Kingsley Plantation
Kingsley Plantation | |
U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
 | |
 Show map of Florida  Show map of the US | |
| Location | within the Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve, Jacksonville, Florida |
|---|---|
| Nearest city | Jacksonville, Florida, U.S. |
| Coordinates | 30°26′18″N 81°26′17″W / 30.43833°N 81.43806°W / 30.43833; -81.43806Coordinates: 30°26′18″N 81°26′17″W / 30.43833°N 81.43806°W / 30.43833; -81.43806 |
| Area | 60 acres (24.3 ha) |
| Built | 1797 or 1798 |
| Architectural style | Other |
| NRHP reference # | 70000182[1] |
| Added to NRHP | September 29, 1970 |
Kingsley Plantation (also known as the Zephaniah Kingsley Plantation Home and Buildings) is the site of a former estate in Jacksonville, Florida, that was named for an early owner, Zephaniah Kingsley, who spent 25 years there. It is located at the northern tip of Fort George Island at Fort George Inlet, and is part of the Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve managed by the U.S. National Park Service.
The plantation was originally 1,000 acres (4.0 km2), most of which has been taken over by forest; the structures and grounds of the park now comprise approximately 60 acres (242,811.385 m2).[2] Evidence of Pre-Columbian Timucua life is on the island, as are the remains of a Spanish mission named San Juan del Puerto. Under British rule in 1765, a plantation was established that cycled through several owners while Florida was transferred back to Spain and then the United States. The longest span of ownership was under Kingsley and his family, a polygamous and multiracial household controlled by and resistant to the issues of race and slavery.
Free blacks and several private owners lived at the plantation until it was transferred to the State of Florida in 1955. It was acquired by the National Park Service in 1991. The most prominent features of Kingsley Plantation are the owner's house—a structure of architectural significance built probably between 1797 and 1798 that is cited as being the oldest surviving plantation house in the state[3]—and an attached kitchen house, barn, and remains of 25 anthropologically valuable slave cabins that endured beyond the U.S. Civil War (1861–1865). The foundations of the house, kitchen, barn and the slave quarters were constructed of cement tabby, making them notably durable. Archeological evidence found in and around the slave cabins has given researchers insight into African traditions among slaves who had recently arrived in North America.
Zephaniah Kingsley wrote a defense of slavery and the three-tier social system that acknowledged the rights of free people of color that existed in Florida under Spanish rule. Kingsley briefly served on the Florida Territorial Council, planning the transition when Florida was annexed by the United States. During his time on the council, he attempted to influence Florida lawmakers to recognize free people of color and allow mixed-race children to inherit property. In addition to the architectural qualities, the site is significant as his home and that of his unique family.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Pre-Columbian settlement and colonization
1.2 Kingsley's family
1.3 Post-Kingsley inhabitants
2 Slavery on Fort George Island
3 Kingsley's house and other structures
4 Activities and restoration
5 Notes
6 Citations
7 Bibliography
8 External links
History
Pre-Columbian settlement and colonization

Shell mound left by Timucua inhabitants of Fort George Island was used as building material at Kingsley Plantation
Fort George Island is located in Duval County, several miles northeast of downtown Jacksonville. It is a marsh island at the mouth of the St. Johns River, surrounded by tidal estuaries, Little Talbot Island, and the Nassau River.[4] The north Atlantic coast of Florida had been inhabited for approximately 12,000 years when Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León landed near Cape Canaveral in 1513. The Spanish met the Saturiwa, a Timucua tribe, who were the largest group of indigenous people in the region, numbering about 14,000. Bands of Timucua extended into central Florida and south Georgia. An estimated 35 chiefdoms existed in the territory,[5] and their societies were complex with large villages sustained by fishing, hunting, and agriculture, but they frequently warred with each other and unrelated groups of Native Americans.[6] The Spanish concentrated their efforts of exploration and settlement on the Gulf Coast of Florida. By 1562, Jean Ribault led French explorers to the mouth of the St. Johns River where they built a garrison in 1564, calling it Fort Caroline. Within 200 years the population of the indigenous people of Florida was decimated by disease and constant fighting.[7] They left behind evidence of their existence in massive middens or shell mounds filled with discarded food byproducts. On Fort George Island, the shells were primarily oysters.
