Arabic numerals
| Numeral systems |
|---|
 |
Hindu–Arabic numeral system |
|
East Asian |
|
Alphabetic |
|
Former |
|
Positional systems by base |
|
Non-standard positional numeral systems |
|
List of numeral systems |
Arabic numerals, also called Hindu–Arabic numerals,[1][2] are the ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9; or numerals written using them[a] in the Hindu–Arabic numeral system[5] (where the position of a digit indicates the power of 10 to multiply it by). It is the most common system for the symbolic representation of numbers in the world today.
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system was developed by Indian mathematicians around AD 500[5] using quite different forms of the numerals. From India, the system was adopted by Arabic mathematicians in Baghdad and passed on to the Arabs farther west. The current form of the numerals developed in North Africa. It was in the North African city of Bejaia that the Italian scholar Fibonacci first encountered the numerals; his work was crucial in making them known throughout Europe. The use of Arabic numerals spread around the world through European trade, books and colonialism.
The term Arabic numerals is ambiguous, it may also be intended to mean the numerals used by Arabs, in which case it generally refers to the Eastern Arabic numerals. Although the phrase "Arabic numeral" is frequently capitalized, it is sometimes written in lower case: for instance in its entry in the Oxford English Dictionary,[6] which helps to distinguish it from "Arabic numerals" as the Eastern Arabic numerals.
Alternative names are Western Arabic numerals, Western numerals, Hindu–Arabic numerals and Unicode calls them digits.[7]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Origins
1.1.1 Popular myths
1.2 Adoption in Europe
1.3 Adoption in Russia
1.4 Adoption in China
2 Evolution of symbols
2.1 Encoding
3 See also
4 Notes
5 References
6 Sources
7 Further reading
8 External links
History
Origins

The numeral "zero" as it appears in two numbers (50 and 270) in an inscription in Gwalior. Dated to the 9th century.[8][9]
The decimal Hindu–Arabic numeral system with zero was developed in India by around AD 700.[10] The development was gradual, spanning several centuries, but the decisive step was probably provided by Brahmagupta's formulation of zero as a number in AD 628. The system was revolutionary by including zero in positional notation, thereby limiting the number of individual digits to ten. It is considered an important milestone in the development of mathematics. One may distinguish between this positional system, which is identical throughout the family, and the precise glyphs used to write the numerals, which varied regionally.
The first universally accepted inscription containing the use of the 0 glyph in India is first recorded in the 9th century, in an inscription at Gwalior in Central India dated to 870. Numerous Indian documents on copper plates exist, with the same symbol for zero in them, dated back as far as the 6th century AD, but their dates are uncertain. Inscriptions in Indonesia and Cambodia dating to AD 683 have also been found.[11]

Brahmi numerals (lower row) in India in the 1st century AD

The numerals used in the Bakhshali manuscript, dated to sometime between the 3rd and 7th century AD.

Modern-day Arab telephone keypad with two forms of Arabic numerals: Western Arabic/European numerals on the left and Eastern Arabic numerals on the right
The numeral system came to be known to the court of Baghdad, where mathematicians such as the Persian Al-Khwarizmi, whose book On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals was written about 825 in Arabic, and the Arab mathematician Al-Kindi, who wrote four volumes, On the Use of the Indian Numerals (Ketab fi Isti'mal al-'Adad al-Hindi) about 830, propagated it in the Arab world. Their work was principally responsible for the diffusion of the Indian system of numeration in the Middle East and the West.[12]
In the 10th century, Middle-Eastern mathematicians extended the decimal numeral system to include fractions, as recorded in a treatise by Syrian mathematician Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi in 952–953. The decimal point notation was introduced by Sind ibn Ali, who also wrote the earliest treatise on Arabic numerals.
A distinctive West Arabic variant of the symbols begins to emerge around the 10th century in the Maghreb and Al-Andalus (sometimes called ghubar numerals, though the term is not always accepted), which are the direct ancestor of the modern "Arabic numerals" used throughout the world.[13]
Woepecke has proposed that the Western Arabic numerals were already in use in Spain before the arrival of the Moors, purportedly received via Alexandria, but this theory is not accepted by scholars.[14][15][16]
Popular myths
Some popular myths have argued that the original forms of these symbols indicated their numeric value through the number of angles they contained, but no evidence exists of any such origin.[17]
Adoption in Europe

