Regular 4-polytope
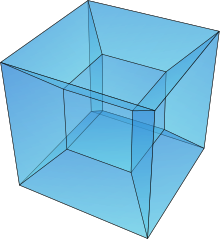
The tesseract is one of 6 convex regular 4-polytopes
In mathematics, a regular 4-polytope is a regular four-dimensional polytope. They are the four-dimensional analogs of the regular polyhedra in three dimensions and the regular polygons in two dimensions.
Regular 4-polytopes were first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century, although the full set were not discovered until later.
There are six convex and ten star regular 4-polytopes, giving a total of sixteen.
Contents
1 History
2 Construction
3 Regular convex 4-polytopes
3.1 Properties
3.2 As configurations
3.3 Visualization
4 Regular star (Schläfli–Hess) 4-polytopes
4.1 Names
4.2 Symmetry
4.3 Properties
5 See also
6 References
6.1 Citations
6.2 Bibliography
7 External links
History
The convex regular 4-polytopes were first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century. He discovered that there are precisely six such figures.
Schläfli also found four of the regular star 4-polytopes: the grand 120-cell, great stellated 120-cell, grand 600-cell, and great grand stellated 120-cell). He skipped the remaining six because he would not allow forms that failed the Euler characteristic on cells or vertex figures (for zero-hole tori: F − E + V = 2). That excludes cells and vertex figures as {5,5/2} and {5/2,5}.
Edmund Hess (1843–1903) published the complete list in his 1883 German book Einleitung in die Lehre von der Kugelteilung mit besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Anwendung auf die Theorie der Gleichflächigen und der gleicheckigen Polyeder.
Construction
The existence of a regular 4-polytope {p,q,r}{displaystyle {p,q,r}}

- sinπpsinπr<cosπq.{displaystyle sin {frac {pi }{p}}sin {frac {pi }{r}}<cos {frac {pi }{q}}.}
to ensure that the cells meet to form a closed 3-surface.
The six convex and ten star polytopes described are the only solutions to these constraints.
There are four nonconvex Schläfli symbols {p,q,r} that have valid cells {p,q} and vertex figures {q,r}, and pass the dihedral test, but fail to produce finite figures: {3,5/2,3}, {4,3,5/2}, {5/2,3,4}, {5/2,3,5/2}.
Regular convex 4-polytopes
The regular convex 4-polytopes are the four-dimensional analogs of the Platonic solids in three dimensions and the convex regular polygons in two dimensions.
Five of them may be thought of as close analogs of the Platonic solids. One additional figure, the 24-cell, has no close three-dimensional equivalent.
Each convex regular 4-polytope is bounded by a set of 3-dimensional cells which are all Platonic solids of the same type and size. These are fitted together along their respective faces in a regular fashion.
Properties
The following tables lists some properties of the six convex regular 4-polytopes. The symmetry groups of these 4-polytopes are all Coxeter groups and given in the notation described in that article. The number following the name of the group is the order of the group.
| Names | Image | Family | Schläfli Coxeter | V | E | F | C | Vert. fig. | Dual | Symmetry group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5-cell pentachoron pentatope 4-simplex | 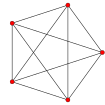 | n-simplex (An family) | {3,3,3} | 5 | 10 | 10 {3} | 5 {3,3} | {3,3} | (self-dual) | A4 [3,3,3] | 120 |
8-cell octachoron tesseract 4-cube | 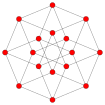 | n-cube (Bn family) | {4,3,3} | 16 | 32 | 24 {4} | 8 {4,3} | {3,3} | 16-cell | B4 [4,3,3] | 384 |
16-cell hexadecachoron 4-orthoplex | 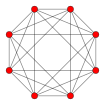 | n-orthoplex (Bn family) | {3,3,4} | 8 | 24 | 32 {3} | 16 {3,3} | {3,4} | 8-cell | B4 [4,3,3] | 384 |
24-cell icositetrachoron octaplex polyoctahedron (pO) | 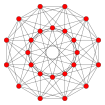 | Fn family | {3,4,3} | 24 | 96 | 96 {3} | 24 {3,4} | {4,3} | (self-dual) | F4 [3,4,3] | 1152 |
120-cell hecatonicosachoron dodecacontachoron dodecaplex polydodecahedron (pD) | 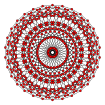 | n-pentagonal polytope (Hn family) | {5,3,3} | 600 | 1200 | 720 {5} | 120 {5,3} | {3,3} | 600-cell | H4 [5,3,3] | 14400 |