Ownership of Florida transferred to the United Kingdom in 1763. Spanish settlers had established missions—including one on Fort George Island named San Juan del Puerto that eventually gave the nearby St. Johns River its name—but their frequent battles with the Timucua and a decline in mission activity curbed development.[7][8] When the British controlled Florida, they established several plantations in the region. Richard Hazard owned the first plantation on Fort George Island in 1765, harvesting indigo with several dozen enslaved Africans. Spain regained ownership of Florida in 1783 after the American Revolution and recruited new Americans with promises of free land.[9]
In 1793, American Revolution veteran John "Lightning" McQueen (1751–1807) was lured to Fort George Island from South Carolina by the Spanish government, which rewarded McQueen with the island. McQueen settled with 300 slaves and constructed a large house in a unique architectural style exhibiting four corner pavilions surrounding a great room. McQueen was soon bankrupt due to misfortunes, and the possession of the plantation turned over to John McIntosh (1773–1836) from Georgia who revived it in 1804.[10] McIntosh, however, took a leading role in the Patriot Rebellion, an insurgency by Americans to hasten the annexation of Florida to the United States. The rebellion was unsuccessful, and McIntosh fled back into Georgia to escape punishment from the Spanish.[11]
Kingsley's family
Born in Bristol, England and educated in London after his family moved to colonial South Carolina, Zephaniah Kingsley (1765–1843) established his career as a slave trader and shipping magnate, which allowed him to travel widely.[12] He settled on Fort George Island in 1814 after leasing it from McIntosh. He purchased the land and buildings for $7,000 in 1817 ($94,019 in 2009). Kingsley owned several plantations around the lower St. Johns River in what is today Jacksonville, and Drayton Island in central Florida; two of them may have been managed part-time by his wife, a former slave named Anna Madgigine Jai (1793–1870).[12] Kingsley married Anna in 1806 when she was 13 years old, recently arrived in Cuba from West Africa.[13] He freed her in 1811 and charged her with running his Laurel Grove plantation at Doctors Lake in modern-day Orange Park. His legal emancipation submitted to the Spanish colonial government read
Let it be known that I ... possessed as a slave a black woman called Anna, around eighteen years of age, bought as a bozal [newly imported African][14] in the port of Havana from a slave cargo, who with the permission of the government was introduced here; the said black woman has given birth to three mulatto children: George, about 3 years 9 months, Martha, 20 months old, an Mary, one month old. And regarding the good qualities shown by the said black woman, the nicety and fidelity which she has shown me, and for other reasons, I have resolved to set her free ... and the same to her three children.[15]

Etching of the owner's house on Fort George Island, showing one of the unique pavilions
Marriages between white plantation owners and African women were common in East Florida.[16] The Spanish government provided for a separate class of free people of color, and encouraged slaves to purchase their freedom. Slavery under Spain in Florida was not considered a lifelong condition, and free blacks were involved in the economic development of the region, many of them owning their own slaves.[17] Anna oversaw 60 slaves at Fort George Island which grew sea island cotton, citrus, corn, sugarcane, beans, and potatoes. John Maxwell, the fourth child, was born in 1824 when Kingsley and Anna lived on Fort George Island.[18] Kingsley also maintained relationships with three other African women who acted as co-wives or concubines: Flora H., Sarah M.; and Munsilna McGundo. Anna Jai remained the matriarch in the polygamous family. Historian Daniel Schafer posits that Anna Jai would have been familiar with the concepts of polygamy and marrying a slave master to acquire one's freedom.[19][note 1] Visitors to the plantation were invited to a dinner table where Kingsley displayed his multi-racial children with pride. He provided them with the best education he could afford, and considered them a shield from any potential racial uprising.[12]
Authors of an ethnological study of slavery at Kingsley Plantation characterized Kingsley as a man of complex paradoxes, defiantly proud of his success as a slaveholder, yet dedicated to his multiracial family.[20] Kingsley published a defense of slavery in 1828, identifying himself only as "An Inhabitant of Florida". He rationalized the institution as a necessary condition for any society, beneficial to owner and slave alike, and to the overall economy.[21] He did not consider race the only factor that should determine servitude status, writing, "Few, I think will deny that color and condition, if properly considered, are two very separate qualities ... our legislators ... have mistaken the shadow for the substance, and confounded together two very different things; thereby substantiating by law a dangerous and inconvenient antipathy, which can have no better foundation than prejudice."[21] In 1823 President James Monroe appointed Kingsley to Florida's Territorial Council, where he tried to persuade them to define the rights of free people of color. When it became apparent to him that they could not, he resigned.[22] The council passed laws that increasingly restricted the rights which free blacks enjoyed under Spanish control. The treatise was Kingsley's response to these restrictions; he favored the Spanish three-tier system of white landowners, black slaves, and freed blacks.[21][23] The pamphlet was reprinted again in 1834, and Southerners used its arguments to defend slavery in debates leading to the Civil War.
The Florida Territorial Council passed laws forbidding interracial marriage and the right of free blacks or mixed race descendants to inherit property. To avoid difficulties with the new government in what he termed its "spirit of intolerant prejudice", Kingsley sent his wives, children, and a few slaves to Haiti, by that time free black republic. His two daughters had already each married white planters and remained in Florida.[24][25] He sold the plantation to his nephew, Kingsley Beatty Gibbs in 1839, and transferred some of the slaves to his plantation in San Jose, now a neighborhood in Jacksonville.[note 2] Kingsley started a plantation in Haiti that was worked by former Fort George Island slaves, who had become indentured servants; slavery was not allowed in Haiti. They were to earn their freedom in nine years.[17] In 1842 Kingsley gave an interview to the abolitionist Lydia Child. When she asked him if he was aware that his occupation as a slave trader might be perceived as being akin to piracy, he responded "Yes; and I am glad of it. They will look upon a slaveholder just so, by and by. Slave trading was a very respectable business when I was young. The first merchants in England and America were engaged in it. Some people hide things which they think other people don’t like. I never conceal anything."[26]
He went on to exhibit considerable pride in the Haitian plantation built with the help of his sons:
I wish you would go there. [Anna] would give you the best in the house. You ought to go, to see how happy the human race can be. It is a fine, rich valley, about thirty miles from Port Platte; heavily timbered with mahogany all round; well watered; flowers so beautiful; fruits in abundance, so delicious that you could not refrain from stopping to eat, till you could eat no more. My sons have laid out good roads, and built bridges and mills; the people are improving, and everything is prosperous.[14]
Kingsley died in the next year, while en route to New York City to work on a land deal.[27] Anna returned to Florida in 1846 to settle an inheritance dispute with some of her husband's white relatives; because the will had been made under Spanish law, when inheritance by free blacks was legal, the court ruled in her favor and control of the Kingsley's holdings in Florida remained with her and her children for several years.[28] Kingsley Beatty Gibbs sold the Fort George Island plantation in 1852 and moved to St Augustine.[29]
Post-Kingsley inhabitants

Esther Bartley, born a slave on the plantation, shown living on the grounds in the early 20th century
Anna Jai moved with about 70 former slaves to the Arlington neighborhood of Jacksonville to live out her remaining years. The ownership of the island and farms immediately following its sale by Gibbs is unknown, but after the American Civil War, the Freedmen's Bureau managed the island and recently emancipated freedmen lived in the former slave quarters and farmed the land.[30] A New Hampshire farmer named John Rollins purchased the island in 1869 and, finding agriculture in Florida not as successful as he wished, transitioned the island into a tourist resort, building a large luxury hotel and attracting celebrities such as banker William Astor and writer Harriet Beecher Stowe. The slave quarters were displayed as tourist attractions. After the hotel burned down in 1888, the Rollins family successfully cultivated citrus until a freeze in 1894 destroyed their crop. Rollins' daughter's family was the last to live in the main house; she sold the island to private investors in 1923.[31]