Adoption of the Hindu numerals through the Arabs by Europe

Woodcut showing the 16th century astronomical clock of Uppsala Cathedral, with two clockfaces, one with Arabic and one with Roman numerals.

A German manuscript page teaching use of Arabic numerals (Talhoffer Thott, 1459). At this time, knowledge of the numerals was still widely seen as esoteric, and Talhoffer presents them with the Hebrew alphabet and astrology.

Late 18th-century French revolutionary "decimal" clockface.
In 825 Al-Khwārizmī wrote a treatise in Arabic, On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals,[18] which survives only as the 12th-century Latin translation, Algoritmi de numero Indorum.[19][20]Algoritmi, the translator's rendition of the author's name, gave rise to the word algorithm.[21]
The first mentions of the numerals in the West are found in the Codex Vigilanus of 976.[22]
From the 980s, Gerbert of Aurillac (later, Pope Sylvester II) used his position to spread knowledge of the numerals in Europe. Gerbert studied in Barcelona in his youth. He was known to have requested mathematical treatises concerning the astrolabe from Lupitus of Barcelona after he had returned to France.
Leonardo Fibonacci (Leonardo of Pisa), a mathematician born in the Republic of Pisa who had studied in Béjaïa (Bougie), Algeria, promoted the Indian numeral system in Europe with his 1202 book Liber Abaci:
When my father, who had been appointed by his country as public notary in the customs at Bugia acting for the Pisan merchants going there, was in charge, he summoned me to him while I was still a child, and having an eye to usefulness and future convenience, desired me to stay there and receive instruction in the school of accounting. There, when I had been introduced to the art of the Indians' nine symbols through remarkable teaching, knowledge of the art very soon pleased me above all else and I came to understand it.
The numerals are arranged with their lowest value digit to the right, with higher value positions added to the left. This arrangement is the same in Arabic as well as the Indo-European languages.
The reason the digits are more commonly known as "Arabic numerals" in Europe and the Americas is that they were introduced to Europe in the 10th century by Arabic-speakers of North Africa, who were then using the digits from Libya to Morocco. Arabs, on the other hand, call the base-10 system (not just these digits) "Hindu numerals",[23][24] referring to their origin in India. This is not to be confused with what the Arabs call the "Hindi numerals", namely the Eastern Arabic numerals (.mw-parser-output .script-arabic,.mw-parser-output .script-Arab{font-family:Scheherazade,Lateef,LateefGR,Amiri,"Noto Naskh Arabic","Droid Arabic Naskh",Harmattan,"Arabic Typesetting","Traditional Arabic","Simplified Arabic","Times New Roman",Arial,"Sakkal Majalla","Microsoft Uighur",Calibri,"Microsoft Sans Serif","Segoe UI",serif,sans-serif;font-weight:normal}٠ - ١ - ٢ - ٣ -٤ - ٥ - ٦ - ٧ - ٨ - ٩) used in the Middle East, or any of the numerals currently used in Indian languages (e.g. Devanagari: ०.१.२.३.४.५.६.७.८.९).[17]
The European acceptance of the numerals was accelerated by the invention of the printing press, and they became widely known during the 15th century. Early evidence of their use in Britain includes: an equal hour horary quadrant from 1396,[25] in England, a 1445 inscription on the tower of Heathfield Church, Sussex; a 1448 inscription on a wooden lych-gate of Bray Church, Berkshire; and a 1487 inscription on the belfry door at Piddletrenthide church, Dorset; and in Scotland a 1470 inscription on the tomb of the first Earl of Huntly in Elgin Cathedral. (See G.F. Hill, The Development of Arabic Numerals in Europe for more examples.) In central Europe, the King of Hungary Ladislaus the Posthumous, started the use of Arabic numerals, which appear for the first time in a royal document of 1456.[26] By the mid-16th century, they were in common use in most of Europe.[27]Roman numerals remained in use mostly for the notation of anno Domini years, and for numbers on clockfaces.
Today, Roman numerals are still used for enumeration of lists (as an alternative to alphabetical enumeration), for sequential volumes, to differentiate monarchs or family members with the same first names, and (in lower case) to number pages in prefatory material in books.
Adoption in Russia
Cyrillic numerals were a numbering system derived from the Cyrillic alphabet, used by South and East Slavic peoples. The system was used in Russia as late as the early 18th century when Peter the Great replaced it with Arabic numerals.
Adoption in China