600-cell hexacosichoron tetraplex polytetrahedron (pT) | 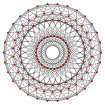 | n-pentagonal polytope (Hn family) | {3,3,5} | 120 | 720 | 1200 {3} | 600 {3,3} | {3,5} | 120-cell | H4 [5,3,3] | 14400 |
John Conway advocates the names simplex, orthoplex, tesseract, octaplex or polyoctahedron (pO), dodecaplex or polydodecahedron (pD), and tetraplex or polytetrahedron (pT).[1]
Norman Johnson advocates the names n-cell, or pentachoron, tesseract or octachoron, hexadecachoron, icositetrachoron, hecatonicosachoron (or dodecacontachoron), and hexacosichoron, coining the term polychoron being a 4D analogy to the 3D polyhedron, and 2D polygon, expressed from the Greek roots poly ("many") and choros ("room" or "space").[2][3]
The Euler characteristic for all 4-polytopes is zero, we have the 4-dimensional analog of Euler's polyhedral formula:
- N0−N1+N2−N3=0{displaystyle N_{0}-N_{1}+N_{2}-N_{3}=0,}
where Nk denotes the number of k-faces in the polytope (a vertex is a 0-face, an edge is a 1-face, etc.).
The topology of any given 4-polytope is defined by its Betti numbers and torsion coefficients.[4]
As configurations
The elements of the regular polytopes can be expressed in a configuration matrix. Rows and columns reference vertices, edges, faces, and cells, with diagonal element their counts (f-vectors). The nondiagonal elements represent the number of row elements are incident to the column element. The configurations for dual polytopes can be seen by rotating the matrix elements by 180 degrees.[5][6]
5-cell {3,3,3} | 16-cell {3,3,4} | tesseract {4,3,3} | 24-cell {3,4,3} | 600-cell {3,3,5} | 120-cell {5,3,3} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[546421033331024645]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}5&4&6&4\2&10&3&3\3&3&10&2\4&6&4&5end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  | [86128224443332246416]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}8&6&12&8\2&24&4&4\3&3&32&2\4&6&4&16end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  | [16464232334424281268]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}16&4&6&4\2&32&3&3\4&4&24&2\8&12&6&8end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  | [2481262963333962612824]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}24&8&12&6\2&96&3&3\3&3&96&2\6&12&8&24end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  | [1201230202720553312002464600]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}120&12&30&20\2&720&5&5\3&3&1200&2\4&6&4&600end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  | [6004642120033557202203012120]{displaystyle {begin{bmatrix}{begin{matrix}600&4&6&4\2&1200&3&3\5&5&720&2\20&30&12&120end{matrix}}end{bmatrix}}}  |
Visualization
The following table shows some 2-dimensional projections of these 4-polytopes. Various other visualizations can be found in the external links below. The Coxeter-Dynkin diagram graphs are also given below the Schläfli symbol.
| A4 = [3,3,3] | BC4 = [4,3,3] | F4 = [3,4,3] | H4 = [5,3,3] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-cell | 8-cell | 16-cell | 24-cell | 120-cell | 600-cell |
| {3,3,3} | {4,3,3} | {3,3,4} | {3,4,3} | {5,3,3} | {3,3,5} |
| Solid 3D orthographic projections | |||||
 Tetrahedral envelope (cell/vertex-centered) |  Cubic envelope (cell-centered) |  cubic envelope (cell-centered) |  Cuboctahedral envelope (cell-centered) |  Truncated rhombic triacontahedron envelope (cell-centered) |  pentakis icosidodecahedral envelope (vertex-centered) |
| Wireframe Schlegel diagrams (Perspective projection) | |||||
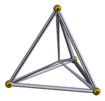 Cell-centered |  Cell-centered |  Cell-centered |  Cell-centered |  Cell-centered |  Vertex-centered |
| Wireframe stereographic projections (3-sphere) | |||||
 | 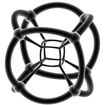 |  |  |  |  |
Regular star (Schläfli–Hess) 4-polytopes

This shows the relationships among the four-dimensional starry polytopes. The 2 convex forms and 10 starry forms can be seen in 3D as the vertices of a cuboctahedron.[7]

A subset of relations among 8 forms from the 120-cell, polydodecahedron (pD). The three operations {a,g,s} are commutable, defining a cubic framework. There are 7 densities seen in vertical positioning, with 2 dual forms having the same density.
