 78 (5): 928–32. PMID 3763306.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Albers AC (2001). "Should there be laws mandating seatbelts in all school busses? Writing for the pro position". MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 26 (1): 8. doi:10.1097/00005721-200101000-00002. PMID 11198463.
^ Begley CE, Biddle AK; Biddle (1988). "Cost-benefit analysis of safety belts in Texas school buses". Public Health Rep. 103 (5): 479–85. PMC 1478133. PMID 3140273.
^ "''Pros, Cons of School Bus Seatbelts''". Wxia.com. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
[permanent dead link]
^ Garzon DL (2001). "Should there be laws mandating seatbelts in all school buses? Writing for the con position". MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 26 (1): 9. doi:10.1097/00005721-200101000-00003. PMID 11198464.
^ Why don’t school buses have seat belts? - American School Bus Council Archived 2016-01-27 at the Wayback Machine.
^ NHTSA reverses course, now wants seat belts on school buses
^ "EU law makes seat belts obligatory in long distance buses and coaches". European Public Health Alliance. 2006-07-19. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
^ Griffths M; Paine M; Moore R (2005-06-15). "Three point seat belts on coaches - the first decade in Australia" (PDF). U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
^ "NHTSA Announces Final Rule Requiring Seat Belts on Motorcoaches". NHTSA. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
^ "Assessment of Three-point Passenger Restraints (seatbelts) Fitted to Seats on Rail Vehicles" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-02-02.
^ "GUIDANCE FOR TURBULENCE MANAGEMENT" (PDF). International Air Transport Association. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04.
^ http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/CFR-2012-title14-vol1/pdf/CFR-2012-title14-vol1-sec23-785.pdf
^ "ICAO Manual Provides New Recommended Practices For Aircraft Cabin Child Restraint Systems".
External links
 Media related to Seat belts at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Seat belts at Wikimedia Commons- Seatbelt convincer crash simulator device