List of seas

Marginal seas as defined by the International Maritime Organization
This is a list of seas – large divisions of the World Ocean, including areas of water variously, gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Contents
1 Terminology
2 Marginal seas
2.1 Atlantic Ocean
2.1.1 Americas
2.1.2 Europe, Africa, and Asia
2.1.3 Northern islands
2.2 Arctic Ocean
2.3 Southern Ocean
2.4 Indian Ocean
2.5 Pacific Ocean
2.5.1 Americas
2.5.2 Asia and Oceania
3 Defined by currents
4 Not included
5 See also
6 Notes
7 References
8 External links
Terminology
World Ocean – the single connected salty body of water that covers the majority of Earth's surface.
Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocean" in the name. See Borders of the oceans for details.
Sea has several definitions:[a]- A marginal sea - a marginal sea is a division of an ocean, partially enclosed by islands, archipelagos, or peninsulas, adjacent to or widely open to the open ocean at the surface, and/or bounded by submarine ridges on the sea floor.[4]
- A division of an ocean, delineated by landforms,[5] currents (e.g. Sargasso Sea), or specific latitude or longitude boundaries. This includes but is not limited to marginal seas, and this is the definition used for inclusion in this list.
- The World Ocean. For example, the Law of the Sea states that all of the World Ocean is "sea",[6][7][8][b] and this is also common usage for "the sea".
- Any large body of water with "Sea" in the name, including lakes.
- A marginal sea - a marginal sea is a division of an ocean, partially enclosed by islands, archipelagos, or peninsulas, adjacent to or widely open to the open ocean at the surface, and/or bounded by submarine ridges on the sea floor.[4]
Strait - a narrow area of water connecting two wider areas of water
There are several terms used for bulges of ocean that result from indentations of land, which overlap in definition, and which are not consistently differentiated:[10]
Bay – generic term; though most features with "Bay" in the name are small, some are very large
Gulf – a very large bay, often a top-level division of an ocean or sea
Fjord – a long bay with steep sides, typically formed by a glacier
Bight – a bay that is typically shallower than a sound
Sound – a large, wide bay which is typically deeper than a bight, or a strait
Cove – a very small, typically sheltered bay
Many features could be considered to be more than one of these, and all of these terms are used in place names inconsistently; especially bays, gulfs, and bights, which can be very large or very small. This list includes large areas of water no matter the term used in the name.
Marginal seas
Sources differ over which seas are considered marginal seas as well as which ocean a given sea is considered a marginal part of. There is no single ultimate authority on the matter.
Atlantic Ocean
Sometimes the Arctic Ocean itself is considered a marginal sea of the Atlantic,[11][12] in addition to the below.
Americas
(coast-wise north to south)
- Davis Strait
- Labrador Sea
- Gulf of St. Lawrence
Gulf of Maine
- Bay of Fundy
- Massachusetts Bay
- Cape Cod Bay
- Nantucket Sound
- Vineyard Sound
- Buzzards Bay
- Narragansett Bay
- Rhode Island Sound
- Block Island Sound
- Fishers Island Sound
Long Island Sound
- Shelter Island Sound
- Noyack Bay
- Peconic Bay
- Gardiners Bay
- Tobaccolot Bay
- Sag Harbor Bay
- Three Mile Harbor
- Long Beach Bay
- Dering Harbor
- Pipes Cove
- Southold Bay
- Flanders Bay
- Napeague Bay
- Fort Pond Bay
- North Sea Harbor
New York Bay
- Upper New York Bay
- Lower New York Bay
- Jamaica Bay
- Raritan Bay
- Sandy Hook Bay
- Delaware Bay
- Chesapeake Bay
- Albemarle Sound
- Pamlico Sound
Gulf of Mexico
- Florida Bay
- Tampa Bay
- Pensacola Bay
- Mobile Bay
- Vermillion Bay
- Bay of Campeche
Caribbean Sea
Gulf of Gonâve (Haiti)- Gulf of Honduras
- Golfo de los Mosquitos
- Gulf of Venezuela
- Gulf of Paria
- Gulf of Darién
- Argentine Sea
Europe, Africa, and Asia