Iron plate with an order 6 magic square in Persian/ Arabic numbers from China, dating to the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368).
Arabic numerals were introduced to China during the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368) by the Muslim Hui people. In the early 17th century, European-style Arabic numerals were introduced by Spanish and Portuguese Jesuits.[28][29][30]
Evolution of symbols
The numeral system employed, known as algorism, is positional decimal notation. Various symbol sets are used to represent numbers in the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, potentially including both symbols that evolved from the Brahmi numerals, and symbols that developed independently. The symbols used to represent the system have split into various typographical variants since the Middle Ages:
- The widespread Western Arabic numerals used with the Latin script, in the table below labelled European, descended from the West Arabic numerals developed in al-Andalus (Andalucía, Spain) and the Maghreb. Spanish scholars, because of the geographic proximity, trade, and constant warfare with the Muslim kingdoms of Southern Spain, saw a potential in the simplicity of Arabic numbers, and decided to adopt those symbols, and later other Europeans followed suit. There are two typographic styles for rendering European numerals, known as lining figures and text figures.
- The Arabic–Indic or Eastern Arabic numerals, used with the Arabic script, developed primarily in what is now Iraq. A variant of the Eastern Arabic numerals used in the Persian and Urdu languages is shown below as East Arabic-Indic.
- The Devanagari numerals used with Devanagari and related variants are grouped as Indian numerals.
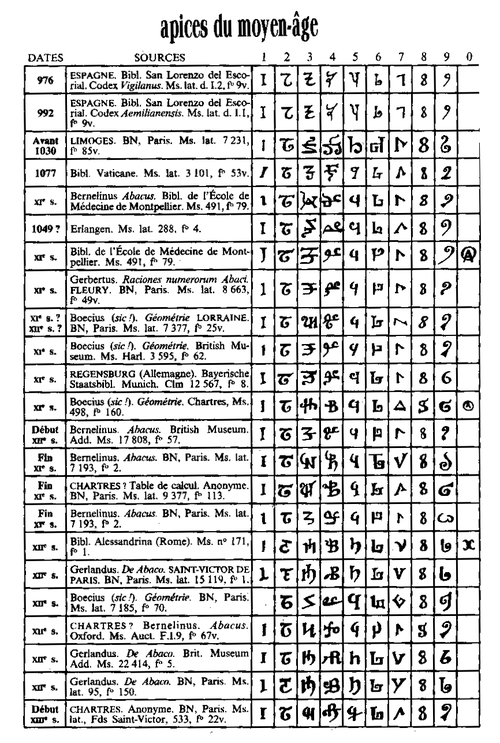
The evolution of the numerals in early Europe is shown here in a table created by the French scholar Jean-Étienne Montucla in his Histoire de la Mathematique, which was published in 1757:

Encoding
The Arabic numerals 0–9 are encoded in ASCII at positions 0x30 to 0x39. Masking to the lower 4 binary bits (or taking the last hexadecimal digit) gives the value of the digit, a great help in converting text to numbers on early computers. These positions were inherited in Unicode[31] and in virtually all other encodings based in any way on ASCII. EBCDIC used different values, but also had the lower 4 bits equal to the digit value.
| Binary | Octal | Decimal | Hex | Glyph | Unicode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0011 0000 | 060 | 48 | 30 | 0 | U+0030 DIGIT ZERO |
| 0011 0001 | 061 | 49 | 31 | 1 | U+0031 DIGIT ONE |
| 0011 0010 | 062 | 50 | 32 | 2 | U+0032 DIGIT TWO |
| 0011 0011 | 063 | 51 | 33 | 3 | U+0033 DIGIT THREE |
| 0011 0100 | 064 | 52 | 34 | 4 | U+0034 DIGIT FOUR |
| 0011 0101 | 065 | 53 | 35 | 5 | U+0035 DIGIT FIVE |
| 0011 0110 | 066 | 54 | 36 | 6 | U+0036 DIGIT SIX |
| 0011 0111 | 067 | 55 | 37 | 7 | U+0037 DIGIT SEVEN |
| 0011 1000 | 070 | 56 | 38 | 8 | U+0038 DIGIT EIGHT |
| 0011 1001 | 071 | 57 | 39 | 9 | U+0039 DIGIT NINE |
See also
- Abjad numerals
- Chinese numerals
Counting rods – decimal positional numeral system with zero- Decimal
- Greek numerals
- Japanese numerals
- Maya numerals
- Regional variations in modern handwritten Arabic numerals
Notes
^ In mathematics, a numeral means an entire sequence of digits used to represent a number.[3][4]
References
^
Schipp, Bernhard; Krämer, Walter (2008), Statistical Inference, Econometric Analysis and Matrix Algebra: Festschrift in Honour of Götz Trenkler, Springer, p. 387, ISBN 9783790821208.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Lumpkin, Beatrice; Strong, Dorothy (1995), Multicultural science and math connections: middle school projects and activities, Walch Publishing, p. 118, ISBN 9780825126598
^ Jensen, Gary R. (2003), Arithmetic for Teachers: With Applications and Topics from Geometry, American Mathematical Soc., pp. 19–20, ISBN 978-0-8218-7194-2
^ Numbers and Numerals, The MathForum, November 1998, January 2002, retrieved October 24, 2018
^ ab Bulliet, Richard; Crossley, Pamela; Headrick,, Daniel; Hirsch, Steven; Johnson, Lyman (2010). The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History, Volume 1. Cengage Learning. p. 192. ISBN 1439084742.Indian mathematicians invented the concept of zero and developed the "Arabic" numerals and system of place-value notation used in most parts of the world today
[better source needed]
^ "Arabic", Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition
^ Official Unicode Consortium code chart
^ Smith, David Eugene; Karpinski, Louis Charles (1911). The Hindu-Arabic numerals. Boston, London, Ginn and Company. p. 52.
^ For a modern image
^ O'Connor, J. J. and E. F. Robertson. 2000. Indian Numerals, MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St. Andrews, Scotland.
^ Plofker 2009, p. 45.
^ The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive
^
Kunitzsch, The Transmission of Hindu-Arabic Numerals Reconsidered 2003, pp. 12–13: "While specimens of Western Arabic numerals from the early period—the tenth to thirteenth centuries—are still not available, we know at least that Hindu reckoning (called ḥisāb al-ghubār) was known in the West from the tenth century onward..."
^
Kunitzsch, The Transmission of Hindu-Arabic Numerals Reconsidered 2003, pp. 12–13: "Since edition of and research on the Pseudo-Boethius[41] we now know that the texts running under his name and carrying Arabic numerals date from the eleventh century. Thus the assumed way of transmission from Alexandria to Spain is impossible and this theory can no longer be taken as serious."