Two clubs were constructed on the island for wealthy Jacksonville residents. One used the plantation house as a headquarters until they constructed their own building. Private clubs were popular until the Great Depression and they subsequently went out of fashion during World War II. The Florida Park Service acquired most of Fort George Island in 1955, including the plantation houses, barn, and slave quarters, calling it the Kingsley Plantation State Historic Site. An effort to restore the property to its appearance while the Kingsley family was in residence began in 1967.[32] The Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve was created by the National Park Service and established under President Ronald Reagan in 1988. Several sites, including Fort Caroline and other ecologically significant properties in Jacksonville, are under the management of the Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve. Kingsley Plantation was transferred to the National Park Service in 1991.[33]
Slavery on Fort George Island
Labor at Kingsley Plantation was carried out by the task system: each slave was given an assigned set of tasks for the day, such as processing 20–30 lb (9–14 kg) of cotton or constructing three barrels for a slave who was a cooper. When the day's jobs were completed, slaves were free to do as they chose.[34] Kingsley Beatty Gibbs described the task system in his journal:
October 5, 1841—No work was done today, as all the people have it to gather their own crop—It is a rule which we have, to give all the negroes one day in the spring to plant, and one day in the fall to reap, and as there is a rule on Sea Island plantations fixing the tasks required each day to be done, it occurs, during the long days of summer, that the hand is generally done his task by 2 p.m., often sooner, so they have abundance of time to work their own crop, fish, etc., etc.[35]
This task system of slavery was common among sea island plantations in the Southeastern United States. In contrast, cotton and tobacco plantations in Virginia and other parts of the South practiced the gang system, where an overseer who was also a slave drove slaves to work the entire day.[34]

Row of slave house ruins as they appeared in 2007; the forested area behind them was where the fields were located

Slave overseer's house restored by the National Park Service
Slaves on Fort George Island were African or first generation African-American. Records and archeological information show they were Igbo and Calabari from Nigeria, and others from the area around what is today Guinea, and a few from Zanzibar. Archeologist Charles H. Fairbanks received a Florida Park Service grant to study artifacts found at the slave quarters. His findings, published in 1968, initiated further interest and research in African-American archeology in the U.S.[36] Concentrating on two particular cabins bordering on Palmetto Avenue, Fairbanks found cooking pots used in fireplaces, animal bones—fish, pigs, raccoons, and turtles—discarded as food byproducts, and musket balls and fishing weights.[37]
Fairbanks described Kingsley as "an unusually permissive slave owner"[38] who wrote about the physical superiority of Africans to Europeans, armed his slaves for protection, and gave them padlocks for their cabins.[21][39] Historian Daniel Stowell suggests that the cabins and Kingsley's hands-off approach to slave management was intended to prevent the slaves from running away. Kingsley himself wrote about not interfering in his slaves' family lives and "encouraged as much as possible dancing, merriment and dress, for which Saturday afternoon and night, and Sunday morning were dedicated ... they were perfectly honest and obedient, and appeared quite happy, having no fear but that of offending me; and I hardly ever had occasion to apply other correction than shaming them."[21]
Kingsley used the plantation as his slave trading headquarters, training slaves for specific tasks to increase their value at sale.[12][40] He developed them as skilled artisans and educated them about agriculture and planting. Those who had been trained by Kingsley fetched a much higher price at sale, on average 50 percent higher than market price.[12][note 3] A 2006 excavation sponsored by the University of Florida uncovered artifacts from the slave cabins, such as the tools the slaves used. In one cabin an intact sacrificed chicken on top of an egg was unearthed, adding evidence to the hypothesis that African slaves kept many of their traditions alive in North America. Archeologists also discovered evidence of an added-on porch to one of the cabins facing away from the main house, an atypical feature for a slave cabin, as owners and overseers constructed quarters to be within their view at all times.[38]
