Snub dodecadodecahedron
| Snub dodecadodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 84, E = 150 V = 60 (χ = −6) |
| Faces by sides | 60{3}+12{5}+12{5/2} |
| Wythoff symbol | |2 5/2 5 |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | U40, C49, W111 |
| Dual polyhedron | Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron |
| Vertex figure |  3.3.5/2.3.5 |
| Bowers acronym | Siddid |
In geometry, the snub dodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U40. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5/2,5}, as a snub great dodecahedron.
Contents
1 Cartesian coordinates
2 Related polyhedra
2.1 Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a snub dodecadodecahedron are all the even permutations of
- (±2α, ±2, ±2β),
- (±(α+β/τ+τ), ±(-ατ+β+1/τ), ±(α/τ+βτ-1)),
- (±(-α/τ+βτ+1), ±(-α+β/τ-τ), ±(ατ+β-1/τ)),
- (±(-α/τ+βτ-1), ±(α-β/τ-τ), ±(ατ+β+1/τ)) and
- (±(α+β/τ-τ), ±(ατ-β+1/τ), ±(α/τ+βτ+1)),
with an even number of plus signs, where
- β = (α2/τ+τ)/(ατ−1/τ),
where τ = (1+√5)/2 is the golden mean and
α is the positive real root of τα4−α3+2α2−α−1/τ, or approximately 0.7964421.
Taking the odd permutations of the above coordinates with an odd number of plus signs gives another form, the enantiomorph of the other one.
Related polyhedra
Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron
| Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron | |
|---|---|
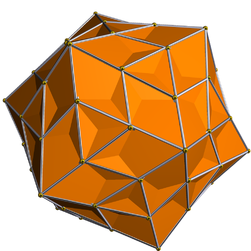 | |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face |  |
| Elements | F = 60, E = 150 V = 84 (χ = −6) |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | DU40 |
| dual polyhedron | Snub dodecadodecahedron |
The medial pentagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the snub dodecadodecahedron. It has 60 intersecting irregular pentagonal faces.
See also
- List of uniform polyhedra
- Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron
References
Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511569371, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5, MR 0730208.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Snub dodecadodecahedron". MathWorld.
- Uniform polyhedra and duals
This polyhedron-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |