Fibonacci number

A tiling with squares whose side lengths are successive Fibonacci numbers
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers (named after mathematician Fibonacci) are the numbers in the following integer sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, and characterized by the fact that every number after the first two is the sum of the two preceding ones:[1][2]
- 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144,…{displaystyle 1,;1,;2,;3,;5,;8,;13,;21,;34,;55,;89,;144,;ldots }
Often, especially in modern usage, the sequence is extended by one more initial term:
0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144,…{displaystyle 0,;1,;1,;2,;3,;5,;8,;13,;21,;34,;55,;89,;144,;ldots }[3]

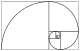
The Fibonacci spiral: an approximation of the golden spiral created by drawing circular arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling;[4] this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 and 21.
By definition, the first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence are either 1 and 1, or 0 and 1, depending on the chosen starting point of the sequence, and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two.
The sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation:
- Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2,{displaystyle F_{n}=F_{n-1}+F_{n-2},}
with seed values[1][2]
- F1=1,F2=1{displaystyle F_{1}=1,;F_{2}=1}
or[5]
- F0=0,F1=1.{displaystyle F_{0}=0,;F_{1}=1.}
Fibonacci numbers appear to have first arisen in perhaps 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of poetry formed from syllables of two lengths. The Fibonacci sequence is named after Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, known as Fibonacci. His 1202 book Liber Abaci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics,[6] although the sequence had been described earlier in Indian mathematics.[7][8][9] The sequence described in Liber Abaci began with F1 = 1. Fibonacci numbers were later independently discussed by Johannes Kepler in 1611 in connection with approximations to the pentagon. Their recurrence relation appears to have been understood from the early 1600s, but it has only been in the past very few decades that they have in general become widely discussed.[10]
Fibonacci numbers appear unexpectedly often in mathematics, so much so that there is an entire journal dedicated to their study, the Fibonacci Quarterly. Applications of Fibonacci numbers include computer algorithms such as the Fibonacci search technique and the Fibonacci heap data structure, and graphs called Fibonacci cubes used for interconnecting parallel and distributed systems. They also appear in biological settings,[11] such as branching in trees, phyllotaxis (the arrangement of leaves on a stem), the fruit sprouts of a pineapple,[12] the flowering of an artichoke, an uncurling fern and the arrangement of a pine cone's bracts.[13]
Fibonacci numbers are also closely related to Lucas numbers Ln{displaystyle L_{n}}


Contents
1 Origins
2 List of Fibonacci numbers
3 Use in mathematics
4 Relation to the golden ratio
4.1 Closed-form expression
4.2 Computation by rounding
4.3 Limit of consecutive quotients
4.4 Decomposition of powers of the golden ratio
5 Matrix form
6 Recognizing Fibonacci numbers
7 Combinatorial identities
7.1 Symbolic method
8 Other identities
8.1 Cassini's and Catalan's identities
8.2 d'Ocagne's identity
9 Power series
10 Reciprocal sums
11 Primes and divisibility
11.1 Divisibility properties
11.2 Primality testing
11.3 Fibonacci primes
11.4 Prime divisors of Fibonacci numbers
11.5 Periodicity modulo n
12 Right triangles
13 Magnitude
14 Applications
15 In nature
15.1 The bee ancestry code
15.2 The human X chromosome inheritance tree
16 Generalizations
17 See also
18 References
19 External links
Origins

Thirteen ways of arranging long and short syllables in a cadence of length six. Five end with a long syllable and eight end with a short syllable.

A page of Fibonacci's Liber Abaci from the Biblioteca Nazionale di Firenze showing (in box on right) the Fibonacci sequence with the position in the sequence labeled in Latin and Roman numerals and the value in Hindu-Arabic numerals.
The Fibonacci sequence appears in Indian mathematics, in connection with Sanskrit prosody.[8][14] In the Sanskrit poetic tradition, there was interest in enumerating all patterns of long (L) syllables of 2 units duration, juxtaposed with short (S) syllables of 1 unit duration. Counting the different patterns of successive L and S with a given total duration results in the Fibonacci numbers: the number of patterns of duration m units is Fm + 1.[9]
Knowledge of the Fibonacci sequence was expressed as early as Pingala (c.450 BC–200 BC). Parmanand Singh cites Pingala's cryptic formula misrau cha ("the two are mixed") and scholars who interpret it in context as saying that the number of patterns for m beats (Fm+1) is obtained by adding one [S] to the Fm cases and one [L] to the Fm−1 cases. [15]Bharata Muni also expresses knowledge of the sequence in the Natya Shastra (c. 100 BC–c. 350 AD).[16][7]
However, the clearest exposition of the sequence arises in the work of Virahanka (c. 700 AD), whose own work is lost, but is available in a quotation by Gopala (c. 1135):
Variations of two earlier meters [is the variation]... For example, for [a meter of length] four, variations of meters of two [and] three being mixed, five happens. [works out examples 8, 13, 21]... In this way, the process should be followed in all mātrā-vṛttas [prosodic combinations].[a]
Hemachandra (c. 1150) is credited with knowledge of the sequence as well.[7]

The number of rabbit pairs form the Fibonacci sequence
Outside India, the Fibonacci sequence first appears in the book Liber Abaci (1202) by Fibonacci.[6][18] using it to calculate the growth of rabbit populations.[19][20] Fibonacci considers the growth of a hypothetical, idealized (biologically unrealistic) rabbit population, assuming that: a newly born pair of rabbits, one male, one female, are put in a field; rabbits are able to mate at the age of one month so that at the end of its second month a female can produce another pair of rabbits; rabbits never die and a mating pair always produces one new pair (one male, one female) every month from the second month on. Fibonacci posed the puzzle: how many pairs will there be in one year?
- At the end of the first month, they mate, but there is still only 1 pair.
- At the end of the second month the female produces a new pair, so now there are 2 pairs of rabbits in the field.
- At the end of the third month, the original female produces a second pair, making 3 pairs in all in the field.
- At the end of the fourth month, the original female has produced yet another new pair, and the female born two months ago also produces her first pair, making 5 pairs.
At the end of the nth month, the number of pairs of rabbits is equal to the number of new pairs (that is, the number of pairs in month n − 2) plus the number of pairs alive last month (that is, n − 1). This is the nth Fibonacci number.[21]
The name "Fibonacci sequence" was first used by the 19th-century number theorist Édouard Lucas.[22]
List of Fibonacci numbers
The first 21 Fibonacci numbers Fn for n = 0, 1, 2, ..., 20 are:[23]
F0
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
F11
F12
F13
F14
F15
F16
F17
F18
F19
F20
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
34
55
89
144
233
377
610
987
1597
2584
4181
6765
The sequence can also be extended to negative index n using the re-arranged recurrence relation
- Fn−2=Fn−Fn−1,{displaystyle F_{n-2}=F_{n}-F_{n-1},}
which yields the sequence of "negafibonacci" numbers[24] satisfying
- F−n=(−1)n+1Fn.{displaystyle F_{-n}=(-1)^{n+1}F_{n}.}
Thus the bidirectional sequence is
F−8
F−7
F−6
F−5
F−4
F−3
F−2
F−1
F0
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
−21
13
−8
5
−3
2
−1
1
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
Use in mathematics