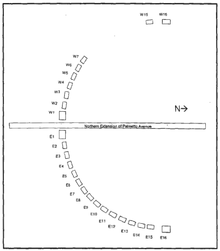
Layout of the slave cabins; the owner's house is several hundred yards to the north
The slave houses were constructed out of tabby and built by the slaves probably in the 1820s or 1830s,[41] although evidence exists that indicates two of them were inhabited by 1814.[38] Tabby was constructed of shells left over from Timucua middens, burned by the barrel-full in open pits or kilns, then pounded into lime particles, mixed with water, sand, and whole oyster or clam shells, then poured into wooden foundations about 1 foot (0.3 m) high, and set to dry. The process was repeated and stacked until the desired height of the wall was reached.[42] The floors of the kitchen house and the basement of the owner's house were also constructed of tabby. The material made the houses remarkably durable, resistant to weather and insects, better insulated than wood, and the ingredients were accessible and cheap, although labor-intensive.[43] The slave quarters at Kingsley Plantation are widely considered some of the best surviving examples of the use of this building material.[44]
Each cabin consisted of a room, fireplace, and sleeping loft. The arrangement of the quarters is distinctive: there were originally 32 cabins laid out in a semicircular arc interrupted by the main thoroughfare to the plantation, Palmetto Avenue. This formation is unique in plantations in the antebellum U.S. The historian Daniel Stowell surmises that it may have given slave families a modicum of privacy, although he also suggests overseers and slave managers may have arranged the quarters to be able to watch all the slaves from the owner's house at the same time.[45] Author Daniel Schafer, however, suggests that Anna Jai may have been responsible for this layout. West African villages were commonly constructed in a circular pattern with the king or ruling family living in the center.[46]
In the 1890s John Rollins deconstructed several of the slave cabins to build a boat house and dock. The archeological significance of the site is considerable as the majority of slave quarters in the Southern United States were not built with quality materials, and most quarters were destroyed after emancipation.[47] Six graves thought to contain slaves were unearthed in 2011 by archeologists from the University of Florida. The bodies ranged in age from infants to an elderly woman; three were adults who were probably born in West Africa.[48]
Kingsley's house and other structures

Rear of the owner's house of the plantation as it faces Fort George Inlet
The main residence of the Fort George plantation is a unique two-story house that was probably constructed between 1797 and 1798 by John McQueen, who indicated in a letter at the time that he had built a comfortable house for himself. The house—resembling 17th century British gentry homes[44]—has a large center room and four one-story pavilions at each corner that allowed air to circulate through them to keep them cooler in the summer; each was a bedroom that had a fireplace to heat more efficiently in the winter.[49] The second story of the house has two large rooms.[50] On the roof is a deck and the house faces Fort George Inlet and features two porches on the front and rear of the house. A brick walkway joined the back porch to a wharf on the inlet while Kingsley was in residence.[51] The Florida Division of Historical Resources indicates it may be the oldest plantation house in the state.[52]
The main house protected John McQueen's family and neighbors during attacks from invading Creeks in 1802; he wrote that at one time 26 people took refuge there. Following raids from Americans during the Patriot Rebellion in 1813, the house was gutted and vandalized. Plantations as far south as New Smyrna were destroyed by rebels fleeing into Georgia. When Kingsley arrived, there were no metal fixtures in the doors and the wooden slave quarters had been burned down.[53] John Rollins added sections to the east and west sides of the house in between the pavilions in the 1890s and removed at least three of the fireplace chimneys from the pavilions. One of the clubs that owned the island in the 1920s added electricity.[54]

"Ma'am Anna House" where Anna Jai lived with her children over the kitchens; the front of the owner's house is behind it.