^ Smith, D. E.; Karpinski, L. C. (2013) [first published in Boston, 1911], The Hindu-Arabic Numerals, Dover, Chapter V, ISBN 0486155110
^ Gandz, Solomon (November 1931), "The Origin of the Ghubār Numerals, or the Arabian Abacus and the Articuli", Isis, 16 (2): 393–424, doi:10.1086/346615, JSTOR 224714
^ ab Ifrah, Georges (1998). The universal history of numbers: from prehistory to the invention of the computer; translated from the French by David Bellos. London: Harvill Press. pp. 356–357. ISBN 9781860463242.
^ Philosophy Of Mathematics Francis, John – 2008 – Page 38
^ The Ellipse: A Historical and Mathematical Journey Arthur Mazer – 2011
^ "al-Khwarizmi - Muslim mathematician".
^ Models of Computation: An Introduction to Computability Theory – Page 1 Maribel Fernández – 2009
^ "MATHORIGINS.COM_V". www.mathorigins.com.
^ Rowlett, Russ (4 July 2004), Roman and "Arabic" Numerals, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, retrieved 22 June 2009
^ Achenbach, Joel (16 September 1994), Article: Take a Number, Please., The Washington Post, retrieved 22 June 2009
^ "14th century timepiece unearthed in Qld farm shed". ABC News.
^ Erdélyi: Magyar művelődéstörténet 1-2. kötet. Kolozsvár, 1913, 1918
^ Mathforum.org
^ Helaine Selin, ed. (31 July 1997). Encyclopaedia of the history of science, technology, and medicine in non-western cultures. Springer. pp. 198–. ISBN 978-0-7923-4066-9. Retrieved 3 March 2012.
^ Meuleman, Johan H. (23 August 2002). Islam in the era of globalization: Muslim attitudes towards modernity and identity. Psychology Press. p. 272. ISBN 978-0-7007-1691-3. Retrieved 3 March 2012.
^ Peng Yoke Ho (16 October 2000). Li, Qi and Shu: An Introduction to Science and Civilization in China. Courier Dover Publications. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-486-41445-4. Retrieved 3 March 2012.
^ https://www.unicode.org/charts/PDF/U0000.pdf
Sources
Kunitzsch, Paul (2003), "The Transmission of Hindu-Arabic Numerals Reconsidered", in J. P. Hogendijk; A. I. Sabra, The Enterprise of Science in Islam: New Perspectives, MIT Press, pp. 3–22, ISBN 978-0-262-19482-2
Plofker, Kim (2009), Mathematics in India, Princeton University Pres, ISBN 978-0-691-12067-6
Further reading
Ore, Oystein (1988), "Hindu-Arabic numerals", Number Theory and Its History, Dover, pp. 19–24, ISBN 0486656209.
Burnett, Charles (2006), "The Semantics of Indian Numerals in Arabic, Greek and Latin", Journal of Indian Philosophy, Springer-Netherlands, 34 (1–2): 15–30, doi:10.1007/s10781-005-8153-z.
Encyclopædia Britannica (Kim Plofker) (2007), "mathematics, South Asian", Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 189 (4761): 1–12, Bibcode:1961Natur.189S.273., doi:10.1038/189273c0, retrieved 18 May 2007.
Hayashi, Takao (1995), The Bakhshali Manuscript, An ancient Indian mathematical treatise, Groningen: Egbert Forsten, ISBN 906980087X.
Ifrah, Georges (2000), A Universal History of Numbers: From Prehistory to Computers, New York: Wiley, ISBN 0471393401.
Katz, Victor J. (ed.) (20 July 2007), The Mathematics of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, India, and Islam: A Sourcebook, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, ISBN 0691114854CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link) .
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Arabic numerals (category) |
- Development of Hindu Arabic and Traditional Chinese Arithmetic
History of Counting Systems and Numerals. Retrieved 11 December 2005.
The Evolution of Numbers. 16 April 2005.- O'Connor, J. J. and Robertson, E. F. Indian numerals. November 2000.
- History of the numerals
- Arabic numerals
- Hindu-Arabic numerals
- Numeral & Numbers' history and curiosities
Gerbert d'Aurillac's early use of Hindu-Arabic numerals at Convergence