The Fibonacci numbers are the sums of the "shallow" diagonals (shown in red) of Pascal's triangle.
The Fibonacci numbers occur in the sums of "shallow" diagonals in Pascal's triangle (see binomial coefficient):[25]
- Fn=∑k=0⌊n−12⌋(n−k−1k){displaystyle F_{n}=sum _{k=0}^{leftlfloor {frac {n-1}{2}}rightrfloor }{tbinom {n-k-1}{k}}}
These numbers also give the solution to certain enumerative problems.[26] The most common is that of counting the number of compositions of 1s and 2s which sum to a given total n: there are Fn+1 ways to do this.
For example, if n = 5, then Fn+1 = F6 = 8 counts the eight compositions summing to 5:
1+1+1+1+1 = 1+1+1+2 = 1+1+2+1 = 1+2+1+1 = 2+1+1+1 = 2+2+1 = 2+1+2 = 1+2+2.
The Fibonacci numbers can be found in different ways among the set of binary strings, or equivalently, among the subsets of a given set.
- The number of binary strings of length n without consecutive 1s is the Fibonacci number Fn+2. For example, out of the 16 binary strings of length 4, there are F6 = 8 without consecutive 1s – they are 0000, 0001, 0010, 0100, 0101, 1000, 1001 and 1010. By symmetry, the number of strings of length n without consecutive 0s is also Fn+2. Equivalently, Fn+2 is the number of subsets S ⊂ {1,...,n} without consecutive integers: {i, i+1} ⊄ S for every i. The symmetric statement is: Fn+2 is the number of subsets S ⊂ {1,...,n} without two consecutive skipped integers: that is, S = {a1 < ... < ak} with ai+1 ≤ ai + 2.
- The number of binary strings of length n without an odd number of consecutive 1s is the Fibonacci number Fn+1. For example, out of the 16 binary strings of length 4, there are F5 = 5 without an odd number of consecutive 1s – they are 0000, 0011, 0110, 1100, 1111. Equivalently, the number of subsets S ⊂ {1,...,n} without an odd number of consecutive integers is Fn+1.
- The number of binary strings of length n without an even number of consecutive 0s or 1s is 2Fn. For example, out of the 16 binary strings of length 4, there are 2F4 = 6 without an even number of consecutive 0s or 1s – they are 0001, 0111, 0101, 1000, 1010, 1110. There is an equivalent statement about subsets.
Relation to the golden ratio
Closed-form expression
Like every sequence defined by a linear recurrence with constant coefficients, the Fibonacci numbers have a closed-form solution. It has become known as "Binet's formula", though it was already known by Abraham de Moivre:[27]
- Fn=φn−ψnφ−ψ=φn−ψn5{displaystyle F_{n}={frac {varphi ^{n}-psi ^{n}}{varphi -psi }}={frac {varphi ^{n}-psi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}}
where
- φ=1+52≈1.6180339887…{displaystyle varphi ={frac {1+{sqrt {5}}}{2}}approx 1.61803,39887ldots }
is the golden ratio (OEIS: A001622), and
ψ=1−52=1−φ=−1φ≈−0.6180339887….{displaystyle psi ={frac {1-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}=1-varphi =-{1 over varphi }approx -0.61803,39887ldots .}[28]
Since ψ=−φ−1{displaystyle psi =-varphi ^{-1}}
Fn=φn−(−φ)−n5=φn−(−φ)−n2φ−1{displaystyle F_{n}={frac {varphi ^{n}-(-varphi )^{-n}}{sqrt {5}}}={frac {varphi ^{n}-(-varphi )^{-n}}{2varphi -1}}}
To see this,[29] note that φ and ψ are both solutions of the equations
- x2=x+1andxn=xn−1+xn−2,{displaystyle x^{2}=x+1quad {text{and}}quad x^{n}=x^{n-1}+x^{n-2},}
so the powers of φ and ψ satisfy the Fibonacci recursion. In other words,
- φn=φn−1+φn−2{displaystyle varphi ^{n}=varphi ^{n-1}+varphi ^{n-2}}
and
- ψn=ψn−1+ψn−2.{displaystyle psi ^{n}=psi ^{n-1}+psi ^{n-2}.}
It follows that for any values a and b, the sequence defined by
- Un=aφn+bψn{displaystyle U_{n}=avarphi ^{n}+bpsi ^{n}}
satisfies the same recurrence
- Un=aφn−1+bψn−1+aφn−2+bψn−2=Un−1+Un−2.{displaystyle U_{n}=avarphi ^{n-1}+bpsi ^{n-1}+avarphi ^{n-2}+bpsi ^{n-2}=U_{n-1}+U_{n-2}.}
If a and b are chosen so that U0 = 0 and U1 = 1 then the resulting sequence Un must be the Fibonacci sequence. This is the same as requiring a and b satisfy the system of equations:
- {a+b=0φa+ψb=1{displaystyle left{{begin{array}{l}a+b=0\varphi a+psi b=1end{array}}right.}
which has solution
- a=1φ−ψ=15,b=−a,{displaystyle a={frac {1}{varphi -psi }}={frac {1}{sqrt {5}}},quad b=-a,}
producing the required formula.
Taking the starting values U0 and U1 to be arbitrary constants, a more general solution is:
- Un=aφn+bψn{displaystyle U_{n}=avarphi ^{n}+bpsi ^{n}}
where
- a=U1−U0ψ5{displaystyle a={frac {U_{1}-U_{0}psi }{sqrt {5}}}}
b=U0φ−U15{displaystyle b={frac {U_{0}varphi -U_{1}}{sqrt {5}}}}.
Computation by rounding
Since
- |ψn5|<12{displaystyle left|{frac {psi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}right|<{frac {1}{2}}}
for all n ≥ 0, the number Fn is the closest integer to φn5{displaystyle {frac {varphi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}}
- Fn=[φn5], n≥0,{displaystyle F_{n}=left[{frac {varphi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}right], ngeq 0,}
or in terms of the floor function:
- Fn=⌊φn5+12⌋, n≥0.{displaystyle F_{n}=leftlfloor {frac {varphi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}+{frac {1}{2}}rightrfloor , ngeq 0.}
Similarly, if we already know that the number F > 1 is a Fibonacci number, we can determine its index within the sequence by
- n(F)=⌊logφ(F⋅5+12)⌋,{displaystyle n(F)={bigg lfloor }log _{varphi }left(Fcdot {sqrt {5}}+{frac {1}{2}}right){bigg rfloor },}
where logφ(x){displaystyle log _{varphi }(x)}
For example, logφ(x)=ln(x)/ln(φ)=log10(x)/log10(φ){displaystyle log _{varphi }(x)=ln(x)/ln(varphi )=log _{10}(x)/log _{10}(varphi )}
Limit of consecutive quotients
Johannes Kepler observed that the ratio of consecutive Fibonacci numbers converges. He wrote that "as 5 is to 8 so is 8 to 13, practically, and as 8 is to 13, so is 13 to 21 almost", and concluded that these ratios approach the golden ratio φ{displaystyle varphi }
- limn→∞Fn+1Fn=φ{displaystyle lim _{nto infty }{frac {F_{n+1}}{F_{n}}}=varphi }
This convergence holds regardless of the starting values, excluding 0 and 0, or any pair in the conjugate golden ratio −1φ{displaystyle -{frac {1}{varphi }}}
Another consequence is that the limit of the ratio of two Fibonacci numbers offset by a particular finite deviation in index corresponds to the golden ratio raised by that deviation. Or, in other words:
- limn→∞Fn+αFn=φα{displaystyle lim _{nto infty }{frac {F_{n+alpha }}{F_{n}}}=varphi ^{alpha }}

Animated GIF file showing successive tilings of the plane, and a graph of approximations to the Golden Ratio calculated by dividing successive pairs of Fibonacci numbers, one by the other. Uses the Fibonacci numbers 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144
Decomposition of powers of the golden ratio
Since the golden ratio satisfies the equation
- φ2=φ+1,{displaystyle varphi ^{2}=varphi +1,}
this expression can be used to decompose higher powers φn{displaystyle varphi ^{n}}

- φn=Fnφ+Fn−1.{displaystyle varphi ^{n}=F_{n}varphi +F_{n-1}.}
This equation can be proved by induction on n.
This expression is also true for n < 1 if the Fibonacci sequence Fn is extended to negative integers using the Fibonacci rule Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2.{displaystyle F_{n}=F_{n-1}+F_{n-2}.}
Matrix form
A 2-dimensional system of linear difference equations that describes the Fibonacci sequence is
- (Fk+2Fk+1)=(1110)(Fk+1Fk){displaystyle {F_{k+2} choose F_{k+1}}={begin{pmatrix}1&1\1&0end{pmatrix}}{F_{k+1} choose F_{k}}}
alternatively denoted
- F→k+1=AF→k,{displaystyle {vec {F}}_{k+1}=mathbf {A} {vec {F}}_{k},}
which yields F→n=AnF→0{displaystyle {vec {F}}_{n}=mathbf {A} ^{n}{vec {F}}_{0}}