Next to the main house was a two-story kitchen house that was called "Ma'am Anna House" while Anna Jai was on Fort George Island. It was probably built in the 1820s and doubled as a center for food preparation on the ground floor and Anna Jai's residence with her children on the second.[55] In West Africa, polygamy was not uncommon, and wives often lived in separate quarters from their husbands.[56] Kingsley's nephew and his wife also lived on the grounds and Gibbs probably used a part of the second floor for an office. The main house and Ma'am Anna House were surrounded by a grove of orange, lemon, and banana trees with occasional ornamental crepe myrtles. Between 1869 and 1877 Rollins built a roof over the walkway between the kitchen house and the main house.[57]
A barn constructed of tabby sits 150 feet (46 m) from the owner's house. Two wells have survived since Kingsley's ownership and two tombs of unknown origin constructed of tabby before Kingsley came to own the island are also located near the plantation. Ruins of another tabby house sits near the entrance of Palmetto Avenue. Its origins are unclear. It has been called the Munsilna McGundo House for Kingsley's fourth wife, as oral history related that it was left to her and her daughter Fatima in Kingsley's will. More recently it has been referred to as Thomson Tabby House named for a planter who died perhaps while constructing it.[58]
Activities and restoration
Kingsley Plantation currently showcases the remains of 23 slave houses out of 32 original cabins, located approximately 1,000 feet (305 m) south of the main owner's house. One of the slave houses has been restored to appear as it did in the early 19th century; others are in various states of repair or ruin. The kitchen house features a display about slavery on the island, and the garden is also on display. Maintenance of the historical structures is the most significant work being done at Kingsley Plantation. The kitchen and owner's house were closed in 2005 due to severe structural damage caused by termites and humidity.[59] The kitchen building was restored in 2006, but work is ongoing for the owner's house. As of March 2017, the owner's house is open for guided tours on a limited basis each weekend. The barn is being renovated and is now open. Despite the durability of the slave quarters, they are vulnerable to vandalism, and each cabin shows evidence of damage.[60] One room of the kitchen house is open and contains exhibits.
Since 1998 Kingsley Plantation has hosted an annual one-day event in October called the Kingsley Heritage Celebration that coincides with the Kingsley family reunion. Several relatives of Kingsley and Anna Jai are notable. Kingsley's youngest sister's daughter, Anna McNeill, participated with her mother in attempting to block Anna Jai from inheriting Kingsley's property. McNeill served as the model for her son, the artist James Whistler, in his Arrangement in Grey and Black: The Artist's Mother, popularly known as Whistler's Mother.[12] Kingsley Beatty Gibbs' brother was George Couper Gibbs, a planter in St. Johns County, south of Fort George Island near St. Augustine. Former governor of South Carolina Duncan Clinch Heyward is descended from him.[61]
Another branch of Kingsley descendants lives in the Dominican Republic near where John Maxwell Kingsley lived in Haiti.[62] Kingsley and Anna Jai are the great grandparents of Mary Kingsley Sammis, who married Abraham Lincoln Lewis, one of Florida's first black millionaires and an original investor in the all-black American Beach.[63] The Kingsley-Sammis-Lewis-Betsch family has been active in Jacksonville's black community for decades. Spelman College's first black female president, Johnnetta Betsch Cole, is descended from Lewis and Sammis. The Heritage Celebration was moved to Black History Month in February 2008; Cole was the keynote speaker of the 2009 Kingsley Heritage Celebration. Interpretive events such as music, storytelling, and ranger-led talks about history and archeology regularly occur during the Heritage Celebration.[64][65]
Notes
^ Kingsley was often away on business, during which Anna Jai would assume management responsibilities for the plantation. Anna Jai befriended a white woman named Susan L'Engle, who came from Fernandina to visit Kingsley on business, and spent time with Anna Jai. Kingsley's absence and his time spent with his other wives gave L'Engle the impression that Anna Jai was lonely at Fort George Island, despite all her responsibilities. Susan L'Engle told her stories to her great granddaughter, children's author Madeleine L'Engle, who wrote them in her book Summer of the Great Grandmother. Anna Jai is referred to as "the African Princess" in the book; there is some belief that Anna Jai may have been the daughter of a ruling family in West Africa. (Schafer, pp. 5, 15–18, 58.)