The Schläfli–Hess 4-polytopes are the complete set of 10 regular self-intersecting star polychora (four-dimensional polytopes).[8] They are named in honor of their discoverers: Ludwig Schläfli and Edmund Hess. Each is represented by a Schläfli symbol {p,q,r} in which one of the numbers is 5/2. They are thus analogous to the regular nonconvex Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, which are in turn analogous to the pentagram.
Names
Their names given here were given by John Conway, extending Cayley's names for the Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra: along with stellated and great, he adds a grand modifier. Conway offered these operational definitions:
stellation – replaces edges by longer edges in same lines. (Example: a pentagon stellates into a pentagram)
greatening – replaces the faces by large ones in same planes. (Example: an icosahedron greatens into a great icosahedron)
aggrandizement – replaces the cells by large ones in same 3-spaces. (Example: a 600-cell aggrandizes into a grand 600-cell)
John Conway names the 10 forms from 3 regular celled 4-polytopes: pT=polytetrahedron {3,3,5} (a tetrahedral 600-cell), pI=polyicoshedron {3,5,5/2} (an icosahedral 120-cell), and pD=polydodecahedron {5,3,3} (a dodecahedral 120-cell), with prefix modifiers: g, a, and s for great, (ag)grand, and stellated. The final stellation, the great grand stellated polydodecahedron contains them all as gaspD.
Symmetry
All ten polychora have [3,3,5] (H4) hexacosichoric symmetry. They are generated from 6 related Goursat tetrahedra rational-order symmetry groups: [3,5,5/2], [5,5/2,5], [5,3,5/2], [5/2,5,5/2], [5,5/2,3], and [3,3,5/2].
Each group has 2 regular star-polychora, except for two groups which are self-dual, having only one. So there are 4 dual-pairs and 2 self-dual forms among the ten regular star polychora.
Properties
Note:
- There are 2 unique vertex arrangements, matching those of the 120-cell and 600-cell.
- There are 4 unique edge arrangements, which are shown as wireframes orthographic projections.
- There are 7 unique face arrangements, shown as solids (face-colored) orthographic projections.
The cells (polyhedra), their faces (polygons), the polygonal edge figures and polyhedral vertex figures are identified by their Schläfli symbols.
| Name Conway (abbrev.) | Orthogonal projection | Schläfli Coxeter | C {p, q} | F {p} | E {r} | V {q, r} | Dens. | χ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Icosahedral 120-cell polyicosahedron (pI) |  | {3,5,5/2} | 120 {3,5} | 1200 {3} | 720 {5/2} | 120 {5,5/2} | 4 | 480 |
Small stellated 120-cell stellated polydodecahedron (spD) |  | {5/2,5,3} | 120 {5/2,5} | 720 {5/2} | 1200 {3} | 120 {5,3} | 4 | −480 |
Great 120-cell great polydodecahedron (gpD) |  | {5,5/2,5} | 120 {5,5/2} | 720 {5} | 720 {5} | 120 {5/2,5} | 6 | 0 |
Grand 120-cell grand polydodecahedron (apD) |  | {5,3,5/2} | 120 {5,3} | 720 {5} | 720 {5/2} | 120 {3,5/2} | 20 | 0 |
Great stellated 120-cell great stellated polydodecahedron (gspD) | 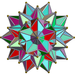 | {5/2,3,5} | 120 {5/2,3} | 720 {5/2} | 720 {5} | 120 {3,5} | 20 | 0 |
Grand stellated 120-cell grand stellated polydodecahedron (aspD) |  | {5/2,5,5/2} | 120 {5/2,5} | 720 {5/2} | 720 {5/2} | 120 {5,5/2} | 66 | 0 |
Great grand 120-cell great grand polydodecahedron (gapD) |  | {5,5/2,3} | 120 {5,5/2} | 720 {5} | 1200 {3} | 120 {5/2,3} | 76 | −480 |
Great icosahedral 120-cell great polyicosahedron (gpI) |  | {3,5/2,5} | 120 {3,5/2} | 1200 {3} | 720 {5} | 120 {5/2,5} | 76 | 480 |
Grand 600-cell grand polytetrahedron (apT) |  | {3,3,5/2} | 600 {3,3} | 1200 {3} | 720 {5/2} | 120 {3,5/2} | 191 | 0 |