- μ→=(φ1){displaystyle {vec {mu }}={varphi choose 1}}
and
- ν→=(−φ−11).{displaystyle {vec {nu }}={-varphi ^{-1} choose 1}.}
As the initial value is
- F→0=(10)=15μ→−15ν→,{displaystyle {vec {F}}_{0}={1 choose 0}={frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}{vec {mu }}-{frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}{vec {nu }},}
it follows that the nth term is
- F→n=15Anμ→−15Anν→=15φnμ→−15(−φ)−nν→ =15(1+52)n(φ1)−15(1−52)n(−φ−11),{displaystyle {begin{aligned}{vec {F}}_{n}&={frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}A^{n}{vec {mu }}-{frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}A^{n}{vec {nu }}\&={frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}varphi ^{n}{vec {mu }}-{frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}(-varphi )^{-n}{vec {nu }}~\&={cfrac {1}{sqrt {5}}}left({cfrac {1+{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)^{n}{varphi choose 1}-{cfrac {1}{sqrt {5}}}left({cfrac {1-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)^{n}{-varphi ^{-1} choose 1},end{aligned}}}
From this, the nth element in the Fibonacci series
may be read off directly as a closed-form expression:
- Fn=15(1+52)n−15(1−52)n.{displaystyle F_{n}={cfrac {1}{sqrt {5}}}left({cfrac {1+{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)^{n}-{cfrac {1}{sqrt {5}}}left({cfrac {1-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)^{n}.}
Equivalently, the same computation may performed by diagonalization of A through use of its eigendecomposition:
- A=SΛS−1,An=SΛnS−1,{displaystyle {begin{aligned}A&=SLambda S^{-1},\A^{n}&=SLambda ^{n}S^{-1},end{aligned}}}
where Λ=(φ00−φ−1){displaystyle Lambda ={begin{pmatrix}varphi &0\0&-varphi ^{-1}end{pmatrix}}}
The closed-form expression for the nth element in the Fibonacci series is therefore given by
- (Fn+1Fn)=An(F1F0)=SΛnS−1(F1F0)=S(φn00(−φ)−n)S−1(F1F0)=(φ−φ−111)(φn00(−φ)−n)15(1φ−1−1φ)(10),{displaystyle {begin{aligned}{F_{n+1} choose F_{n}}&=A^{n}{F_{1} choose F_{0}}\&=SLambda ^{n}S^{-1}{F_{1} choose F_{0}}\&=S{begin{pmatrix}varphi ^{n}&0\0&(-varphi )^{-n}end{pmatrix}}S^{-1}{F_{1} choose F_{0}}\&={begin{pmatrix}varphi &-varphi ^{-1}\1&1end{pmatrix}}{begin{pmatrix}varphi ^{n}&0\0&(-varphi )^{-n}end{pmatrix}}{frac {1}{sqrt {5}}}{begin{pmatrix}1&varphi ^{-1}\-1&varphi end{pmatrix}}{1 choose 0},end{aligned}}}
which again yields
- Fn=φn−(−φ)−n5.{displaystyle F_{n}={cfrac {varphi ^{n}-(-varphi )^{-n}}{sqrt {5}}}.}
The matrix A has a determinant of −1, and thus it is a 2×2 unimodular matrix.
This property can be understood in terms of the continued fraction representation for the golden ratio:
- φ=1+11+11+11+⋱.{displaystyle varphi =1+{cfrac {1}{1+{cfrac {1}{1+{cfrac {1}{1+ddots }}}}}}.}
The Fibonacci numbers occur as the ratio of successive convergents of the continued fraction for φ, and the matrix formed from successive convergents of any continued fraction has a determinant of +1 or −1. The matrix representation gives the following closed-form expression for the Fibonacci numbers:
- (1110)n=(Fn+1FnFnFn−1).{displaystyle {begin{pmatrix}1&1\1&0end{pmatrix}}^{n}={begin{pmatrix}F_{n+1}&F_{n}\F_{n}&F_{n-1}end{pmatrix}}.}
Taking the determinant of both sides of this equation yields Cassini's identity,
- (−1)n=Fn+1Fn−1−Fn2.{displaystyle (-1)^{n}=F_{n+1}F_{n-1}-F_{n}^{2}.}
Moreover, since AnAm = An+m for any square matrix A, the following identities can be derived (they are obtained from two different coefficients of the matrix product, and one may easily deduce the second one from the first one by changing n into n + 1),
- FmFn+Fm−1Fn−1=Fm+n−1,FmFn+1+Fm−1Fn=Fm+n.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}{F_{m}}{F_{n}}+{F_{m-1}}{F_{n-1}}&=F_{m+n-1},\F_{m}F_{n+1}+F_{m-1}F_{n}&=F_{m+n}.end{aligned}}}
In particular, with m = n,
- F2n−1=Fn2+Fn−12F2n=(Fn−1+Fn+1)Fn=(2Fn−1+Fn)Fn.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}F_{2n-1}&=F_{n}^{2}+F_{n-1}^{2}\F_{2n}&=(F_{n-1}+F_{n+1})F_{n}\&=(2F_{n-1}+F_{n})F_{n}.end{aligned}}}
These last two identities provide a way to compute Fibonacci numbers recursively in O(log(n)) arithmetic operations and in time O(M(n) log(n)), where M(n) is the time for the multiplication of two numbers of n digits. This matches the time for computing the nth Fibonacci number from the closed-form matrix formula, but with fewer redundant steps if one avoids recomputing an already computed Fibonacci number (recursion with memoization).[32]
Recognizing Fibonacci numbers
The question may arise whether a positive integer x is a Fibonacci number. This is true if and only if one or both of 5x2+4{displaystyle 5x^{2}+4}

n=logφ(Fn5+5Fn2±42){displaystyle n=log _{varphi }left({frac {F_{n}{sqrt {5}}+{sqrt {5F_{n}^{2}pm 4}}}{2}}right)},
which allows one to find the position in the sequence of a given Fibonacci number.
This formula must return an integer for all n, so the radical expression must be an integer (otherwise the logarithm does not even return a rational number).
Combinatorial identities
Most identities involving Fibonacci numbers can be proved using combinatorial arguments using the fact that Fn can be interpreted as the number of sequences of 1s and 2s that sum to n − 1. This can be taken as the definition of Fn, with the convention that F0 = 0, meaning no sum adds up to −1, and that F1 = 1, meaning the empty sum "adds up" to 0. Here, the order of the summand matters. For example, 1 + 2 and 2 + 1 are considered two different sums.
For example, the recurrence relation
- Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2,{displaystyle F_{n}=F_{n-1}+F_{n-2},}
or in words, the nth Fibonacci number is the sum of the previous two Fibonacci numbers, may be shown by dividing the Fn sums of 1s and 2s that add to n − 1 into two non-overlapping groups. One group contains those sums whose first term is 1 and the other those sums whose first term is 2. In the first group the remaining terms add to n − 2, so it has Fn-1 sums, and in the second group the remaining terms add to n − 3, so there are Fn−2 sums. So there are a total of Fn−1 + Fn−2 sums altogether, showing this is equal to Fn.
Similarly, it may be shown that the sum of the first Fibonacci numbers up to the nth is equal to the (n + 2)-nd Fibonacci number minus 1.[34] In symbols:
- ∑i=1nFi=Fn+2−1{displaystyle sum _{i=1}^{n}F_{i}=F_{n+2}-1}
This is done by dividing the sums adding to n + 1 in a different way, this time by the location of the first 2. Specifically, the first group consists of those sums that start with 2, the second group those that start 1 + 2, the third 1 + 1 + 2, and so on, until the last group, which consists of the single sum where only 1's are used. The number of sums in the first group is F(n), F(n − 1) in the second group, and so on, with 1 sum in the last group. So the total number of sums is F(n) + F(n − 1) + ... + F(1) + 1 and therefore this quantity is equal to F(n + 2).
A similar argument, grouping the sums by the position of the first 1 rather than the first 2, gives two more identities:
- ∑i=0n−1F2i+1=F2n{displaystyle sum _{i=0}^{n-1}F_{2i+1}=F_{2n}}
and
- ∑i=1nF2i=F2n+1−1.{displaystyle sum _{i=1}^{n}F_{2i}=F_{2n+1}-1.}
In words, the sum of the first Fibonacci numbers with odd index up to F2n−1 is the (2n)th Fibonacci number, and the sum of the first Fibonacci numbers with even index up to F2n is the (2n + 1)th Fibonacci number minus 1.[35]
A different trick may be used to prove
- ∑i=1nFi2=FnFn+1,{displaystyle sum _{i=1}^{n}{F_{i}}^{2}=F_{n}F_{n+1},}
or in words, the sum of the squares of the first Fibonacci numbers up to Fn is the product of the nth and (n + 1)th Fibonacci numbers. In this case note that Fibonacci rectangle of size Fn by F(n + 1) can be decomposed into squares of size Fn, Fn−1, and so on to F1 = 1, from which the identity follows by comparing areas.
Symbolic method
The sequence (Fn)n∈N{displaystyle (F_{n})_{nin mathbb {N} }}