^ Kingsley Beatty Gibbs established and gave the name to the fishing community that is now known as Mayport, Florida. (Fretwell, p. 5.)
^ Depending on the condition, training, age, and quality of the slave, a price could range from 50 to 400 pesos in early 19th century Spanish Florida. Pesos were roughly equivalent to dollars. In 2009 the range would be from $686 to $5,487 (Landers, p. 140, 177).
Citations
^ National Park Service (2009-03-13). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Carter, John (October 20, 2004). "Slave history event at Kingsley site: Plantation having 'a sort of family reunion'." Florida Times-Union (Jacksonville), p. N-1.
^ "Archaeology Field School", Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve, National Park Service, accessed 15 May 2010
^ Stowell (1996), p. 2.
^ Milanich, p. 1.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 5.
^ ab Stowell (1996), pp. 15–21.
^ Gannon, p. 57.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 27.
^ Stowell and Tilford, pp. 4–6.
^ Stowell and Tilford, p. 7.
^ abcdef May, Philip (January 1945). "Zephaniah Kingsley, Nonconformist (1765-1843)", The Florida Historical Quarterly 23 (3), pp. 145–159.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 11.
^ ab Jackson and Burns, p. 17.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 19.
^ Schafer (1997), pp. 15–17.
^ ab Tilford, Kathy (Fall 1997). "Anna Kingsley: A Free Woman", OAH Magazine of History, 12 (1), pp. 35–37.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 38.
^ Schafer (2003), p. 31.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. v.
^ abcde Kingsley (1829)
^ Fleszar, pp. 134–135.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 39.
^ Stowell (2000), p. 72.
^ Schafer (1997), pp. 41–42.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. 15.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 45.
^ Schafer (2003), pp. 72–76.
^ Fretwell, p. 11.
^ Stowell and Tilford, pp. 16–17.
^ Stowell and Tilford, pp. 19–20.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. 5.
^ Stowell and Tilford, p. 21.
^ ab Labor, National Park Service (2006). Retrieved on August 15, 2009.
^ Fretwell, pp. 23–24.
^ Jackson and Burns, pp. 5–8.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. 6.
^ abc Davidson, James, et al. Preliminary Results of the 2006 University of Florida Archaeological Field School Excavations at Kingsley Plantation, Fort George Island, Florida African Diaspora Archeology Network. Retrieved on December 30, 2007.
^ Birdwell, April (Summer, 2007). "A Legacy Revealed." Florida; pp. 12–15.
^ Williams, Edwin (October 1949). "Negro Slavery in Florida", The Florida Historical Quarterly 28 (2), p. 94–110.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 72.
^ Stowell (1996), pp. 71–72.
^ Steffen, Colleen (January 6, 2000)."Crumbling past." Florida Times-Union (Jacksonville, FL); p. E-1
^ ab Stowell (1996), p. 81.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 73.
^ Schafer, p. 55.
^ Stowell (1996), pp. 80–81.
^ Sorgel, Matt (November 10, 2011). "UF archaeological team finds six human burials at Kingsley Plantation", Jacksonville.com. Retrieved on November 15, 2011.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 67.
^ Stowell (1996), p. A7.
^ Schafer (2003), p. 46.
^ Florida's History Through Its Places:Duval County Archived 2007-02-16 at the Wayback Machine.. Florida Division of Historical Resources (2009). Retrieved on August 14, 2009.
^ Schafer (1997), p. 27.
^ Stowell (1996), p. A8.
^ Schafer (2003), p. 48.