The Norwegian Sea

Aegean, Adriatic, Ionian, and Tyrrhenian seas
- Norwegian Sea
North Sea
- Wadden Sea
Baltic Sea
- Archipelago Sea
- Bothnian Sea
- Central Baltic Sea
- Gulf of Riga
- Oresund Strait
- Sea of Åland
- English Channel
- Irish Sea
- Celtic Sea
Bay of Biscay
- Cantabrian Sea
Mediterranean Sea
- Adriatic Sea
Aegean Sea
- Argolic Gulf
- Myrtoan Sea
- North Euboean Gulf
- Saronic Gulf
- Sea of Crete
- South Euboean Gulf
- Icarian Sea
- Thermaic Gulf
- Thracian Sea
- Alboran Sea
- Balearic (Catalan) Sea
- Gulf of Lion
- Gulf of Sidra
Ionian Sea
- Gulf of Corinth
Levantine Sea
- Cilician Sea
- Libyan Sea
Ligurian Sea
- Gulf of Genoa
- Sea of Sardinia
Sea of Sicily
- Inland Sea, Gozo
- Tyrrhenian Sea
Sea of Marmara[13]
Black Sea[13]
Sea of Azov[13]
- Gulf of Guinea
Northern islands

The Irish Sea
(east to west)
- Irminger Sea
Denmark Strait (between Greenland and Iceland)
Irish Sea (between Ireland and Great Britain)
Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland
Sea of the Hebrides (Great Britain)
Arctic Ocean
(clockwise from 180°)
- Chukchi Sea
- East Siberian Sea
- Laptev Sea
- Kara Sea
Barents Sea (connected to Kara Sea by Kara Strait)
- Pechora Sea
- White Sea
- Queen Victoria Sea
- Wandel Sea
- Greenland Sea
Lincoln Sea (recognized by IHO but not IMO)- Baffin Bay
The Northwest Passages
- Prince Gustav Adolf Sea
- Amundsen Gulf
- (more to be listed)
- Hudson Strait
Hudson Bay
- James Bay
- Beaufort Sea
Southern Ocean
- Amundsen Sea
- Bass Strait
- Bellingshausen Sea
Cooperation Sea[c]
Cosmonauts Sea[c]
- Davis Sea
- D'Urville Sea
- Drake Passage
- Great Australian Bight
- Gulf St Vincent
- Investigator Strait
King Haakon VII Sea[c]
Lazarev Sea[c]
Mawson Sea[c]
- Riiser-Larsen Sea
- Ross Sea
- Scotia Sea
Somov Sea[c]
- Spencer Gulf
- Weddell Sea
Indian Ocean
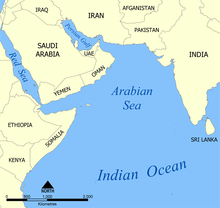
The Arabian Sea as a marginal sea of the Indian Ocean.
Andaman Sea
Gulf of Martaban – An arm of the Andaman Sea in the southern part of Burma
- Arabian Sea
- Bay of Bengal
- Gulf of Aden
- Gulf of Oman
- Laccadive Sea
- Mozambique Channel
- Persian Gulf
- Red Sea
- Timor Sea
- Palk Strait
Pacific Ocean