It follows that the ordinary generating function of the Fibonacci sequence, i.e. ∑i=0∞Fizi{displaystyle sum _{i=0}^{infty }F_{i}z^{i}}

Other identities
Numerous other identities can be derived using various methods. Some of the most noteworthy are:[37]
Cassini's and Catalan's identities
Cassini's identity states that
- Fn2−Fn+1Fn−1=(−1)n−1{displaystyle F_{n}^{2}-F_{n+1}F_{n-1}=(-1)^{n-1}}
Catalan's identity is a generalization:
- Fn2−Fn+rFn−r=(−1)n−rFr2{displaystyle F_{n}^{2}-F_{n+r}F_{n-r}=(-1)^{n-r}F_{r}^{2}}
d'Ocagne's identity
- FmFn+1−Fm+1Fn=(−1)nFm−n{displaystyle F_{m}F_{n+1}-F_{m+1}F_{n}=(-1)^{n}F_{m-n}}
- F2n=Fn+12−Fn−12=Fn(Fn+1+Fn−1)=FnLn{displaystyle F_{2n}=F_{n+1}^{2}-F_{n-1}^{2}=F_{n}left(F_{n+1}+F_{n-1}right)=F_{n}L_{n}}
where Ln is the n'th Lucas number. The last is an identity for doubling n; other identities of this type are
- F3n=2Fn3+3FnFn+1Fn−1=5Fn3+3(−1)nFn{displaystyle F_{3n}=2F_{n}^{3}+3F_{n}F_{n+1}F_{n-1}=5F_{n}^{3}+3(-1)^{n}F_{n}}
by Cassini's identity.
- F3n+1=Fn+13+3Fn+1Fn2−Fn3{displaystyle F_{3n+1}=F_{n+1}^{3}+3F_{n+1}F_{n}^{2}-F_{n}^{3}}
- F3n+2=Fn+13+3Fn+12Fn+Fn3{displaystyle F_{3n+2}=F_{n+1}^{3}+3F_{n+1}^{2}F_{n}+F_{n}^{3}}
- F4n=4FnFn+1(Fn+12+2Fn2)−3Fn2(Fn2+2Fn+12){displaystyle F_{4n}=4F_{n}F_{n+1}left(F_{n+1}^{2}+2F_{n}^{2}right)-3F_{n}^{2}left(F_{n}^{2}+2F_{n+1}^{2}right)}
These can be found experimentally using lattice reduction, and are useful in setting up the special number field sieve to factorize a Fibonacci number.
More generally,[37]
- Fkn+c=∑i=0k(ki)Fc−iFniFn+1k−i.{displaystyle F_{kn+c}=sum _{i=0}^{k}{k choose i}F_{c-i}F_{n}^{i}F_{n+1}^{k-i}.}
Putting k = 2 in this formula, one gets again the formulas of the end of above section Matrix form.
Power series
The generating function of the Fibonacci sequence is the power series
- s(x)=∑k=0∞Fkxk.{displaystyle s(x)=sum _{k=0}^{infty }F_{k}x^{k}.}
This series is convergent for |x|<1φ,{displaystyle |x|<{frac {1}{varphi }},}
- s(x)=x1−x−x2{displaystyle s(x)={frac {x}{1-x-x^{2}}}}
This can be proved by using the Fibonacci recurrence to expand each coefficient in the infinite sum:
- s(x)=∑k=0∞Fkxk=F0+F1x+∑k=2∞(Fk−1+Fk−2)xk=x+∑k=2∞Fk−1xk+∑k=2∞Fk−2xk=x+x∑k=0∞Fkxk+x2∑k=0∞Fkxk=x+xs(x)+x2s(x).{displaystyle {begin{aligned}s(x)&=sum _{k=0}^{infty }F_{k}x^{k}\&=F_{0}+F_{1}x+sum _{k=2}^{infty }left(F_{k-1}+F_{k-2}right)x^{k}\&=x+sum _{k=2}^{infty }F_{k-1}x^{k}+sum _{k=2}^{infty }F_{k-2}x^{k}\&=x+xsum _{k=0}^{infty }F_{k}x^{k}+x^{2}sum _{k=0}^{infty }F_{k}x^{k}\&=x+xs(x)+x^{2}s(x).end{aligned}}}
Solving the equation
- s(x)=x+xs(x)+x2s(x){displaystyle s(x)=x+xs(x)+x^{2}s(x)}
for s(x) results in the above closed form.
Setting x = 1/k, the closed form of the series becomes
- ∑n=0∞Fnkn=kk2−k−1.{displaystyle sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {F_{n}}{k^{n}}}={frac {k}{k^{2}-k-1}}.}
In particular, if k is an integer greater than 1, then this series converges. Further setting k = 10m yields
- ∑n=1∞Fn10m(n+1)=1102m−10m−1{displaystyle sum _{n=1}^{infty }{frac {F_{n}}{10^{m(n+1)}}}={frac {1}{10^{2m}-10^{m}-1}}}
for all positive integers m.
Some math puzzle-books present as curious the particular value that comes from m = 1, which is s(1/10)10=189=.011235…{displaystyle {frac {s(1/10)}{10}}={frac {1}{89}}=.011235ldots }
- s(1/100)100=19899=.0001010203050813213455…{displaystyle {frac {s(1/100)}{100}}={frac {1}{9899}}=.0001010203050813213455ldots }
Reciprocal sums
Infinite sums over reciprocal Fibonacci numbers can sometimes be evaluated in terms of theta functions. For example, we can write the sum of every odd-indexed reciprocal Fibonacci number as
- ∑k=0∞1F2k+1=54ϑ22(0,3−52),{displaystyle sum _{k=0}^{infty }{frac {1}{F_{2k+1}}}={frac {sqrt {5}}{4}}vartheta _{2}^{2}left(0,{frac {3-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right),}
and the sum of squared reciprocal Fibonacci numbers as
- ∑k=1∞1Fk2=524(ϑ24(0,3−52)−ϑ44(0,3−52)+1).{displaystyle sum _{k=1}^{infty }{frac {1}{F_{k}^{2}}}={frac {5}{24}}left(vartheta _{2}^{4}left(0,{frac {3-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)-vartheta _{4}^{4}left(0,{frac {3-{sqrt {5}}}{2}}right)+1right).}
If we add 1 to each Fibonacci number in the first sum, there is also the closed form
- ∑k=0∞11+F2k+1=52,{displaystyle sum _{k=0}^{infty }{frac {1}{1+F_{2k+1}}}={frac {sqrt {5}}{2}},}
and there is a nested sum of squared Fibonacci numbers giving the reciprocal of the golden ratio,
- ∑k=1∞(−1)k+1∑j=1kFj2=5−12.{displaystyle sum _{k=1}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{k+1}}{sum _{j=1}^{k}{F_{j}}^{2}}}={frac {{sqrt {5}}-1}{2}}.}
No closed formula for the reciprocal Fibonacci constant
- ψ=∑k=1∞1Fk=3.359885666243…{displaystyle psi =sum _{k=1}^{infty }{frac {1}{F_{k}}}=3.359885666243dots }
is known, but the number has been proved irrational by Richard André-Jeannin.[40]
The Millin series gives the identity[41]
- ∑n=0∞1F2n=7−52,{displaystyle sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {1}{F_{2^{n}}}}={frac {7-{sqrt {5}}}{2}},}
which follows from the closed form for its partial sums as N tends to infinity:
- ∑n=0N1F2n=3−F2N−1F2N.{displaystyle sum _{n=0}^{N}{frac {1}{F_{2^{n}}}}=3-{frac {F_{2^{N}-1}}{F_{2^{N}}}}.}
Primes and divisibility
Divisibility properties
Every third number of the sequence is even and more generally, every kth number of the sequence is a multiple of Fk. Thus the Fibonacci sequence is an example of a divisibility sequence. In fact, the Fibonacci sequence satisfies the stronger divisibility property[42][43]
- gcd(Fm,Fn)=Fgcd(m,n).{displaystyle gcd(F_{m},F_{n})=F_{gcd(m,n)}.}
Any three consecutive Fibonacci numbers are pairwise coprime, which means that, for every n,
gcd(Fn, Fn+1) = gcd(Fn, Fn+2) = gcd(Fn+1, Fn+2) = 1.
Every prime number p divides a Fibonacci number that can be determined by the value of p modulo 5. If p is congruent to 1 or 4 (mod 5), then p divides Fp − 1, and if p is congruent to 2 or 3 (mod 5), then, p divides Fp + 1. The remaining case is that p = 5, and in this case p divides Fp.
- {p=5⇒p∣Fp,p≡±1(mod5)⇒p∣Fp−1,p≡±2(mod5)⇒p∣Fp+1.{displaystyle {begin{cases}p=5&Rightarrow pmid F_{p},\pequiv pm 1{pmod {5}}&Rightarrow pmid F_{p-1},\pequiv pm 2{pmod {5}}&Rightarrow pmid F_{p+1}.end{cases}}}
These cases can be combined into a single formula, using the Legendre symbol:[44]
- p∣Fp−(5p).{displaystyle pmid F_{p-left({frac {5}{p}}right)}.}
Primality testing
The above formula can be used as a primality test in the sense that if
- n∣Fn−(5n),{displaystyle nmid F_{n-left({frac {5}{n}}right)},}
where the Legendre symbol has been replaced by the Jacobi symbol, then this is evidence that n is a prime, and if it fails to hold, then n is definitely not a prime. If n is composite and satisfies the formula, then n is a Fibonacci pseudoprime. When m is large—say a 500-bit number—then we can calculate Fm (mod n) efficiently using the matrix form. Thus
- (Fm+1FmFmFm−1)≡(1110)m(modn).{displaystyle {begin{pmatrix}F_{m+1}&F_{m}\F_{m}&F_{m-1}end{pmatrix}}equiv {begin{pmatrix}1&1\1&0end{pmatrix}}^{m}{pmod {n}}.}
Here the matrix power Am is calculated using modular exponentiation, which can be adapted to matrices.[45]
Fibonacci primes
A Fibonacci prime is a Fibonacci number that is prime. The first few are:
- 2, 3, 5, 13, 89, 233, 1597, 28657, 514229, ... OEIS: A005478.
Fibonacci primes with thousands of digits have been found, but it is not known whether there are infinitely many.[46]
Fkn is divisible by Fn, so, apart from F4 = 3, any Fibonacci prime must have a prime index. As there are arbitrarily long runs of composite numbers, there are therefore also arbitrarily long runs of composite Fibonacci numbers.
No Fibonacci number greater than F6 = 8 is one greater or one less than a prime number.[47]
The only nontrivial square Fibonacci number is 144.[48] Attila Pethő proved in 2001 that there is only a finite number of perfect power Fibonacci numbers.[49] In 2006, Y. Bugeaud, M. Mignotte, and S. Siksek proved that 8 and 144 are the only such non-trivial perfect powers.[50]
1, 3, 21, 55 are the only triangular Fibonacci numbers, which was conjectured by Vern Hoggatt and proved by Luo Ming.[51]
Prime divisors of Fibonacci numbers
With the exceptions of 1, 8 and 144 (F1 = F2, F6 and F12) every Fibonacci number has a prime factor that is not a factor of any smaller Fibonacci number (Carmichael's theorem).[52] As a result, 8 and 144 (F6 and F12) are the only Fibonacci numbers that are the product of other Fibonacci numbers OEIS: A235383.
The divisibility of Fibonacci numbers by a prime p is related to the Legendre symbol (p5){displaystyle left({tfrac {p}{5}}right)}
- (p5)={0if p=51if p≡±1(mod5)−1if p≡±2(mod5).{displaystyle left({frac {p}{5}}right)={begin{cases}0&{text{if }}p=5\1&{text{if }}pequiv pm 1{pmod {5}}\-1&{text{if }}pequiv pm 2{pmod {5}}.end{cases}}}
If p is a prime number then
Fp≡(p5)(modp)andFp−(p5)≡0(modp).{displaystyle F_{p}equiv left({frac {p}{5}}right){pmod {p}}quad {text{and}}quad F_{p-left({frac {p}{5}}right)}equiv 0{pmod {p}}.}[53][54]
For example,
- (25)=−1,F3=2,F2=1,(35)=−1,F4=3,F3=2,(55)=0,F5=5,(75)=−1,F8=21,F7=13,(115)=+1,F10=55,F11=89.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}({tfrac {2}{5}})&=-1,&F_{3}&=2,&F_{2}&=1,\({tfrac {3}{5}})&=-1,&F_{4}&=3,&F_{3}&=2,\({tfrac {5}{5}})&=0,&F_{5}&=5,\({tfrac {7}{5}})&=-1,&F_{8}&=21,&F_{7}&=13,\({tfrac {11}{5}})&=+1,&F_{10}&=55,&F_{11}&=89.end{aligned}}}
It is not known whether there exists a prime p such that
- Fp−(p5)≡0(modp2).{displaystyle F_{p-left({frac {p}{5}}right)}equiv 0{pmod {p^{2}}}.}
Such primes (if there are any) would be called Wall–Sun–Sun primes.
Also, if p ≠ 5 is an odd prime number then:[55]
- 5Fp±122≡{12(5(p5)±5)(modp)if p≡1(mod4)12(5(p5)∓3)(modp)if p≡3(mod4).{displaystyle 5F_{frac {ppm 1}{2}}^{2}equiv {begin{cases}{tfrac {1}{2}}left(5left({frac {p}{5}}right)pm 5right){pmod {p}}&{text{if }}pequiv 1{pmod {4}}\{tfrac {1}{2}}left(5left({frac {p}{5}}right)mp 3right){pmod {p}}&{text{if }}pequiv 3{pmod {4}}.end{cases}}}
Example 1. p = 7, in this case p ≡ 3 (mod 4) and we have:
- (75)=−1:12(5(75)+3)=−1,12(5(75)−3)=−4.{displaystyle ({tfrac {7}{5}})=-1:qquad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {7}{5}})+3right)=-1,quad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {7}{5}})-3right)=-4.}
- F3=2 and F4=3.{displaystyle F_{3}=2{text{ and }}F_{4}=3.}
- 5F32=20≡−1(mod7) and 5F42=45≡−4(mod7){displaystyle 5F_{3}^{2}=20equiv -1{pmod {7}};;{text{ and }};;5F_{4}^{2}=45equiv -4{pmod {7}}}
Example 2. p = 11, in this case p ≡ 3 (mod 4) and we have:
- (115)=+1:12(5(115)+3)=4,12(5(115)−3)=1.{displaystyle ({tfrac {11}{5}})=+1:qquad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {11}{5}})+3right)=4,quad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {11}{5}})-3right)=1.}
- F5=5 and F6=8.{displaystyle F_{5}=5{text{ and }}F_{6}=8.}
- 5F52=125≡4(mod11) and 5F62=320≡1(mod11){displaystyle 5F_{5}^{2}=125equiv 4{pmod {11}};;{text{ and }};;5F_{6}^{2}=320equiv 1{pmod {11}}}
Example 3. p = 13, in this case p ≡ 1 (mod 4) and we have:
- (135)=−1:12(5(135)−5)=−5,12(5(135)+5)=0.{displaystyle ({tfrac {13}{5}})=-1:qquad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {13}{5}})-5right)=-5,quad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {13}{5}})+5right)=0.}
- F6=8 and F7=13.{displaystyle F_{6}=8{text{ and }}F_{7}=13.}
- 5F62=320≡−5(mod13) and 5F72=845≡0(mod13){displaystyle 5F_{6}^{2}=320equiv -5{pmod {13}};;{text{ and }};;5F_{7}^{2}=845equiv 0{pmod {13}}}
Example 4. p = 29, in this case p ≡ 1 (mod 4) and we have:
- (295)=+1:12(5(295)−5)=0,12(5(295)+5)=5.{displaystyle ({tfrac {29}{5}})=+1:qquad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {29}{5}})-5right)=0,quad {tfrac {1}{2}}left(5({tfrac {29}{5}})+5right)=5.}
- F14=377 and F15=610.{displaystyle F_{14}=377{text{ and }}F_{15}=610.}
- 5F142=710645≡0(mod29) and 5F152=1860500≡5(mod29){displaystyle 5F_{14}^{2}=710645equiv 0{pmod {29}};;{text{ and }};;5F_{15}^{2}=1860500equiv 5{pmod {29}}}
For odd n, all odd prime divisors of Fn are congruent to 1 modulo 4, implying that all odd divisors of Fn (as the products of odd prime divisors) are congruent to 1 modulo 4.[56]
For example,
- F1=1,F3=2,F5=5,F7=13,F9=34=2⋅17,F11=89,F13=233,F15=610=2⋅5⋅61.{displaystyle F_{1}=1,F_{3}=2,F_{5}=5,F_{7}=13,F_{9}=34=2cdot 17,F_{11}=89,F_{13}=233,F_{15}=610=2cdot 5cdot 61.}
All known factors of Fibonacci numbers F(i) for all i < 50000 are collected at the relevant repositories.[57][58]
Periodicity modulo n
If the members of the Fibonacci sequence are taken mod n, the resulting sequence is periodic with period at most 6n.[59] The lengths of the periods for various n form the so-called Pisano periods OEIS: A001175. Determining a general formula for the Pisano periods is an open problem, which includes as a subproblem a special instance of the problem of finding the multiplicative order of a modular integer or of an element in a finite field. However, for any particular n, the Pisano period may be found as an instance of cycle detection.
Right triangles
Starting with 5, every second Fibonacci number is the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with integer sides, or in other words, the largest number in a Pythagorean triple. The length of the longer leg of this triangle is equal to the sum of the three sides of the preceding triangle in this series of triangles, and the shorter leg is equal to the difference between the preceding bypassed Fibonacci number and the shorter leg of the preceding triangle.
The first triangle in this series has sides of length 5, 4, and 3. Skipping 8, the next triangle has sides of length 13, 12 (5 + 4 + 3), and 5 (8 − 3). Skipping 21, the next triangle has sides of length 34, 30 (13 + 12 + 5), and 16 (21 − 5). This series continues indefinitely. The triangle sides a, b, c can be calculated directly:
- an=F2n−1bn=2FnFn−1cn=Fn2−Fn−12.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}a_{n}&=F_{2n-1}\[4pt]b_{n}&=2F_{n}F_{n-1}\[4pt]c_{n}&=F_{n}^{2}-F_{n-1}^{2}.end{aligned}}}
These formulas satisfy an2=bn2+cn2{displaystyle a_{n}^{2}=b_{n}^{2}+c_{n}^{2}}
Any four consecutive Fibonacci numbers Fn, Fn+1, Fn+2 and Fn+3 can also be used to generate a Pythagorean triple in a different way:[60]
- a=FnFn+3b=2Fn+1Fn+2c=Fn+12+Fn+22.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}a&=F_{n}F_{n+3}\b&=2F_{n+1}F_{n+2}\c&=F_{n+1}^{2}+F_{n+2}^{2}.end{aligned}}}
Magnitude
Since Fn is asymptotic to φn/5{displaystyle varphi ^{n}/{sqrt {5}}}