^ Schafer (2003), pp. 50–51.
^ Stowell (1996), p. 68.
^ Stowell (1996), pp. 75–79.
^ Carter, John (March 9, 2005). "Kingsley Plantation to undergo repairs: Work begun on kitchen, other fixes slated for later." Florida Times-Union (Jacksonville); p. K-1.
^ Preservation Work at Kingsley Plantation, National Park Service. Retrieved on August 14, 2009.
^ Jackson and Burns, pp. 19–20.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. 23.
^ Jackson and Burns, p. 24.
^ Lovejoy, Heather (November 7, 2007). "Kingsley Plantation slavery event is moved to February." Florida Times-Union (Jacksonville); p. N-8
^ Kingsley Heritage Celebration Press Release National Park Service (January 28, 2009). Retrieved on August 12, 2009.
Bibliography
- Fleszar, Mark (2009). "The Atlantic Mind: Zephaniah Kingsley, Slavery, and the Politics of Race in the Atlantic World," Georgia State University (dissertation)
- Fretwell, Jacquiline K. (ed.) (1984). Kingsley Beatty Gibbs and His Journal of 1840–1843, St. Augustine Historical Society.
Gannon, Michael (ed.) (1996). A New History of Florida, University Press of Florida.
ISBN 0-8130-1415-8
- Jackson, Antoinette; Burns, Allan (January 2006). Ethnohistorical Study of the Kingsley Plantation Community, National Park Service.
- An Inhabitant of Florida (Kingsley, Zephaniah, Jr). (1829). A Treatise on the Patriarchal or Co-operative System of Society as it Exists in Some Governments, and Colonies in American, and the United States Under the Name of Slavery With its Necessary Advantages, reprinted in 2005 by Eastern National.
- Landers, Jane (1999). Black Society in Spanish Florida, University of Illinois Press.
ISBN 0-252-02446-X
- Milanich, Jerald T. (2000) "The Timucua Indians of Northern Florida and Southern Georgia", in McEwan, Bonnie G. ed. (2000) Indians of the Greater Southeast: Historical Archaeology and Ethnohistory, University Press of Florida.
ISBN 0-8130-1778-5
- Schafer, Daniel L. (1997). Anna Kingsley, St. Augustine Historical Society.
- Schafer, Daniel L. (2003). Anna Madgigine, Jai Kingsley: African Princess, Florida Slave, Plantation Slaveowner, University Press of Florida.
ISBN 0-8130-2616-4
- Stowell, Daniel (October 1996). Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve: Historic Resource Study, National Park Service.
- Stowell, Daniel (ed.) (2000). Balancing Evils Judiciously: The Proslavery Writings of Zephaniah Kingsley, University Press of Florida.
ISBN 0-8130-2400-5
- Stowell, Daniel and Tilford, Kathy (1998). Kingsley Plantation: A History of Fort George Island Plantation, Eastern National.
ISBN 188821323X
External links
 Media related to Kingsley Plantation at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kingsley Plantation at Wikimedia Commons- Official website
- The papers of Zephaniah and Anna Kingsley at the State Archives of Florida
Florida's Office of Cultural and Historical Programs
- Duval County listings
- Duval County markers
Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) No. FL-478, "Kingsley Plantation, 11676 Palmetto Avenue, Jacksonville, Duval County, FL", 92 photos, 1 color transparency, 4 measured drawings, 5 photo caption pages- HABS No. FL-478-A, "Kingsley Plantation, Slave Quarters", 12 photos, 2 measured drawings, 1 photo caption page
- HABS No. FL-478-B, "Kingsley Plantation, House", 43 photos, 1 color transparency, 10 measured drawings, 3 photo caption pages
- HABS No. FL-478-C, "Kingsley Plantation, Kitchen", 26 photos, 3 measured drawings, 2 photo caption pages
- HABS No. FL-478-D, "Kingsley Plantation, Barn", 23 photos, 2 measured drawings, 2 photo caption pages