Coral Sea
Americas
- Bering Sea
- Chilean Sea
- Sea of Chiloé
- Gulf of Alaska
Gulf of California (also known as the Sea of Cortés)
- Mar de Grau
- Salish Sea
Asia and Oceania
- Arafura Sea
- Bali Sea
- Banda Sea
- Bismarck Sea
- Bohai Sea
Bohol Sea (also known as the Mindanao Sea)- Camotes Sea
- Celebes Sea
- Ceram Sea
- Coral Sea
- East China Sea
- Flores Sea
- Gulf of Carpentaria
- Gulf of Thailand
- Halmahera Sea
- Java Sea
- Koro Sea
- Molucca Sea
- Philippine Sea
- Savu Sea
Sea of Japan (also known as East Sea)- Sea of Okhotsk
- Seto Inland Sea
- Sibuyan Sea
- Solomon Sea
- South China Sea
- Sulu Sea
- Tasman Sea
- Visayan Sea
- Yellow Sea
Defined by currents
Sargasso Sea – North Atlantic Gyre
Not included
Entities called "seas" which are not divisions of the Earth's the World Ocean are not included in this list. Excluded are:
Salt lakes with "Sea" in the name: Aral Sea, Caspian Sea, Dead Sea, Salton Sea
Freshwater lakes with "Sea" in the name: Sea of Galilee
Extraterrestrial oceans: List of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System
- Gulfs, bays, and straits of lakes
Other items not included:
- Small fjords too numerous to list: Category: Fjords
- Small bays too numerous to list: Category: Bays
- Small sounds too numerous to list: Sound (geography)
- Small straits too numerous to list: List of straits
- Ocean gyres
- Ocean banks
See also
- Inland sea (geology)
- Oceanography
- Mediterranean sea (oceanography)
Notes
^ There is no accepted technical definition of sea among oceanographers. A rather weak definition is that a sea is a subdivision of an ocean, which means that it must have oceanic basin crust on its floor. This definition, for example, accepts the Caspian Sea, which was once part of an ancient ocean, as a sea.[1] The Introduction to Marine Biology defines a sea as a "landlocked" body of water, adding that the term "sea" is only one of convenience, but the book is written by marine biologists, not oceanographers.[2]The Glossary of Mapping Sciences similarly states that the boundaries between seas and other bodies of water are arbitrary.[3]
^ According to this definition, the Caspian would be excluded as it is legally an "international lake".[9]
^ abcdef Proposed names to the IHO 2002 draft. This draft was never approved by the IHO (or any other organization), and the 1953 IHO document (which does not contain these names which mostly originated from 1962 onward) remains currently in force.[14] Leading geographic authorities and atlases do not use these names, including the 2014 10th edition World Atlas from the National Geographic Society and the 2014 12th edition of the Times Atlas of the World. But Soviet and Russian-issued state maps do include them.[15][16]
References
^ Conforti, B; Bravo, Luigi Ferrari (2005-12-30). "The Italian Yearbook of International Law 2004". ISBN 9789004150270..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Karleskint, George; Turner, Richard L; Small, James W (2009-01-02). "Introduction to Marine Biology". ISBN 9780495561972.
^ The Glossary of the Mapping Sciences – Google Books. Books.google.co.uk. 1994. ISBN 9780784475706. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
^ American Congress on Surveying and Mapping (1994). Glossary of the mapping sciences. ASCE Publications. p. 469. ISBN 978-0-7844-0050-0. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
^ "What's the difference between an ocean and a sea?". Oceanservice.noaa.gov. 11 January 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2013.
^ Vukas, B (2004). "The Law of the Sea: Selected Writings". ISBN 9789004138636.
^ Gupta, Manoj (2010). "Indian Ocean Region: Maritime Regimes for Regional Cooperation". ISBN 9781441959898.
^ "Seven Seas - Discover The Seven Seas of the Earth". Geography.about.com. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
^ Gokay, Bulent (2001-04-07). "The Politics of Caspian Oil". ISBN 9780333739730.
^ "gulf – coastal feature".
^ James C. F. Wang (1992). Handbook on ocean politics & law. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 14–. ISBN 9780313264344. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
^ Longhurt, Alan R. (2007). Ecological Geography of the Sea. Academic Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-12-455521-1. Retrieved 2010. Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
^ abc often treated as part of Mediterranean Sea
^ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd (currently in-force) edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
^ [1]
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-09-10. Retrieved 2015-06-06.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
External links
 The dictionary definition of marginal sea at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of marginal sea at Wiktionary