More generally, in the base b representation, the number of digits in Fn is asymptotic to nlogbφ.{displaystyle nlog _{b}varphi .}
Applications
The Fibonacci numbers are important in the computational run-time analysis of Euclid's algorithm to determine the greatest common divisor of two integers: the worst case input for this algorithm is a pair of consecutive Fibonacci numbers.[61]
Brasch et al. 2012 show how a generalised Fibonacci sequence also can be connected to the field of economics.[62] In particular, it is shown how a generalised Fibonacci sequence enters the control function of finite-horizon dynamic optimisation problems with one state and one control variable. The procedure is illustrated in an example often referred to as the Brock–Mirman economic growth model.
Yuri Matiyasevich was able to show that the Fibonacci numbers can be defined by a Diophantine equation, which led to his solving Hilbert's tenth problem.[63]
The Fibonacci numbers are also an example of a complete sequence. This means that every positive integer can be written as a sum of Fibonacci numbers, where any one number is used once at most.
Moreover, every positive integer can be written in a unique way as the sum of one or more distinct Fibonacci numbers in such a way that the sum does not include any two consecutive Fibonacci numbers. This is known as Zeckendorf's theorem, and a sum of Fibonacci numbers that satisfies these conditions is called a Zeckendorf representation. The Zeckendorf representation of a number can be used to derive its Fibonacci coding.
Fibonacci numbers are used by some pseudorandom number generators.
They are also used in planning poker, which is a step in estimating in software development projects that use the Scrum (software development) methodology.
Fibonacci numbers are used in a polyphase version of the merge sort algorithm in which an unsorted list is divided into two lists whose lengths correspond to sequential Fibonacci numbers – by dividing the list so that the two parts have lengths in the approximate proportion φ. A tape-drive implementation of the polyphase merge sort was described in The Art of Computer Programming.
Fibonacci numbers arise in the analysis of the Fibonacci heap data structure.
The Fibonacci cube is an undirected graph with a Fibonacci number of nodes that has been proposed as a network topology for parallel computing.
A one-dimensional optimization method, called the Fibonacci search technique, uses Fibonacci numbers.[64]
The Fibonacci number series is used for optional lossy compression in the IFF 8SVX audio file format used on Amiga computers. The number series compands the original audio wave similar to logarithmic methods such as µ-law.[65][66]
Since the conversion factor 1.609344 for miles to kilometers is close to the golden ratio (denoted φ), the decomposition of distance in miles into a sum of Fibonacci numbers becomes nearly the kilometer sum when the Fibonacci numbers are replaced by their successors. This method amounts to a radix 2 number register in golden ratio base φ being shifted. To convert from kilometers to miles, shift the register down the Fibonacci sequence instead.[67]
In nature

Yellow Chamomile head showing the arrangement in 21 (blue) and 13 (aqua) spirals. Such arrangements involving consecutive Fibonacci numbers appear in a wide variety of plants.
Fibonacci sequences appear in biological settings,[11] in two consecutive Fibonacci numbers, such as branching in trees, arrangement of leaves on a stem, the fruitlets of a pineapple,[12] the flowering of artichoke, an uncurling fern and the arrangement of a pine cone,[13] and the family tree of honeybees.[68] However, numerous poorly substantiated claims of Fibonacci numbers or golden sections in nature are found in popular sources, e.g., relating to the breeding of rabbits in Fibonacci's own unrealistic example, the seeds on a sunflower, the spirals of shells, and the curve of waves.[69]
Przemysław Prusinkiewicz advanced the idea that real instances can in part be understood as the expression of certain algebraic constraints on free groups, specifically as certain Lindenmayer grammars.[70]