Great grand stellated 120-cell great grand stellated polydodecahedron (gaspD) |  | {5/2,3,3} | 120 {5/2,3} | 720 {5/2} | 1200 {3} | 600 {3,3} | 191 | 0 |
See also
- Regular polytope
- List of regular polytopes
- Infinite regular 4-polytopes:
One regular Euclidean honeycomb: {4,3,4}
Four compact regular hyperbolic honeycombs: {3,5,3}, {4,3,5}, {5,3,4}, {5,3,5}
Eleven paracompact regular hyperbolic honeycombs: {3,3,6}, {6,3,3}, {3,4,4}, {4,4,3}, {3,6,3}, {4,3,6}, {6,3,4}, {4,4,4}, {5,3,6}, {6,3,5}, and {6,3,6}.
Abstract regular 4-polytopes:
11-cell {3,5,3}
57-cell {5,3,5}
Uniform 4-polytope uniform 4-polytope families constructed from these 6 regular forms.- Platonic solid
Kepler-Poinsot polyhedra – regular star polyhedron
Star polygon – regular star polygons
References
Citations
^ Conway, 2008, Chapter 26, Higher Still
^ "Convex and abstract polytopes", Programme and abstracts, MIT, 2005
^ Johnson (2015), Chapter 11, Section 11.5 Spherical Coxeter groups
^ Richeson, D.; Euler's Gem: The Polyhedron Formula and the Birth of Topoplogy, Princeton, 2008.
^ Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, sec 1.8 Configurations
^ Coxeter, Complex Regular Polytopes, p.117
^ The Symmetries of Things, John Conway, (2008), p. 406, Fig 26.2
^ Coxeter, Star polytopes and the Schläfli function f{α,β,γ) p. 122 2. The Schläfli-Hess polytopes
Bibliography
H. S. M. Coxeter, Introduction to Geometry, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1969. .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 0-471-50458-0.- H. S. M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973.
ISBN 0-486-61480-8.
D. M. Y. Sommerville, An Introduction to the Geometry of n Dimensions. New York, E. P. Dutton, 1930. 196 pp. (Dover Publications edition, 1958) Chapter X: The Regular Polytopes
John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, The Symmetries of Things 2008,
ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 26, Regular Star-polytopes, pp. 404–408)
Edmund Hess, (1883) Einleitung in die Lehre von der Kugelteilung mit besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Anwendung auf die Theorie der Gleichflächigen und der gleicheckigen Polyeder [1].
Edmund Hess Uber die regulären Polytope höherer Art, Sitzungsber Gesells Beförderung gesammten Naturwiss Marburg, 1885, 31-57
Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995,
ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [2]
- (Paper 10) H.S.M. Coxeter, Star Polytopes and the Schlafli Function f(α,β,γ) [Elemente der Mathematik 44 (2) (1989) 25–36]
H. S. M. Coxeter, Regular Complex Polytopes, 2nd. ed., Cambridge University Press 1991.
ISBN 978-0-521-39490-1. [3]
- Peter McMullen and Egon Schulte, Abstract Regular Polytopes, 2002, PDF
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Regular polychoron". MathWorld.
- Jonathan Bowers, 16 regular 4-polytopes
- Regular 4D Polytope Foldouts
Catalog of Polytope Images A collection of stereographic projections of 4-polytopes.- A Catalog of Uniform Polytopes
Dimensions 2 hour film about the fourth dimension (contains stereographic projections of all regular 4-polytopes)
Olshevsky, George. "Hecatonicosachoron". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
Olshevsky, George. "Hexacosichoron". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
Olshevsky, George. "Stellation". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
Olshevsky, George. "Greatening". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
Olshevsky, George. "Aggrandizement". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
- Reguläre Polytope
- The Regular Star Polychora