Illustration of Vogel's model for n = 1 ... 500
A model for the pattern of florets in the head of a sunflower was proposed by H. Vogel in 1979.[71] This has the form
- θ=2πϕ2n, r=cn{displaystyle theta ={frac {2pi }{phi ^{2}}}n, r=c{sqrt {n}}}
where n is the index number of the floret and c is a constant scaling factor; the florets thus lie on Fermat's spiral. The divergence angle, approximately 137.51°, is the golden angle, dividing the circle in the golden ratio. Because this ratio is irrational, no floret has a neighbor at exactly the same angle from the center, so the florets pack efficiently. Because the rational approximations to the golden ratio are of the form F(j):F(j + 1), the nearest neighbors of floret number n are those at n ± F(j) for some index j, which depends on r, the distance from the center. It is often said that sunflowers and similar arrangements have 55 spirals in one direction and 89 in the other (or some other pair of adjacent Fibonacci numbers), but this is true only of one range of radii, typically the outermost and thus most conspicuous.[72]
The bee ancestry code
Fibonacci numbers also appear in the pedigrees of idealized honeybees, according to the following rules:
- If an egg is laid by an unmated female, it hatches a male or drone bee.
- If, however, an egg was fertilized by a male, it hatches a female.
Thus, a male bee always has one parent, and a female bee has two.
If one traces the pedigree of any male bee (1 bee), he has 1 parent (1 bee), 2 grandparents, 3 great-grandparents, 5 great-great-grandparents, and so on. This sequence of numbers of parents is the Fibonacci sequence. The number of ancestors at each level, Fn, is the number of female ancestors, which is Fn−1, plus the number of male ancestors, which is Fn−2.[73] This is under the unrealistic assumption that the ancestors at each level are otherwise unrelated.
The human X chromosome inheritance tree

The number of possible ancestors on the X chromosome inheritance line at a given ancestral generation follows the Fibonacci sequence. (After Hutchison, L. "Growing the Family Tree: The Power of DNA in Reconstructing Family Relationships".[74])
Luke Hutchison noticed that the number of possible ancestors on the X chromosome inheritance line at a given ancestral generation also follows the Fibonacci sequence.[74] A male individual has an X chromosome, which he received from his mother, and a Y chromosome, which he received from his father. The male counts as the "origin" of his own X chromosome (F1=1{displaystyle F_{1}=1}




Generalizations
The Fibonacci sequence has been generalized in many ways. These include:
- Generalizing the index to negative integers to produce the negafibonacci numbers.
- Generalizing the index to real numbers using a modification of Binet's formula.[37]
- Starting with other integers. Lucas numbers have L1 = 1, L2 = 3, and Ln = Ln−1 + Ln−2. Primefree sequences use the Fibonacci recursion with other starting points to generate sequences in which all numbers are composite.
- Letting a number be a linear function (other than the sum) of the 2 preceding numbers. The Pell numbers have Pn = 2Pn − 1 + Pn − 2.
- Not adding the immediately preceding numbers. The Padovan sequence and Perrin numbers have P(n) = P(n − 2) + P(n − 3).
- Generating the next number by adding 3 numbers (tribonacci numbers), 4 numbers (tetranacci numbers), or more. The resulting sequences are known as n-Step Fibonacci numbers.[75]
- Adding other objects than integers, for example functions or strings – one essential example is Fibonacci polynomials.
See also
- Elliott wave principle
- Embree–Trefethen constant
- Fibonacci numbers in popular culture
- Fibonacci word
- The Fibonacci Association
- Verner Emil Hoggatt Jr.
- Wythoff array
References
Footnotes
^ "For four, variations of meters of two [and] three being mixed, five happens. For five, variations of two earlier – three [and] four, being mixed, eight is obtained. In this way, for six, [variations] of four [and] of five being mixed, thirteen happens. And like that, variations of two earlier meters being mixed, seven morae [is] twenty-one. In this way, the process should be followed in all mātrā-vṛttas" [17]
Citations
^ ab Beck & Geoghegan 2010.
^ ab Bóna 2011, p. 180.
^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A000045". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ John Hudson Tiner (200). Exploring the World of Mathematics: From Ancient Record Keeping to the Latest Advances in Computers. New Leaf Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-61458-155-0.
^ Lucas 1891, p. 3.
^ ab Pisano 2002, pp. 404–5.
^ abc Goonatilake, Susantha (1998), Toward a Global Science, Indiana University Press, p. 126, ISBN 978-0-253-33388-9
^ ab Singh, Parmanand (1985), "The So-called Fibonacci numbers in ancient and medieval India", Historia Mathematica, 12 (3): 229–44, doi:10.1016/0315-0860(85)90021-7
^ ab Knuth, Donald (2006), The Art of Computer Programming, 4. Generating All Trees – History of Combinatorial Generation, Addison–Wesley, p. 50, ISBN 978-0-321-33570-8,it was natural to consider the set of all sequences of [L] and [S] that have exactly m beats. ...there are exactly Fm+1 of them. For example the 21 sequences when m = 7 are: [gives list]. In this way Indian prosodists were led to discover the Fibonacci sequence, as we have observed in Section 1.2.8 (from v.1)
^ Wolfram, Stephen (2002). A New Kind of Science. Wolfram Media, Inc. p. 891. ISBN 978-1-57955-008-0.
^ ab Douady, S; Couder, Y (1996), "Phyllotaxis as a Dynamical Self Organizing Process" (PDF), Journal of Theoretical Biology, 178 (3): 255–74, doi:10.1006/jtbi.1996.0026, archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-05-26
^ ab Jones, Judy; Wilson, William (2006), "Science", An Incomplete Education, Ballantine Books, p. 544, ISBN 978-0-7394-7582-9
^ ab Brousseau, A (1969), "Fibonacci Statistics in Conifers", Fibonacci Quarterly (7): 525–32
^ Knuth, Donald (1968), The Art of Computer Programming, 1, Addison Wesley, p. 100, ISBN 978-81-7758-754-8,Before Fibonacci wrote his work, the sequence Fn had already been discussed by Indian scholars, who had long been interested in rhythmic patterns... both Gopala (before 1135 AD) and Hemachandra (c. 1150) mentioned the numbers 1,2,3,5,8,13,21 explicitly [see P. Singh Historia Math 12 (1985) 229–44]" p. 100 (3d ed)...
^ Agrawala, VS (1969), Pāṇinikālīna Bhāratavarṣa (Hn.). Varanasi-I: TheChowkhamba Vidyabhawan,SadgurushiShya writes that Pingala was a younger brother of Pāṇini [Agrawala 1969, lb]. There is an alternative opinion that he was a maternal uncle of Pāṇini [Vinayasagar 1965, Preface, 121]. ... Agrawala [1969, 463–76], after a careful investigation, in which he considered the views of earlier scholars, has concluded that Pāṇini lived between 480 and 410 BC
^ Singh, Parmanand (1985). "The So-called Fibonacci Numbers in Ancient and Medieval India" (PDF). Historia Mathematica. Academic Press. 12: 232.
^ Velankar, HD (1962), 'Vṛttajātisamuccaya' of kavi Virahanka, Jodhpur: Rajasthan Oriental Research Institute, p. 101
^ "Fibonacci's Liber Abaci (Book of Calculation)". The University of Utah. 13 December 2009. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
^ Hemenway, Priya (2005). Divine Proportion: Phi In Art, Nature, and Science. New York: Sterling. pp. 20–21. ISBN 1-4027-3522-7.
^ Knott, Dr. Ron (25 September 2016). "The Fibonacci Numbers and Golden section in Nature - 1". University of Surrey. Retrieved 27 November 2018.
^ Knott, Ron. "Fibonacci's Rabbits". University of Surrey Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences.
^ Gardner, Martin (1996), Mathematical Circus, The Mathematical Association of America, p. 153, ISBN 978-0-88385-506-5,It is ironic that Leonardo, who made valuable contributions to mathematics, is remembered today mainly because a 19th-century French number theorist, Édouard Lucas... attached the name Fibonacci to a number sequence that appears in a trivial problem in Liber abaci
^ Knott, R, "Fib table", Fibonacci, UK: Surrey has the first 300 Fn factored into primes and links to more extensive tables.
^ Knuth, Donald (2008-12-11), "Negafibonacci Numbers and the Hyperbolic Plane", Annual meeting, The Fairmont Hotel, San Jose, CA: The Mathematical Association of America
^ Lucas 1891, p. 7.
^ Stanley, Richard (2011). Enumerative Combinatorics I (2nd ed.). Cambridge Univ. Press. p. "121, Ex 1.35". ISBN 978-1-107-60262-5.
^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Binet's Fibonacci Number Formula". MathWorld.
^ Ball 2003, p. 156.
^ Ball 2003, pp. 155–6.
^ Kepler, Johannes (1966), A New Year Gift: On Hexagonal Snow, Oxford University Press, p. 92, ISBN 978-0-19-858120-8
^ Strena seu de Nive Sexangula, 1611
^ Dijkstra, Edsger W. (1978), In honour of Fibonacci (PDF)
^ Gessel, Ira (October 1972), "Fibonacci is a Square" (PDF), The Fibonacci Quarterly, 10 (4): 417–19, retrieved April 11, 2012
^ Lucas 1891, p. 4.
^ Vorobiev, Nikolaĭ Nikolaevich; Martin, Mircea (2002), "Chapter 1", Fibonacci Numbers, Birkhäuser, pp. 5–6, ISBN 978-3-7643-6135-8
^ Flajolet, Philippe; Sedgewick, Robert (2009). Analytic Combinatorics. Cambridge University Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0521898065.
^ abc Weisstein, Eric W. "Fibonacci Number". MathWorld.
^ Glaister, P (1995), "Fibonacci power series", The Mathematical Gazette, 79 (486): 521–525, doi:10.2307/3618079, JSTOR 3618079
^ Köhler, Günter (February 1985), "Generating functions of Fibonacci-like sequences and decimal expansions of some fractions" (PDF), The Fibonacci Quarterly, 23 (1): 29–35, retrieved December 31, 2011
^ André-Jeannin, Richard (1989), "Irrationalité de la somme des inverses de certaines suites récurrentes", Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série I, 308 (19): 539–541, MR 0999451
^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Millin Series". MathWorld.
^ Ribenboim, Paulo (2000), My Numbers, My Friends, Springer-Verlag
^ Su, Francis E (2000), "Fibonacci GCD's, please", Mudd Math Fun Facts, et al, HMC
^ Williams, H. C. (1982), "A note on the Fibonacci quotient Fp−ε/p{displaystyle F_{p-varepsilon }/p}", Canadian Mathematical Bulletin, 25 (3): 366–370, doi:10.4153/CMB-1982-053-0, MR 0668957. Williams calls this property "well known".
^ Prime Numbers, Richard Crandall, Carl Pomerance, Springer, second edition, 2005, p.142.
^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Fibonacci Prime". MathWorld.
^ Honsberger, Ross (1985), "Mathematical Gems III", AMS Dolciani Mathematical Expositions (9): 133, ISBN 978-0-88385-318-4
^ Cohn, JHE (1964), "Square Fibonacci Numbers etc", Fibonacci Quarterly, 2: 109–13
^ Pethő, Attila (2001), "Diophantine properties of linear recursive sequences II", Acta Mathematica Academiae Paedagogicae Nyíregyháziensis, 17: 81–96
^ Bugeaud, Y; Mignotte, M; Siksek, S (2006), "Classical and modular approaches to exponential Diophantine equations. I. Fibonacci and Lucas perfect powers", Ann. Math., 2 (163): 969–1018, arXiv:math/0403046, Bibcode:2004math......3046B, doi:10.4007/annals.2006.163.969
^ Ming, Luo (1989), "On triangular Fibonacci numbers" (PDF), Fibonacci Quart., 27 (2): 98–108
^ Knott, Ron, The Fibonacci numbers, UK: Surrey
^ Ribenboim, Paulo (1996), The New Book of Prime Number Records, New York: Springer, p. 64, ISBN 978-0-387-94457-9
^ Lemmermeyer 2000, pp. 73–4, ex. 2.25–28.
^ Lemmermeyer 2000, pp. 73–4, ex. 2.28.
^ Lemmermeyer 2000, p. 73, ex. 2.27.
^ Fibonacci and Lucas factorizations, Mersennus collects all known factors of F(i) with i < 10000.
^ Factors of Fibonacci and Lucas numbers, Red golpe collects all known factors of F(i) with 10000 < i < 50000.
^ Freyd, Peter; Brown, Kevin S. (1993), "Problems and Solutions: Solutions: E3410", The American Mathematical Monthly, 99 (3): 278–279, doi:10.2307/2325076, JSTOR 2325076
^ Koshy, Thomas (2007), Elementary number theory with applications, Academic Press, p. 581, ISBN 978-0-12-372487-8
^ Knuth, Donald E (1997), The Art of Computer Programming, 1: Fundamental Algorithms (3rd ed.), Addison–Wesley, p. 343, ISBN 978-0-201-89683-1
^ Brasch, T. von; Byström, J.; Lystad, L.P. (2012), "Optimal Control and the Fibonacci Sequence", Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 154 (3): 857–78, doi:10.1007/s10957-012-0061-2, hdl:11250/180781
^ Harizanov, Valentina (1995), "Review of Yuri V. Matiyasevich, Hibert's Tenth Problem", Modern Logic, 5 (3): 345–355.
^ Avriel, M; Wilde, DJ (1966), "Optimality of the Symmetric Fibonacci Search Technique", Fibonacci Quarterly (3): 265–9
^ Amiga ROM Kernel Reference Manual, Addison–Wesley, 1991
^ "IFF", Multimedia Wiki
^ "Zeckendorf representation", Encyclopedia of Math
^ "Marks for the da Vinci Code: B–". Maths. Computer Science For Fun: CS4FN.
^ Simanek, D. "Fibonacci Flim-Flam". LHUP. Archived from the original on 2010-02-01.
^ Prusinkiewicz, Przemyslaw; Hanan, James (1989), Lindenmayer Systems, Fractals, and Plants (Lecture Notes in Biomathematics), Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-97092-9
^ Vogel, H (1979), "A better way to construct the sunflower head", Mathematical Biosciences, 44 (3–4): 179–89, doi:10.1016/0025-5564(79)90080-4
^ Prusinkiewicz, Przemyslaw; Lindenmayer, Aristid (1990), The Algorithmic Beauty of Plants, Springer-Verlag, pp. 101–7, ISBN 978-0-387-97297-8
^ "The Fibonacci sequence as it appears in nature" (PDF), The Fibonacci Quarterly, 1 (1): 53–56, 1963
^ ab Hutchison, Luke (September 2004). "Growing the Family Tree: The Power of DNA in Reconstructing Family Relationships" (PDF). Proceedings of the First Symposium on Bioinformatics and Biotechnology (BIOT-04). Retrieved 2016-09-03.
^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Fibonacci n-Step Number". MathWorld.
Works cited
Ball, Keith M (2003), "8: Fibonacci's Rabbits Revisited", Strange Curves, Counting Rabbits, and Other Mathematical Explorations, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-11321-0.
Beck, Matthias; Geoghegan, Ross (2010), The Art of Proof: Basic Training for Deeper Mathematics, New York: Springer, ISBN 978-1-4419-7022-0.
Bóna, Miklós (2011), A Walk Through Combinatorics (3rd ed.), New Jersey: World Scientific, ISBN 978-981-4335-23-2.
Bóna, Miklós (2016), A Walk Through Combinatorics (4th Revised ed.), New Jersey: World Scientific, ISBN 978-981-3148-84-0.
Lemmermeyer, Franz (2000), Reciprocity Laws: From Euler to Eisenstein, Springer Monographs in Mathematics, New York: Springer, ISBN 978-3-540-66957-9.
Lucas, Édouard (1891), Théorie des nombres (in French), 1, Paris: Gauthier-Villars, https://books.google.com/books?id=_hsPAAAAIAAJ.
Pisano, Leonardo (2002), Fibonacci's Liber Abaci: A Translation into Modern English of the Book of Calculation, Sources and Studies in the History of Mathematics and Physical Sciences, Sigler, Laurence E, trans, Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-95419-6
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Fibonacci number |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Fibonacci number program |
Periods of Fibonacci Sequences Mod m at MathPages- Scientists find clues to the formation of Fibonacci spirals in nature
Fibonacci Sequence on In Our Time at the BBC
Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001) [1994], "Fibonacci numbers", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
OEIS sequence A000045 (Fibonacci numbers)



















![{displaystyle F_{n}=left[{frac {varphi ^{n}}{sqrt {5}}}right], ngeq 0,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f284c42fe2e2d38c49ba4d1a8a3f16eb5afed8ed)








































































![{begin{aligned}a_{n}&=F_{2n-1}\[4pt]b_{n}&=2F_{n}F_{n-1}\[4pt]c_{n}&=F_{n}^{2}-F_{n-1}^{2}.end{aligned}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/075b65f38d3430a6810dc2aa094fcc22ee0c5900)